Approximately 15-20% of grafted plants fail to take root due to the lack of fusion between the scion and the rootstock; therefore, the study and implementation of techniques aimed at improving the rooting speed and increasing the quality of the resulting plants is a task whose results can lead to an important productive improvement.
Currently, numerous physical techniques are employed in the treatment of agricultural crops. These techniques include treatment with magnetic fields, exposure to microwave radiation and others that influence the physiological and biochemical processes of seeds and plants.
They promote greater vegetative growth, as well as higher yields and improved crop quality. One potential approach to improve fusion between scions and rootstocks involves the application of plasma-activated water or cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) treatment, generally recognised for its effectiveness in deactivating bacteria.
It consists of ionised gas with a low ion and particle temperature but a high electron temperature. The study conducted by researchers at the Federal Scientific Agroengineering Centre and the Prokhorov Institute of General Physics in Moscow (Russia) describes a new technique for winter grafting of the sweet cherry variety 'Revna'.
The innovation of this method lies in the use of a portable device designed by the authors to produce cold plasma and a plasma-treated solution. The application of low-temperature plasma to the cut surfaces of the plant cuttings showed as first effect smoothing of the surface, reduced surface roughness and, in addition, the treatment facilitates the reabsorption of the insulating layer, which hinders the growth process due to its composition of decomposed products and dead cells.
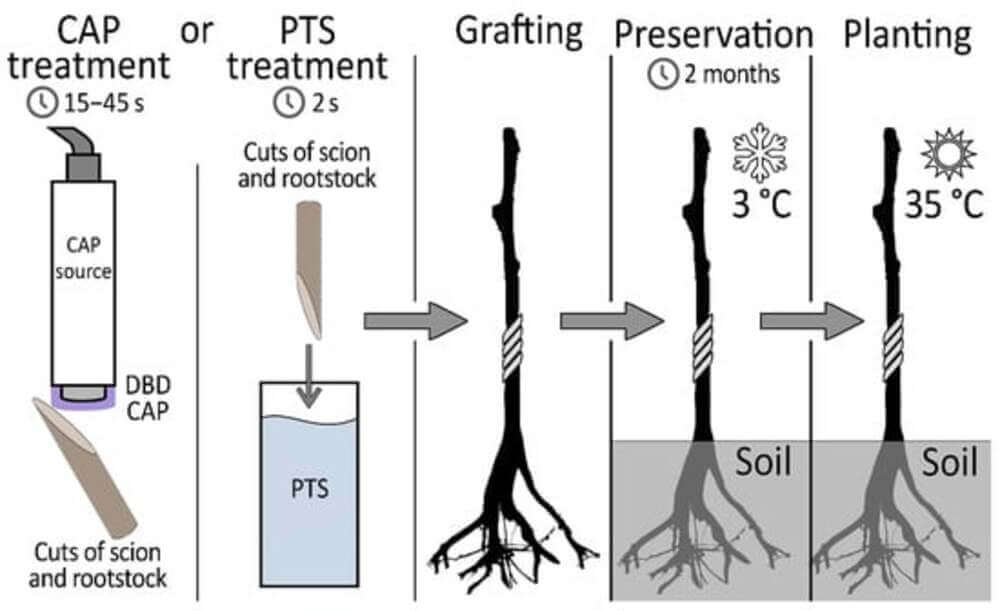 Image 1: The proposed method involves a DBD CAP or PTS cold plasma treatment on the cutting surface of the graft and rootstock prior to grafting. The rootstock-graft combinations are then stored in cold storage for 2 months. This is followed by transplanting into the greenhouse.
Image 1: The proposed method involves a DBD CAP or PTS cold plasma treatment on the cutting surface of the graft and rootstock prior to grafting. The rootstock-graft combinations are then stored in cold storage for 2 months. This is followed by transplanting into the greenhouse.
It was determined that cold plasma treatment induces a 17-28% reduction in the growth length of 'Revna' cherry plants, accompanied by a 20-23% increase in root collar diameter. Compared to the control, exposure to plasma or plasma-activated water resulted in an average decrease of 14% in electrical resistivity in the grafting point.
