The colour of the sweet cherry fruit is a significant factor in determining the fruit's quality and market value. Anthocyanin is responsible for the red colour, and its presence has a direct impact on the colour of fruits.
Multiple biotic and abiotic factors, such as nutrition, temperature, light, and injury, have a direct influence on anthocyanin accumulation. Among them, temperature serves a crucial role in regulating the accumulation of anthocyanin. In fact, low temperature can induce anthocyanin biosynthesis and the expression of related genes, whereas high temperature accelerates anthocyanin degradation and is detrimental to anthocyanin biosynthesis.
During the development of plant tissue, adaptations to variations in the external environment cause colour changes. The weather during this period can have some strong and rapid fluctuations, which may have a significant impact on the colour of fruit. Under global warming, this phenomenon will be a prevalent problem in the production of sweet cherries, directly affecting the colour and quality of the fruit.
In this study, conducted by the researchers of the Shandong Institute of Pomology and the Shandong Agricultural University (China), physiological and transcriptomic techniques were used to examine anthocyanin, sugar, plant hormones, and related gene expression in order to determine the effects of high temperature on fruit colouring and the underlying mechanism.
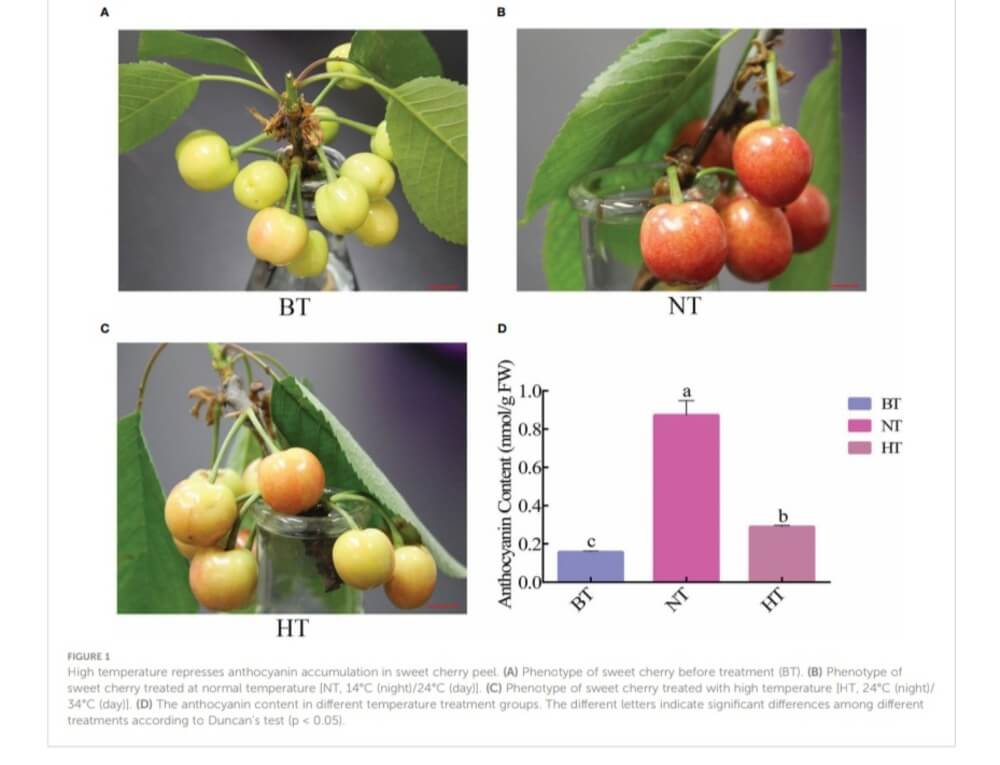
The trial had the aim to test two different temperature regimes on similar branches from 25 days after full blooming: normal temperature (NT: 24°C day/14°C night) and high temperature (HT: 34°C day/24°C night). Results demonstrated that elevated temperature inhibited anthocyanin accumulation in fruit peel and slowed down the colouring process. After 4 days of exposure to normal temperature and high temperature, the total anthocyanin content of fruit epidermis increased by 455% and 84%, respectively.
Likewise, the amount of eight anthocyanin monomers was significantly greater in NT than in HT. High temperature also altered the concentrations of plant polysaccharides and hormones. The total soluble sugar content of NT and HT increased by 29.49% and 16.88%, respectively, after four days of treatment. Auxins, gibberellic acid and abscisic acid (ABA) increased in both regimens, but at a slower rate in HT. In contrast, the levels of jasmonic acids and cis-zeatins decreased faster in HT than in NT.
The correlation analysis revealed a significant relationship between the abscisic acid concentrations and the total anthocyanin concentrations, thus indicating that the presence of this hormone leads to the inhibition of anthocyanin biosynthesis. HT also inhibited the activation of structural genes in anthocyanin biosynthesis as well as the repression of genes dominating the catabolism and inactivation of abscisic acid with a consequent slowing in fruit colouring.
These findings suggest that ABA may be a key regulator in the inhibition of sweet cherry fruit colouring by elevated temperatures.
Overall, our findings indicate that a high temperature inhibits the colouring of sweet cherry significantly. ABA, a key positive regulator of the maturation and colouring of non-climacteric fruits, likely plays a crucial role in this process.
An increase in temperature delays the downregulation of crucial genes expression during fruit colouring, resulting in increased ABA catabolism and ABA inactivation. This reduces the amount of ABA in fruit skin and delays colouring.
Source: Tan Y, Wen B, Xu L, Zong X, Sun Y, Wei G and Wei H (2023), High temperature inhibited the accumulation of anthocyanin by promoting ABA catabolism in sweet cherry fruits. Front. Plant Sci. 14:1079292. doi:10.3389/fpls.2023.1079292.
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











