The cherries are in the midst of the harvest, and what seemed like a dream season is now facing its first obstacle: in various regions, there has been a case of fruit abortion, a phenomenon known in Spanish as pasma. In light of this, and to provide insight into what is being observed in the field, Mundoagro spoke with consultants to get their opinions.
According to the experts, although some growers have experienced more cases of fruit abortion compared to other seasons, overall, the production and exports for the 2024-2025 season will not be affected. Jordi Casas, an agronomist and national and international consultant specializing in deciduous fruit trees, explains that the number of abortions has been higher than expected.
“We had low temperatures in July and early August, which was very positive as we could have had a good amount of reserves. Therefore, the abortions should not have occurred. In any case, we experienced a higher-than-normal number of abortions in two very prominent varieties, Regina and Lapins, which were associated with cold and late areas, such as San Fernando, Curicó, Cordillera, Chimbarongo, and Talca.”
Casas explained that the higher number of abortions compared to the previous season was recorded mainly in early zones with poor-quality cold, which caused uneven ripening and fruit set. “This season, the abortions occurred in colder areas. Nonetheless, this does not affect the production and export of the campaign, which will range between 110 and 115 million boxes.”
The consultant emphasizes that several aspects of the campaign still need to be assessed, and measures that should or should not have been taken need to be analyzed. Patricio Morales, an agronomist and international consultant for stone fruits and cherries, indicated that during his visits to the fields, he observed abortions in fruits affecting varieties like Santina, Regina, and Lapins: “It was not so aggressive, so it does not affect the decline in industry estimates. In fact, this week, I was in Chillán, visited four growers, and they all had plenty of fruit.”
The abortions have been recorded throughout the country, Morales notes, citing the Metropolitan, Sixth, Seventh, Curicó, Linares, Talca, and Chillán areas. “I think it was positive because we managed to reduce orchard volumes, which helped improve fruit calibers and sizes. Imagine if everything had set; we would have had smaller fruits.”
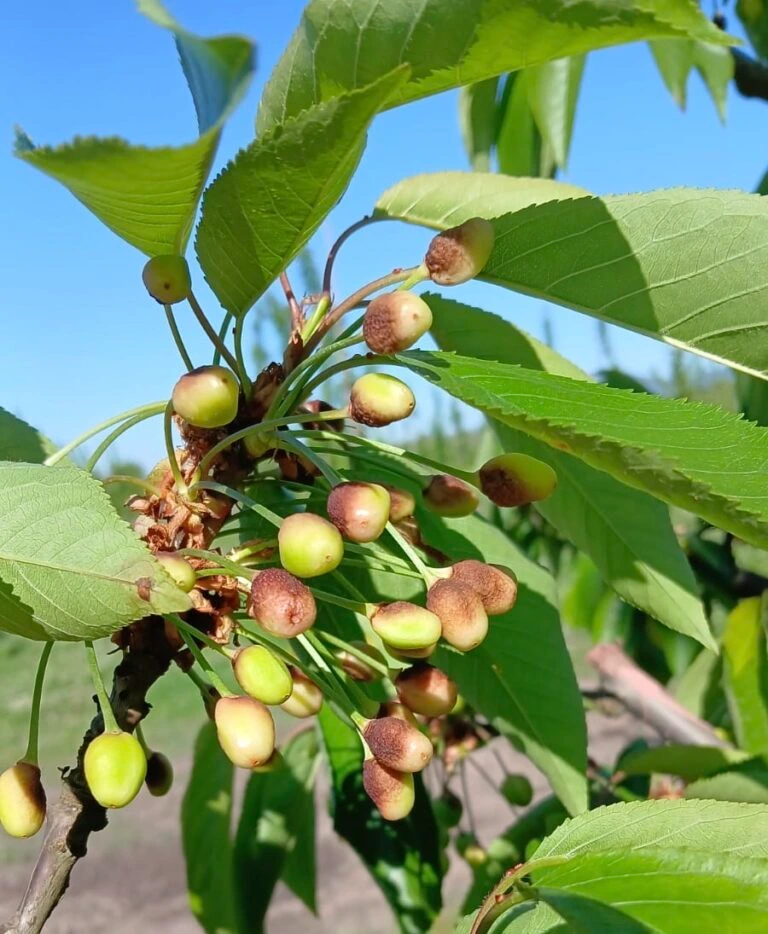

Why does this phenomenon occur?
According to reports, abortion or pasma occurs 25-30 days after full flowering, when the fruit has already formed and then falls. This is related to competition, especially for sugars and carbohydrates. A tree with an excessive load, for example, will naturally abort more fruits due to competition for photosynthates.
According to Morales, these abortions were caused by several factors. “The first was the very cold spring, combined with a very abundant flowering, which affected transpiration and caused a carbohydrate deficit, leading to flower drop. Moreover, during many flowering situations, there were cloudy or cold days, which didn’t help. On the other hand, I saw many growers who pruned too late, pruned poorly in winter, didn’t thin enough, and this led to a higher number of plant abortions.”
Casas explains that it was a very strong start to flowering along with a very high fruit set, which imposed greater demands on the plant. “For instance, if the plant has a waterlogged soil, its roots cannot grow much. Therefore, root growth is delayed, which means reserves run out before the plant can acquire the supplements it needs and perform photosynthesis. That’s why abortions occurred.”
Both Morales and Casas agree that abortions occurred in orchards with and without roofs. “We found a higher number of abortions under covers, but I believe it was due to a lack of discipline in managing the covers. So, overall, we observed both roofed and non-roofed orchards.”
First Mundoagro Congress: Cherry Special
Jordi Casas and Patricio Morales are among the leading experts who will speak at the “First Mundoagro Congress: Cherry Special,” which will take place on May 14 at the Monticello Hotel in San Francisco de Mostazal.
The event, organized by Mundoagro and the consultancy firm Asesorías y Servicios Agrícola, will provide information on key technical issues for the sector to produce high-quality fruit.
For more information, visit the following link https://congresos.mundoagro.cl/congresos/especial-cerezas/.
Read the full program here (in Spanish)
Source: Mundoagro
Image: Muindoagro
Cherry Times - All rights reserved