This decrease suggested that the rootstock and scion transport fibres fused more effectively. Additional methodologies were suggested and outlined to facilitate winter grafting of fruit crops.
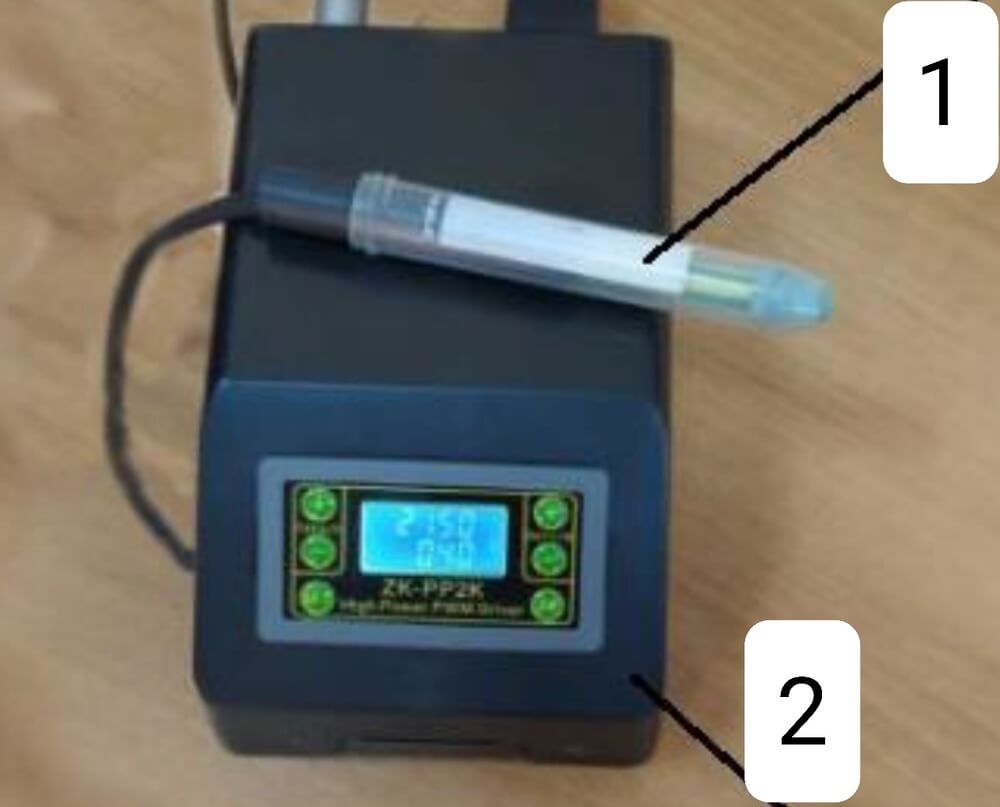 Image 2: Mobile device for the creation of cold plasma (CAP). 1: replaceable module on the surface of which the CAP is created; 2: hardware control block for CAP DBD creation modes.
Image 2: Mobile device for the creation of cold plasma (CAP). 1: replaceable module on the surface of which the CAP is created; 2: hardware control block for CAP DBD creation modes.
It was possible to improve the quality of one-year-old plants obtained by accelerating regenerative processes at graft sites by describing exposure to a cold plasma source, exposure times and concentrations of plasma-treated solutions.
In conclusion, 15-45 seconds of cold plasma exposure prior to grafting on fresh sections of scions and rootstocks increases root collar diameter and growth length. There is considerable potential for CAP implementation in agriculture, as this approach to improve plant productivity has several advantages over similar physical methods, including plant safety, scalability, and ease of use.
Source: Zmailov, A.; Khort, D.; Filippov, R.; Pishchalnikov, R.Y.; Simakin, A.V.; Shogenov, Y., Improvement of Winter Graft Techniques Using Cold Plasma and Plasma-Treated Solution on Cherry Cultures. Appl. Sci. 12, 2022, 4953. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104953.
Image: The Orchard Project
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












