Cherry cultivation in China is particularly important in the northern and northeastern regions, where this species has become one of the most economically significant crops. A recent Chinese study examined the photosynthetic characteristics of various sweet cherry varieties cultivated on the Loess Plateau, a region with a semi-arid continental climate that presents unique environmental challenges.
The study analyzed the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), water use efficiency (WUE), and transpiration rate (Tr), along with other ecological variables that influence the photosynthetic process in sweet cherry plants.
The results showed that sweet cherry photosynthesis generally follows a bimodal pattern, with a first peak in the early morning and a second in the late afternoon, interrupted by a midday reduction.
This decrease is mainly due to stomatal mechanisms, as observed in the “Rainier” and “Summit” varieties. However, in some cases, as seen in other cultivars, the drop in photosynthesis is not associated with a reduction in stomatal opening but rather with decreased photosynthetic activity in the chloroplasts.
 Image 1 - Location of the Loess Plateau and the study plot
Image 1 - Location of the Loess Plateau and the study plot
Another important factor influencing the photosynthetic rate is water use efficiency. “Rainier” and “Summit” varieties demonstrated high water use efficiency, despite being grown in soils with lower water content than other varieties. This indicates that these cultivars are particularly efficient in utilizing available water, a key factor for their productivity in a semi-arid environment.
Conversely, “Tieon” variety exhibited lower efficiency, suggesting that simply having water available is insufficient to ensure optimal photosynthesis. However, in general, water absorption from the roots and irrigation management practices are crucial for optimizing photosynthesis. In addition to water, leaf temperature and light intensity also play an important role.
The study demonstrated that the use of plastic coverings (tunnel) has a significant effect on radiation intensity and ambient temperature. Therefore, proper orchard management should take microclimatic conditions into account; generally, an excessive leaf temperature reduces photosynthetic efficiency.
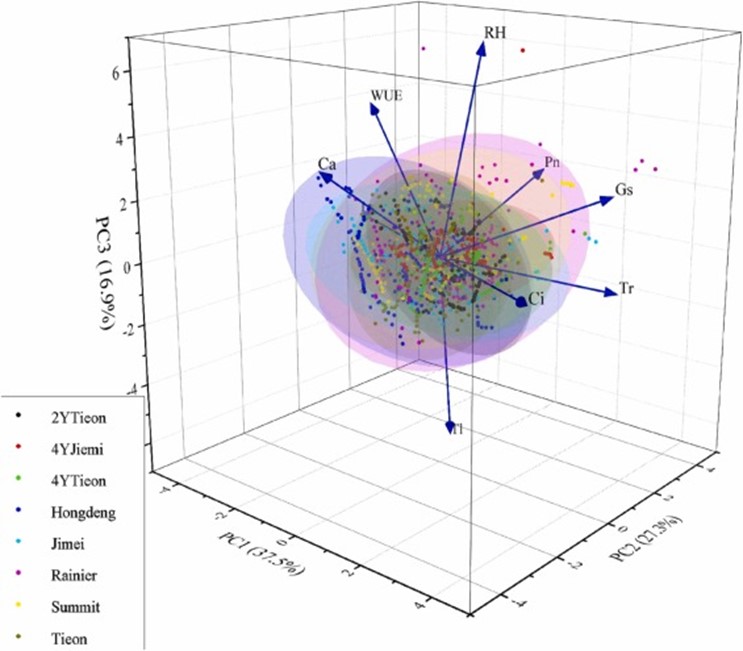 Image 2 - Principal component analysis was conducted on the photosynthetic characteristics of various cherry varieties
Image 2 - Principal component analysis was conducted on the photosynthetic characteristics of various cherry varieties
The study's results provide useful insights for improving sweet cherry orchard management in semi-arid regions like China’s Loess Plateau. Practices such as irrigation, appropriate use of plastic covers, and monitoring leaf temperature can help optimize the photosynthetic yield of various sweet cherry varieties. In particular, the “Rainier” variety emerged as one of the top performers under the study conditions, thanks to its ability to maintain high photosynthetic levels even in less favorable conditions.
In conclusion, the study highlighted how sweet cherry varieties respond differently to ecological and management variables, offering a scientific basis for selecting cultivars best suited for Loess Plateau cultivation and for developing more effective management strategies across different growing areas.
Photos: Muhao et al., 2024; SL Fruit Service
Source: Chen, M., Feng, S., Gao, M., Liu, M., Wang, K., Wang, J., Shangguan, Z. & Zhang, Y. (2024). The difference in the photosynthetic characteristics and soil moisture of different varieties of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Agricultural Water Management, 302, 109002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2024.109002
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












