Sweet cherry production in France has been in decline since the 1980s, influenced by climate change and biological pressures. Traditional selection is long and complex due to the prolonged juvenile stage and the complexity of polygenic traits, but advances in genetic research have identified key markers through quantitative locus mapping (QTL) and genome-wide association studies (GWAS).
However, genotyping by sequencing (GBS) is emerging as a cost-effective solution to analyse high-density SNPs and improve selection strategies.
'Horticulture Research' published in September 2023 a study entitled 'Genome-wide association mapping in a sweet cherry germplasm collection (Prunus avium L.) reveals candidate genes for fruit quality traits'. This study used a germplasm collection of 116 sweet cherry accessions to analyse 23 agronomic fruit quality traits over a period of 2-6 years, showing high phenotypic variation.
Subsequently, SNPs were analysed by GBS, and GWAS studies identified 65 unique SNP-trait associations for eight traits, including candidate genes in phytohormone, calcium and cell wall metabolisms. In order to identify colocalising SNP-trait associations for fruit quality traits, the researchers synthesised the results of this study and nine previous articles, identifying a total of 11 and 12 candidate genes for fruit size and fruit splitting traits.
The study's methodology characterised phenotypic variation, revealing high broad-spectrum heritability for many traits, suggesting a strong genetic component. GBS sequencing produced a rich set of SNPs, facilitating the identification of genetic associations between multiple traits. Analysis of population structure revealed distinct subpopulations, contributing to a deeper understanding of genetic diversity in the collection.
The identified SNP-tract associations, supported by a thorough literature review, improve the understanding of genetic control of fruit quality in sweet cherry. This knowledge is crucial for the development of marker-assisted selection strategies, accelerating selection efforts to meet consumer preferences and producer requirements by addressing the complexity of the genetic architecture of sweet cherry and its impact on fruit quality traits.
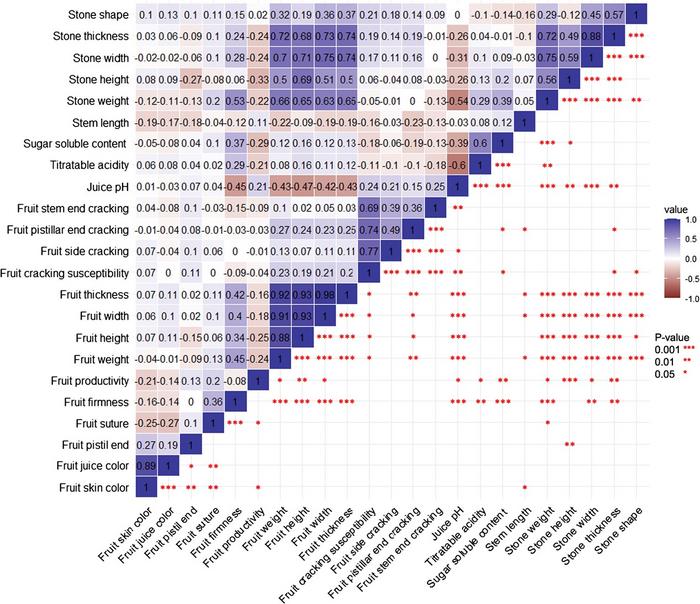 Image 1: Pearson correlation matrix of the 23 studied traits.
Image 1: Pearson correlation matrix of the 23 studied traits.
Read the full article: EurekAlert!
Image: Horticulture Research
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











