Improving productivity and sustainability in cherry growing may seem like an ambitious goal, but the results of research conducted on this topic are encouraging.
To improve yield, the starting point must be the enhancement of plant status. But how? Biostimulants, such as glycine betaine or seaweed-based biostimulants (e.g., Ecklonia maxima), can represent a sustainable approach to improve plant conditions, even under adverse environmental circumstances.
Despite their potential, few studies have focused on the effects of the exogenous application of these biostimulants on cherry tree physiology. To fill this research gap, a study was conducted in a commercial sweet cherry orchard in Portugal, using the Lapins and Early Bigi cultivars.
Experimental setup and treatments
The trees were treated with products based on glycine betaine and Ecklonia maxima at two different concentrations (0.25% and 0.40% for glycine betaine; 0.30% and 0.15% for Ecklonia maxima). Additionally, a treatment combining the lowest concentrations of both biostimulants (Mix — 0.25% glycine betaine and 0.15% Ecklonia maxima) was applied, along with a control group treated with water.
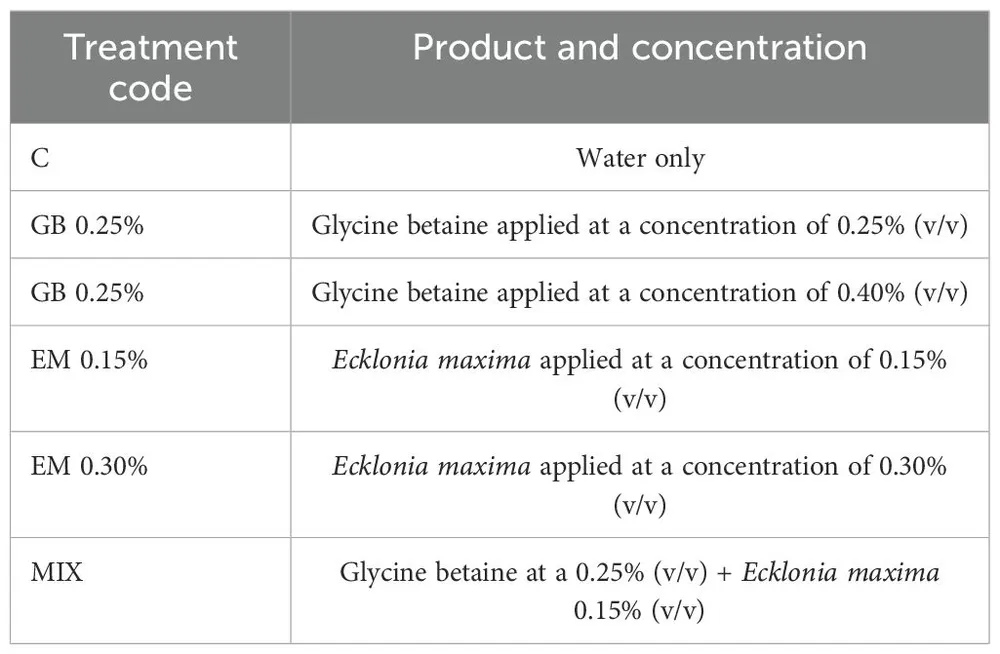 Image 1. Experimental treatments and their concentrations.
Image 1. Experimental treatments and their concentrations.
Applications were carried out for three consecutive years (2019, 2020, and 2021) at three different phenological stages, according to the BBCH scale: 77, 81, and 86 BBCH.
Key findings and physiological effects
The results revealed significant differences between cultivars and years, with notable effects observed in 2021, a hotter and drier year compared to 2019. Moreover, the results showed that, in general, the application of biostimulants led to improvements in water status compared to the control samples.
Additionally, biostimulants reduced pigment loss in the leaves and also improved their biosynthesis. The Chlorophyll a/Chlorophyll b ratio, ranging from 2 to 4, indicated a greater capacity for light absorption, with higher photosynthetic rates. Therefore, the application of biostimulants helped maintain lower stress levels in treated leaves.
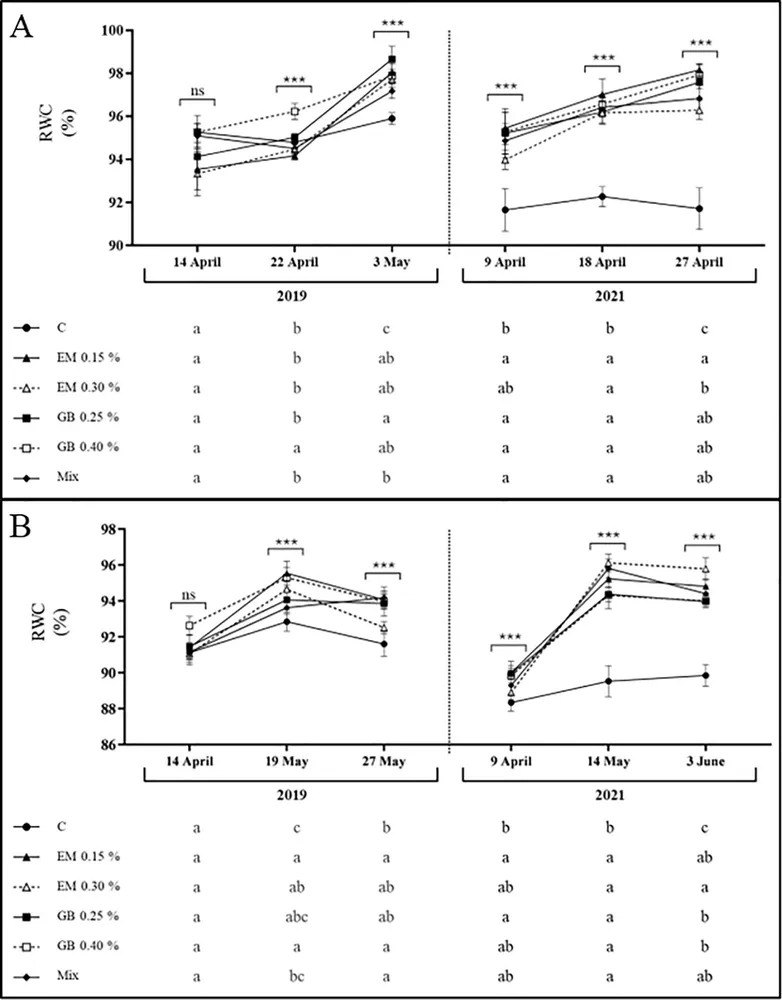 Image 2. Relative water content (RWC, %) of cherry leaves cv. Early Bigi (A) and cv. Lapins (B) after spray treatment application in 2019 and 2021. Data are presented as mean ± SD of eight replicates.
