The product integrates into the plasma membranes of plant cells because they have the same composition (vegetable phospholipids). This same characteristic ensures that it does not cover the stomata and does not interfere with the dynamism of the plant's plasma membrane.
The commercial expansion of cherry cultivation is still limited due to the frequent risk of losses in productivity and fruit quality caused by weather problems, such as spring rains that cause cracking.
The damage to the fruit is caused by the destruction of the cherry cells, which spreads like a cascade effect. All cells have a structure called the plasma membrane, which is essentially a phospholipid bilayer.
In plants, there is the cell wall, which helps provide greater mechanical strength to protect the cell. To reduce cellular damage caused by rain, it is essential to use strategies aimed at strengthening and increasing phospholipids in the membranes. This enhances the elastic capacity of plant cells to withstand a greater volume of water without breaking. It is therefore reasonable and predictable that the use of such a strategy would reduce the incidence of cracking.
In this context, the decision was made to evaluate the product Biotens. This product was created in 2001 by the national chemist Mario Reyes Salinas, who studied with Dr. Derek Barton (Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 1969). Biotens, in its composition, corresponds to vegetable phospholipids dissolved in water, free of chemical solvents and calcium.
Biotens and its Characteristics
Biotens is a product that integrates into the plasma membranes of plant cells because it has the same composition (vegetable phospholipids). Biotens, due to this characteristic, does not cover the stomata and does not interfere with the dynamism of the plant's plasma membrane, meaning the cell maintains absolute control over what enters and exits it.
- Increases the elastic capacity of plant cells (fruit) against volume increases caused by rain.
- Protects fruits from damage caused by rain.
- The absence of alcohols and carboxylic acids in its composition prevents the lipid peroxidation process that generates microfractures in the plant's plasma membrane. When this phenomenon occurs, it is observed as a crack during packaging and/or at the destination.
- Facilitates the transport of nutrients and/or molecules of interest into the cell, increasing their bioavailability and effectiveness.
- Improves the coverage and distribution of applied products, optimizing water usage.
Biotens is a tool free of calcium. This mineral is part of the plasma membrane and the cell wall, providing greater resistance to intercellular bonds and increasing tissue rigidity. If we apply a product for cracking that contains phospholipids and calcium in its composition, we will achieve a low incidence of cracking but at the cost of sacrificing the size of our cherries. Phospholipids and their interactions, if not adequately understood, are often a double-edged sword.
Dr. Richard Bastías (UdeC 2015) conducted a field study that involved electron microscopy analysis of the surface of fruits treated and untreated with Biotens to determine the presence of microfractures in the cuticle. For this purpose, tissue samples were taken from the peduncle, lateral, and distal areas of the fruits of each treatment.
Visual aspect of the microfractures in the cuticle of fruits treated with Biotens (a and b) and untreated (c and d). The upper images correspond to the distal area of the fruit, while the lower ones correspond to the peduncle area. Fruits treated with Biotens show the formation of a film that provides greater integrity to the cuticle (photos 4a and 4b).
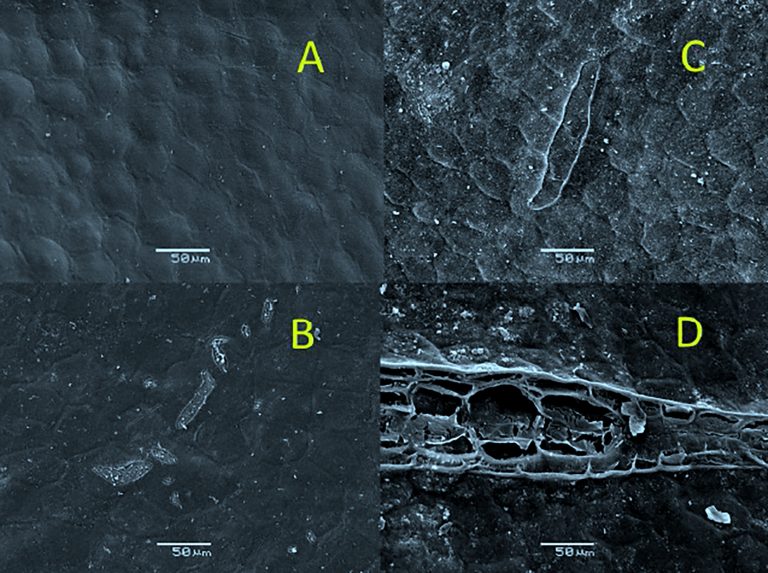 Image 1.
Image 1.
The image 2 shows that both the length and width of the cuticle microfractures were reduced with the application of Biotens, with differences observed in the distal, peduncular, and lateral areas of the fruit.
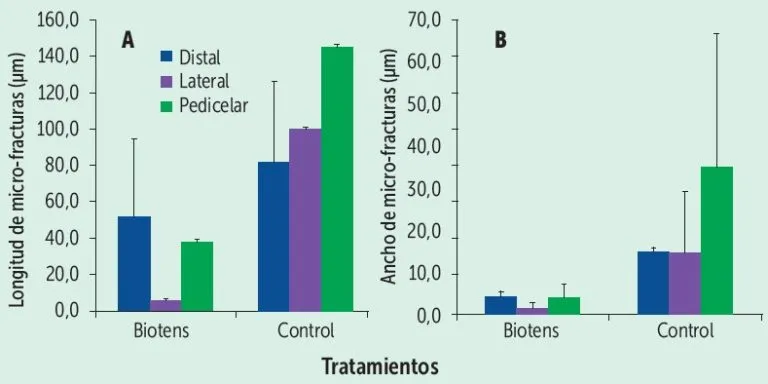
In conclusion, the application of Biotens to cherries, under field conditions, effectively reduces the susceptibility of fruits to cracking damage.
Source: Redagrícola
Image: Redagrícola
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












