The volume of irrigation water to be applied to the cherry orchard is the amount needed to replenish the moisture removed from the soil by atmospheric conditions and the water lost through plant transpiration. The sum of these two factors is defined as evapotranspiration, abbreviated as ET.
Calculating this quantity in the field, however, can be a difficult task, as the most precise instruments such as water balances and Eddy covariance towers are expensive and therefore rarely used by the average fruit grower. Consequently, ET is usually approximated by calculating reference evapotranspiration (ET0), which is also known as atmospheric evaporative demand.
These methods, despite their widespread use, often lack spatial precision and may not account for variations in soil and plant water status across different areas of the orchard, potentially resulting in over-irrigation or under-irrigation. Another possible alternative for determining how much water to provide to the plants is the measurement of water potential, an indicator that is widely recognized for its reliability by the scientific community.
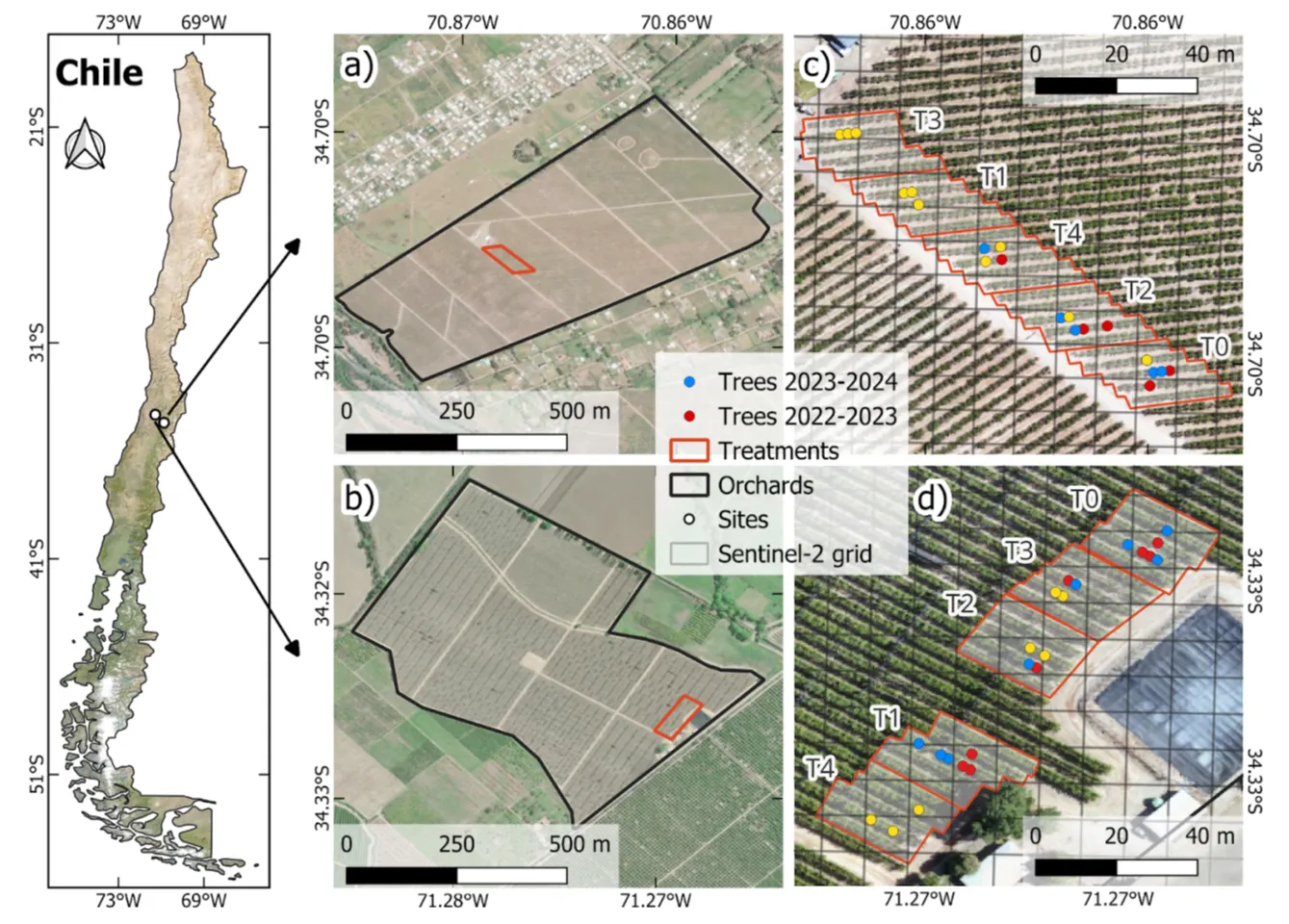 Image 1: Study Area. The map on the left shows the orchards' location in Chile's central region. The maps on the right display the orchards in (a) Rio Claro and (b) La Esperanza, and (c) and (d) represent the irrigation treatments (T0, T1, T2, T3, T4). The red and blue dots represent the experimental trees selected for the 2022‐2023 and 2023‐2024 seasons, respectively, while the yellow dots indicate the trees selected for both seasons. Source: Zambrano et al., 2024.
Image 1: Study Area. The map on the left shows the orchards' location in Chile's central region. The maps on the right display the orchards in (a) Rio Claro and (b) La Esperanza, and (c) and (d) represent the irrigation treatments (T0, T1, T2, T3, T4). The red and blue dots represent the experimental trees selected for the 2022‐2023 and 2023‐2024 seasons, respectively, while the yellow dots indicate the trees selected for both seasons. Source: Zambrano et al., 2024.