Image 2. Relative water content (RWC, %) of cherry leaves cv. Early Bigi (A) and cv. Lapins (B) after spray treatment application in 2019 and 2021. Data are presented as mean ± SD of eight replicates.
Furthermore, biostimulants also contributed to the preservation of cell membrane integrity. These improvements were most evident after the application of both concentrations of the seaweed-based biostimulant E. maxima and the glycine betaine 0.40% treatment, which positively influenced the performance of the cherry trees.
Impact on biochemical components
The content of soluble sugars and starch decreased during fruit development in both cultivars and years; however, biostimulants increased these contents, with increases of about 15% to 30% in leaves treated with Ecklonia maxima.
The soluble protein content also showed the same trend in treated leaves. Biostimulants, particularly Ecklonia maxima, demonstrated a significant positive effect (p ≤ 0.001) on the total phenolic content, with increases of 25% to 50% in treated leaves.
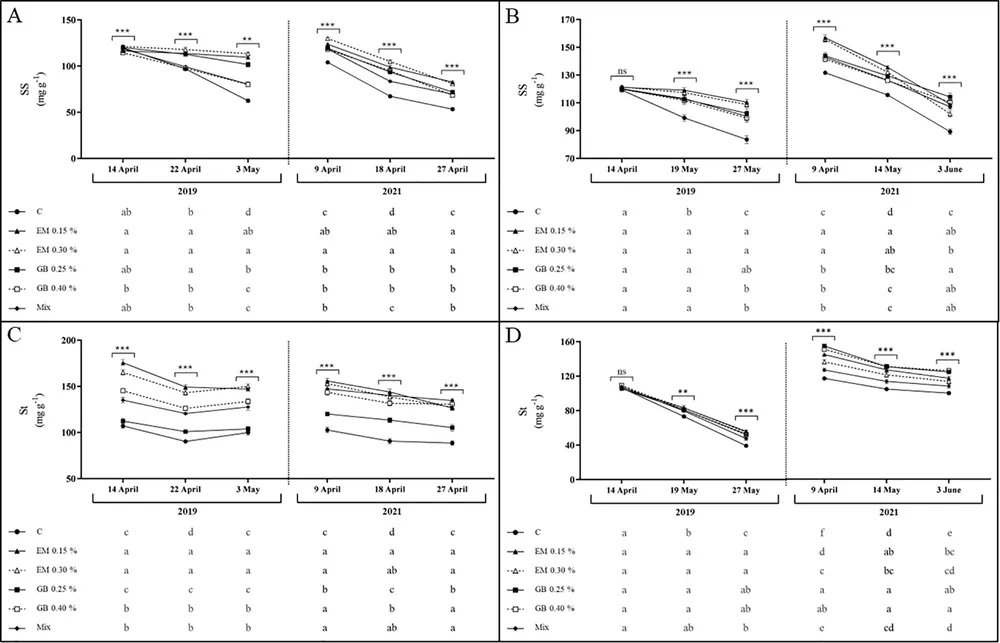 Image 3. Soluble sugars (SS, mg g -1 DW) and starch content (St, mg g -1 DW) of cv. Early Bigi leaf cherry (A, C) and Lapins (B, D) after application of the spray treatment in 2019 and 2021. Data are mean ± SD of eight replicates.
Image 3. Soluble sugars (SS, mg g -1 DW) and starch content (St, mg g -1 DW) of cv. Early Bigi leaf cherry (A, C) and Lapins (B, D) after application of the spray treatment in 2019 and 2021. Data are mean ± SD of eight replicates.
These results indicate the potential of biostimulants to mitigate the impact of environmental stress and improve physiological processes in sweet cherry cultivation, contributing to improved crop performance.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the application of biostimulants, especially those based on algae, represents an innovative and sustainable approach in fruit production systems.
Source: Afonso S, Oliveira I, Guedes F, Meyer AS and Gonçalves B (2024) GLYCINE betaine and seaweed-based biostimulants improved leaf water status and enhanced photosynthetic activity in sweet cherry trees. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1467376. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1467376
Images: Silvia Alfonso et al., 2024; SL Fruit Service
Melissa Venturi
University Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved













