Root rot is one of the most significant diseases affecting sweet cherry trees, causing substantial economic losses. This disease, linked to the presence of pathogenic fungi such as Ilyonectria, Cylindrocarpon, and Fusarium, compromises root health, reducing the plant's ability to absorb nutrients and water. The most evident symptoms include stunted growth, yellowed leaves, and a drastic decrease in production.
A recent study thoroughly analyzed the effects of root rot on plant metabolism, soil physicochemical properties, and the composition of the root and rhizosphere microbiome. The results demonstrate that root rot is not merely an isolated disease but a condition that disrupts the entire system.
Plants affected by this disease exhibit significant physiological alterations. Researchers observed a decrease in tree height, leaf area, and chlorophyll content, all indicators of compromised photosynthesis and reduced vegetative development. At the same time, elevated levels of proline and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) were detected, typical markers of oxidative stress and plant's immune response. These changes reflect the tree’s efforts to counteract the infection but also highlight its limitations in managing prolonged pathogenic attacks.
From the soil perspective, root rot modifies its chemical properties, reducing total nitrogen levels while increasing electrical conductivity and moisture. These conditions can favor the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and further degrade the environment for beneficial microbiota.
 Immagine 1: Effetti della malattia del marciume radicale sul microbioma e sui metaboliti delle radici e del suolo della rizosfera del ciliegio dolce.
Immagine 1: Effetti della malattia del marciume radicale sul microbioma e sui metaboliti delle radici e del suolo della rizosfera del ciliegio dolce.
A key finding of the study is the transformation of the soil and rhizosphere microbiome. In healthy sweet cherry trees, beneficial bacteria such as Actinobacteriota and fungi from the Mortierella genus dominate, known for their antagonistic properties against root rot pathogens. However, in trees affected by root rot, an increase in pathogenic fungi and bacteria like Bacillus is observed. While Bacillus can sometimes be beneficial, its presence here may indicate an emergency response by the plant, attempting to recruit microbial help. This microbiome imbalance introduces an additional layer of vulnerability.
Plant metabolism undergoes deep changes as well. In diseased roots, there is a significant reduction in essential metabolites such as phenylpropanoids, polyketides, lipids, and organic oxygen compounds. These compounds play a fundamental role in plant growth and immune defense, contributing to lignin production and stress signaling. The metabolic profile in the
rhizosphere also changes, with alterations in benzenoid compounds and volatile organic molecules, which can influence interactions between plant and microorganisms.
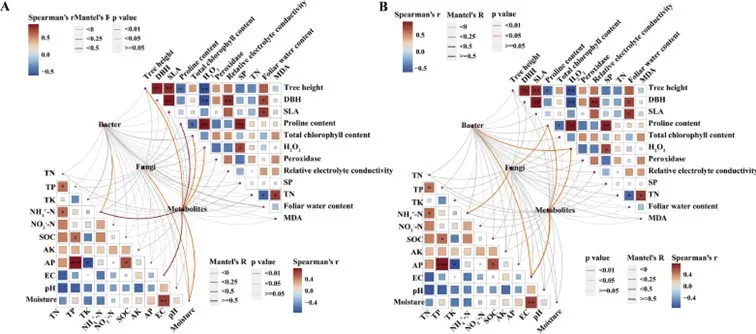 Immagine 2: Correlazione di funghi, batteri e composizione dei metaboliti con l'ambiente del suolo della rizosfera e i fattori fisiologici della pianta nella radice (A) e nel suolo della rizosfera (B). Confronti a coppie tra i fattori ambientali del suolo della rizosfera e i fattori fisiologici delle piante con un gradiente di colore che indica il coefficiente di correlazione di Spearman. I gruppi tassonomici (funghi, batteri e metaboliti) sono stati correlati a ciascun fattore ambientale del suolo della rizosfera e ai fattori fisiologici delle piante, come determinato dal test di Mantel. L'ampiezza dei bordi corrisponde alla statistica r di Mantel per le corrispondenti correlazioni di distanza. Il colore dei bordi rappresenta il livello di significatività P.
Immagine 2: Correlazione di funghi, batteri e composizione dei metaboliti con l'ambiente del suolo della rizosfera e i fattori fisiologici della pianta nella radice (A) e nel suolo della rizosfera (B). Confronti a coppie tra i fattori ambientali del suolo della rizosfera e i fattori fisiologici delle piante con un gradiente di colore che indica il coefficiente di correlazione di Spearman. I gruppi tassonomici (funghi, batteri e metaboliti) sono stati correlati a ciascun fattore ambientale del suolo della rizosfera e ai fattori fisiologici delle piante, come determinato dal test di Mantel. L'ampiezza dei bordi corrisponde alla statistica r di Mantel per le corrispondenti correlazioni di distanza. Il colore dei bordi rappresenta il livello di significatività P.
Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+), on the other hand, plays an important role, affecting the level of metabolites linked to beneficial bacteria. The plant utilizes these metabolites, such as flavonoids, to attract nitrogen-fixing bacteria, thereby improving its ability to respond to stress.
The study highlights how root rot affects not only the roots but also disrupts the entire plant-soil system. Addressing this complex network of interactions could open new possibilities for disease control. Targeted strategies, such as boosting beneficial microorganisms or improving soil conditions, could mitigate the impact of root rot in sweet cherry trees, enhancing cultivation outcomes.
Source: Chen, X., Zhang, N., Zheng, Z., Yu, H., Wu, Y., & Shi, F. (2024). Effects of root rot disease on the microbiome and metabolites in roots and rhizosphere soil of sweet cherry. Scientia Horticulturae, 338, 113734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113734.
Images: Xiaoxia Chen et al, 2024.
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












