Donato Gerin, Stefania Pollastro, Rita Milvia De Miccolis Angelini, Francesco Faretra, Franco Nigro
Department of Soil, Plant, and Food Sciences - University of Bari Aldo Moro
The prokaryote Candidatus Phytoplasma pruni is the agent responsible for the disease in stone fruit plants known as X-disease, which is causing significant economic losses in the United States and Canada.
This phytoplasma is transmitted by at least eight species of pests to plants of the genus Prunus, but it has a wide range of host species, especially in the Asteraceae and Brassicaceae families. Furthermore, like most phytoplasmas, it can be transmitted through grafting and easily spread through propagation material.
On cherry trees, the fruits appear discolored and distorted, with a bitter or tasteless flavor. Initially, symptoms appear on a single branch or often only on a single cluster of fruits, spreading to the entire tree in subsequent seasons. During the growing season, the leaves show chlorosis, curling, reduced size, and premature shedding (Figure 1), while in later stages, bronzing or anthocyanosis along the central and basal veins is observed. The type and severity of symptoms may vary depending on the cherry variety and the strain of Ca. Phytoplasma pruni.
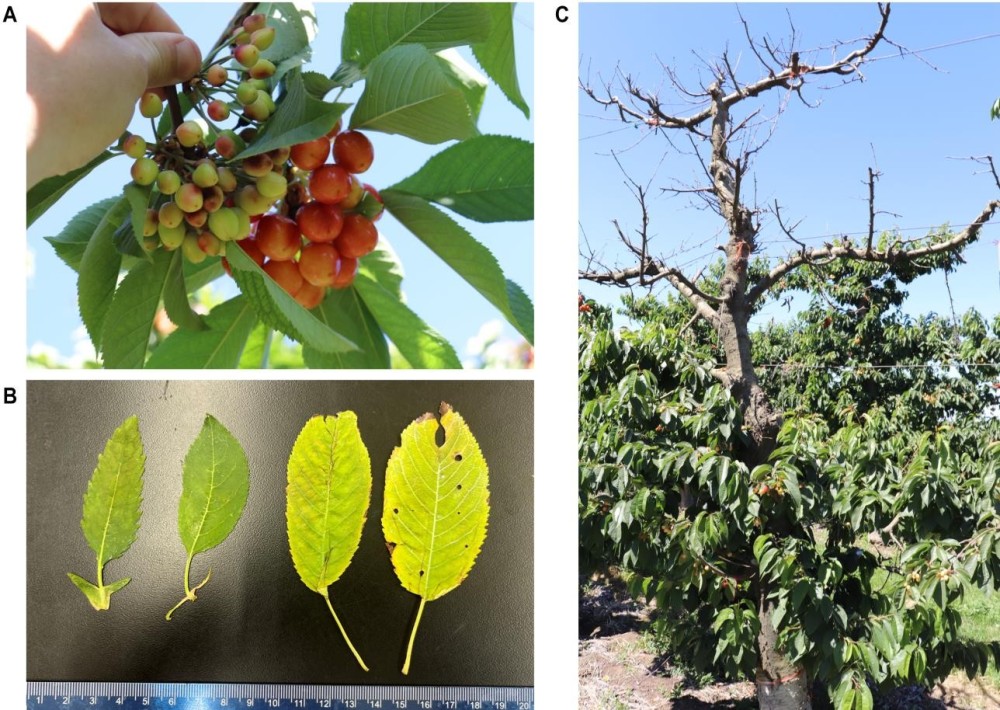 Figure 1. Symptoms caused by X-disease on sweet cherry (Harper et al., 2023). A, size, color, and shape of infected fruits compared to normally developed fruits; B, reduced-sized leaves with enlarged leaf stipules; C, branch dieback.
Figure 1. Symptoms caused by X-disease on sweet cherry (Harper et al., 2023). A, size, color, and shape of infected fruits compared to normally developed fruits; B, reduced-sized leaves with enlarged leaf stipules; C, branch dieback.
Considering the increasing incidence of X-disease observed in recent years in both the United States and Canada, an intervention plan has been published (Harper et al., 2023) with the aim of providing information on the biology of Ca. Phytoplasma pruni, the expression of the disease, host-pathogen and pathogen-vector interactions.
Furthermore, the plan includes strategies to prevent the spread of the pathogen through management programs that, as outlined in suitable phytosanitary regulations for containment, are based on the use of certified propagation material, the removal of infected plants, and the control of weed hosts, as well as vectors.
Download the full document (Harper, et al. (2023). Recovery Plan for X-Disease in Stone Fruit Caused by ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma pruni’. Plant Health Progress, 24(2), 258-295. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-02-23-0016-RP
Cover Photo: WSU Tree Fruit
Cherry Times - All rights reserved.











