In Russia, the industrial cultivation of cherries is concentrated in the southern part of the country, particularly in the regions of Voronezh, Belgorod, and Kursk. However, this crop is also spreading more widely in the central region of the country.
Increasing the number of plants in the field is crucial for boosting economic yield, and for this reason, there is significant interest in propagating early, high-yielding, and disease-resistant varieties. Many researchers have worked and are still working on cherry propagation techniques, using rootstocks of both sweet and sour cherries.
Types of rootstocks and their characteristics
For example, trees grafted onto Mahaleb cherry rootstocks have a short lifespan and low yields. When grafted onto steppe cherry rootstocks (Prunus fruticosa, dwarfing), they show great resistance to drought, good resistance of the root system to winter cold, strong growth, and resistance to chlorosis.
However, these trees have weaker growth and suffer from chlorosis when grown on soils containing carbonates. Cherry growers have created and widely implemented clonal rootstocks that propagate easily through vegetative means, are disease-resistant, and exhibit controlled growth.
Advantages of clonal rootstocks
These trees can grow on different types of soil with varying degrees of water availability. Clonal rootstocks are of interest and deserve attention. Promising rootstocks have been developed and are increasingly being used in the production of cherry seedlings.
The use of such rootstocks accelerates the time it takes for plantations to enter commercial production, increases yield, and reduces maintenance costs, especially for harvesting operations. It is necessary to assess the survival rate of certain cherry varieties on clonal rootstocks and evaluate the growth and development of variety-rootstock combinations in fruit nursery plantations.
Study on variety-rootstock combinations
The aim of the study conducted at the Voronezh State Agrarian University (Russia) was to investigate the propagation technology of cherry seedlings on clonal rootstocks and evaluate the growth and development characteristics of variety-rootstock combinations.
In this study, large-fruited cherry varieties were used: Improved Caucasica (control), Golubushka, Nalchinskaya, Ruby of Kuban, and Morning of Kuban, grafted onto medium-vigor clonal rootstocks VSL-1 and LC-52.
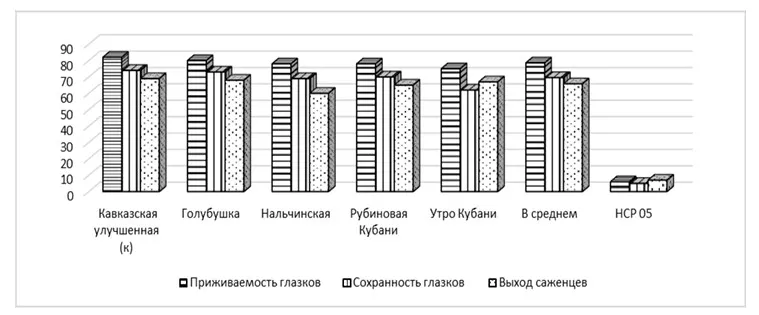 Figure 1. Yield of cherry seedlings on clonal rootstock VSL-1, %.
Figure 1. Yield of cherry seedlings on clonal rootstock VSL-1, %.
Results of the study
On the VSL-1 rootstock, the highest rate of rootstocks was achieved for the varieties: Improved Caucasica (69%), Golubushka (68%), Morning of Kuban (67%), and Ruby of Kuban (65%).
On the LC-52 rootstock, the best results were observed in the seedlings of the varieties Golubushka (73%), Ruby of Kuban (71%), and Morning of Kuban (69%). The variety Nalchinskaya showed the lowest values for both rootstocks, 65% and 60%, respectively.
 Figure 2 - Yield of sweet cherry on clonal rootstock LC-52, %
Figure 2 - Yield of sweet cherry on clonal rootstock LC-52, %
Growth characteristics of seedlings
The average height of the cherry seedlings for the varieties ranged from 167 to 171 cm, with 4-7 shoots per seedling. The average length of the shoots was 55-61 cm, and their total length amounted to 278-330 cm per plant, with a stem diameter of 1.6 cm.
These indicators suggest good development of one-year-old cherry seedlings in the considered nursery.
Source: Nozdracheva R. G., Kostennikov R. I. " PECULIARITIES OF CHERRY PROPAGATION ON CLONAL ROOTSTOCKS " Materials of the International Youth Scientific and Practical Conference "FORESTRY-BIOLOGICAL FOUNDATIONS OF SUSTAINABILITY OF NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL PHYTOCOENOSES" (2024): 242-248. DOI: 10.58168/FBFSNAP2024_242-248 url: https://bibl.vgltu.ru/en/nauka/conference_article/11753/view (Date of access 15.03.2025).
Images: Ноздрачева Р. Г., Костенников Р. И., 2024; SL Fruit Service
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