The tension of water within the plant, which is also called water potential, is directly reflected in the solute concentration and water pressure of the leaf or stem. However, these measurements are time-consuming, require a lot of work, and are not suitable for large-scale applications or continuous monitoring.
The main objective of the work conducted in Chile in collaboration with the German research center for artificial intelligence was to predict the daily spatial variation of plant water potentials through the use of machine learning models. During the 2022–2023 and 2023–2024 seasons, from October to April, 30 trees were monitored on a weekly and biweekly basis. The trees were planted with the sweet cherry variety Regina and the study area was the central region of Chile.
Support vector machine (SVM), extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), and random forest (RF) models were used to predict the water potential. As meteorological parameters, relative humidity, temperature, reference evapotranspiration (ET0), and vapor pressure deficit (VPD) were considered.
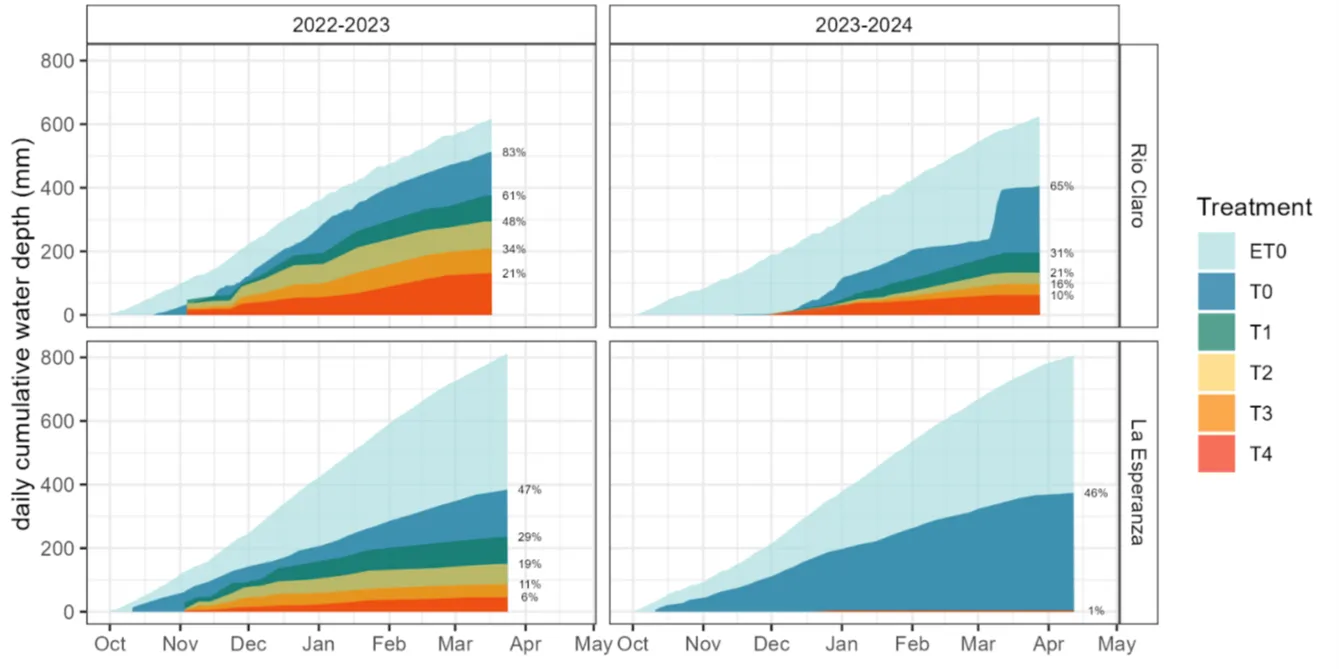 Image 2: Variation of daily cumulative water depth (mm) applied by irrigation per treatment in comparison with reference evapotranspiration (ET0). The starting point for the accumulation of ET0 corresponds to the first day of irrigation for each orchard and season. Source: Zambrano et al., 2024.
Image 2: Variation of daily cumulative water depth (mm) applied by irrigation per treatment in comparison with reference evapotranspiration (ET0). The starting point for the accumulation of ET0 corresponds to the first day of irrigation for each orchard and season. Source: Zambrano et al., 2024.
Furthermore, biophysical parameters derived from Sentinel-2 and vegetation indices were used. The researchers conducted a comparison between two schemes: one for estimation and the other for prediction. The preliminarily published results show that XGBoost and RF were the most effective for both objectives. The estimation scheme had a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.76.
On the other hand, the forecasting model showed an R2 of 0.59. It was observed that the weather predictors, including temperature, ET0, and VPD, had a greater weight in the model, as indicated by the variable importance analysis. These are followed by vegetation indices that employ shortwave infrared regions, which emphasize the water stress index. Unlike the use of evapotranspiration, this model provides an alternative approach to optimize irrigation in cherry plantations.
The effectiveness of the model could be improved by conducting additional measurements of water potential at high levels of plant water stress. Moreover, there is a need to add the evaluation of the effectiveness of the measurements on cloudy days.
Source: Francisco Zambrano, Abel Herrera, Mauricio Olguín, Miro Miranda, Jesica Garrido, Andrea Miyasaka, Prediction of the daily spatial variation of stem water potential in cherry orchards using weather and Sentinel-2 data, 2024, https://doi.org/10.31223/X53H6S.
Images: Zambrano et al.
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












