The identification of different sweet cherry cultivars has made a significant leap forward with the application of Machine Learning (ML). This technological advancement is described in a 2020 Polish study. The study focused on the endocarp (pit) of sweet cherry, and the results achieved can bring substantial benefits to industries requiring precise cultivar identification, since traditional methods can be time consuming and subjective.
The aim was to assess the textural and geometric properties of sweet cherry endocarp, studying it through image analysis, to distinguish cultivars with remarkable accuracy.
The study concentrated on the sweet cherry cultivars “Kordia,” “Lapins,” and “Büttner’s Red”. The pits of each cultivar were meticulously scanned and analyzed. By converting the images into various “color channels” and examining their textures and geometric characteristics, the study developed discriminative models capable of identifying the cultivar from the pits with high precision.
These models were tested in different color spaces: RGB, Lab, and XYZ, and in individual color channels such as G, L, and Y. The accuracy of these models reached 100% in distinguishing “Kordia” from “Lapins” and “Kordia” from “Büttner’s Red.” Even the more complex comparison between “Lapins” and “Büttner’s Red” achieved high accuracy, up to 96%.
This level of precision is significant for industries where the chemical composition of cherry pits can influence the quality of the final product. For example, the oil contained in cherry pits, rich in unsaturated fatty acids, change in its composition among different cultivars. This variation is crucial for applications in food, cosmetic, and biofuel sectors. Misidentifying the pits could lead to mixing materials with different chemical properties, potentially compromising the quality of the final product.
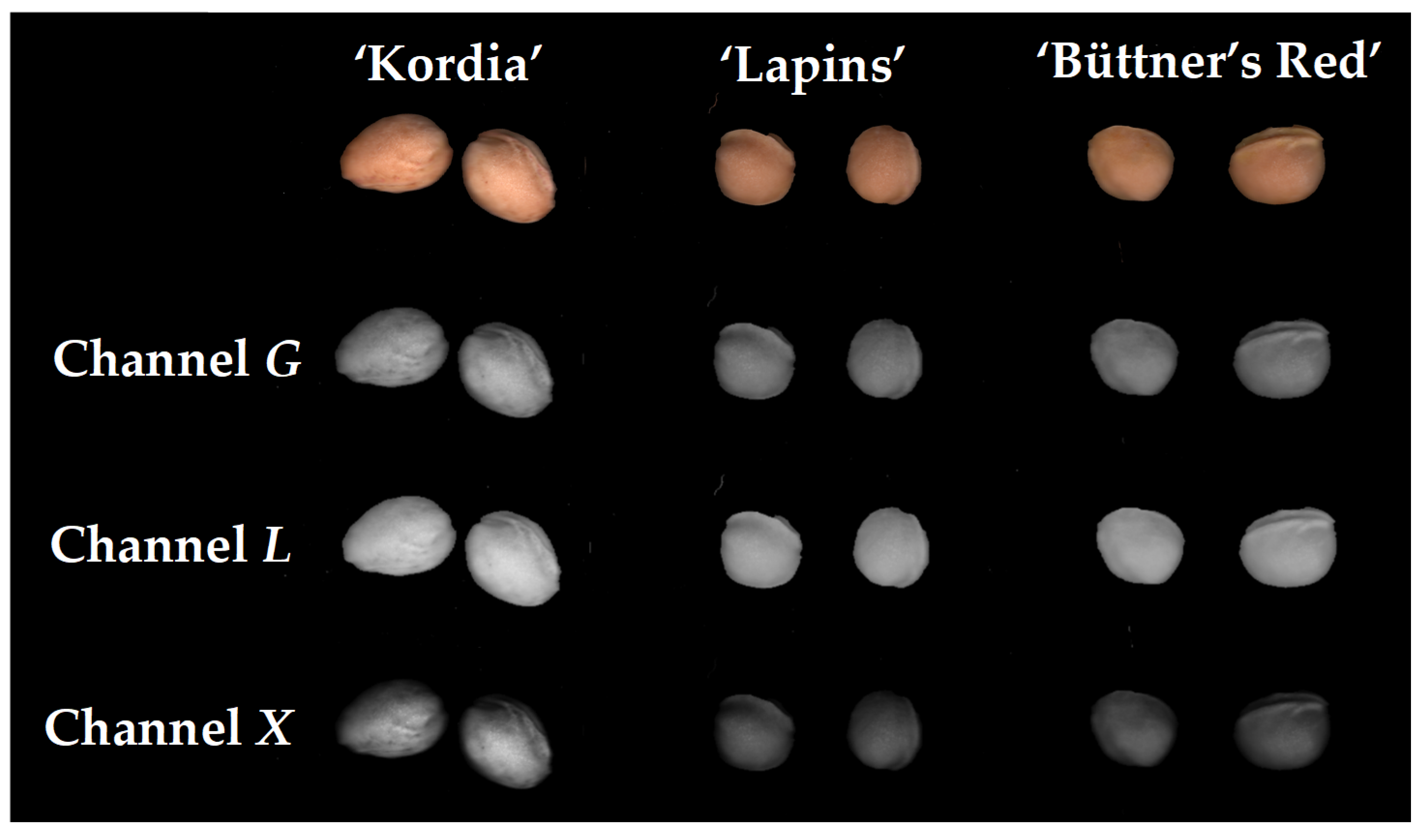 Image 1.
Image 1.
The study’s approach combines image processing techniques with machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze the endocarp. Image processing leads to the extraction of texture and geometric data. These parameters are then used to build ML models that can classify the pits based on the cultivar. Using image analysis for this purpose not only enhances accuracy but also offers a repeatable and scalable solution at a relatively low cost.
The findings of this research can be extended to other fruits. The methodology developed can be applied to other species where objectivity and rapid cultivar identification are necessary. This technology provides an interesting alternative to manual classification, reducing the
probability of human errors and the associated labor and time costs. As the agricultural sector continues to shift towards digital technologies, integrating ML for cultivar discrimination could become standard practice, improving efficiency and ensuring high quality agricultural products.
In conclusion, the developed models can be used in practice for identifying sweet cherry cultivars based on the endocarp, economically, quickly, and objectively. The success of this study highlights the potential of machine learning in agriculture and paves the way for further innovations in the field.
Source: Ropelewska E. The Application of Machine Learning for Cultivar Discrimination of Sweet Cherry Endocarp. Agriculture. 2021; 11(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11010006.
Image: Ropelewska, 2024
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved