The research conducted by Washington State University addressed the challenge of managing spring frost in sweet cherry production, particularly vulnerable to cold damage in early spring. In the 2022-23 season, the net yield of fruits in the state of Washington witnessed a significant reduction of 21% due to cold damage occurring at the end of winter and early spring, as reported by USDA NASS in 2022.
The acclimatization of buds to cold temperatures in early spring is a crucial phenomenon, as occasionally warmer temperatures can accelerate bud break, making them more susceptible to subsequent frost damage. Consequently, understanding the critical temperature at which buds are damaged is essential for the timely implementation of mitigation measures, such as the use of heaters and wind machines.
Current cold hardiness models use air temperature as a predictive indicator to estimate specific critical temperatures for the cultivar. However, crop tissues have a unique ability to retain heat, influencing tissue temperature during clear nights or direct exposure to daylight.
In the spring seasons of 2022 and 2023, experiments were conducted on three blocks of sweet cherry (Prunus avium cv. Chelan) in Central Washington. A direct contact sensor (thermocouple) and a non-contact sensor (radiative frost) were tested against the control of a standard air temperature sensor.
Precision type E thermocouples were inserted into dormant flower buds to directly measure bud tissue temperature (Tc). Similarly, radiative frost sensors were tested, designed to simulate leaf temperature (Trf) during spring frost events.
The results highlighted a significant difference between nightly average temperatures (1800 - 0700 hours) of air temperature, radiative frost temperature, and direct bud tissue temperature (Ta, Trf, and Tc). This difference emphasizes that both air temperature and radiative sensors record different temperatures than the actual bud tissue temperature.
In particular, the exclusive use of air temperature could lead to inaccuracies in predicting critical temperatures, resulting in premature or delayed activation of frost mitigation measures. The observed offsets revealed that radiative frost sensors recorded lower bud tissue temperatures, attributable to their large sensitive surface compared to direct thermocouple measurements.
Furthermore, it emerged that air temperature was consistently higher than bud tissue temperature (Tc). These results raise doubts about the reliability of cold hardiness models based solely on air temperature, suggesting that the use of bud tissue temperature could improve the accuracy of predictions.
As a result, further research is needed to accurately estimate errors in predictions of cold hardiness models based on air temperature rather than bud tissue temperature. This deepening is crucial for enhancing frost management strategies and mitigating errors that could negatively impact sweet cherry production.
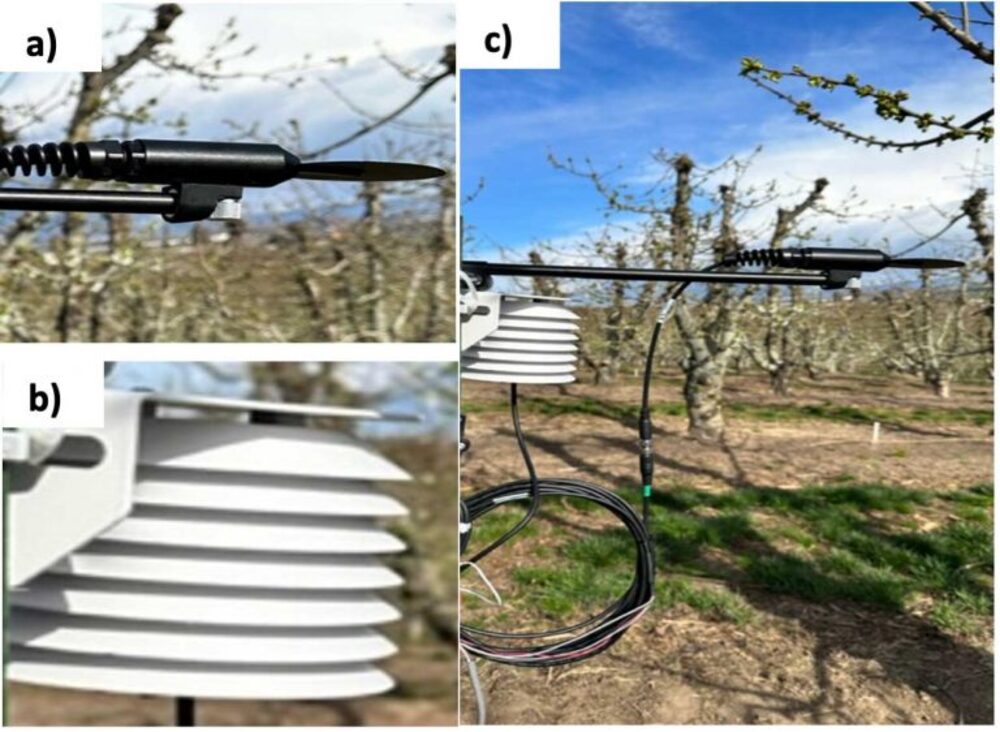 Figure 2. a) Radiative frost sensor, b) aspirated air temperature and relative humidity probe, and c) integrated sensing system deployed in the orchard at 5 feet AGL.
Figure 2. a) Radiative frost sensor, b) aspirated air temperature and relative humidity probe, and c) integrated sensing system deployed in the orchard at 5 feet AGL.
Read the full article: Washington State University
Image: Washington State University
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











