In a global agricultural context increasingly affected by climate change, water resource management represents a major challenge for the sustainability of fruit production. Sweet cherry, appreciated for the sensory quality of its fruits, is an interesting species for areas with limited water availability, thanks to its rusticity and moderate water requirements.
A study conducted between 2022 and 2023 in Romania, at the Research Station for Fruit Growing in Iași, investigated the ecophysiological behavior of three sweet cherry cultivars: “Van”, “Andreiaș”, and “Margonia”, grown without irrigation systems.
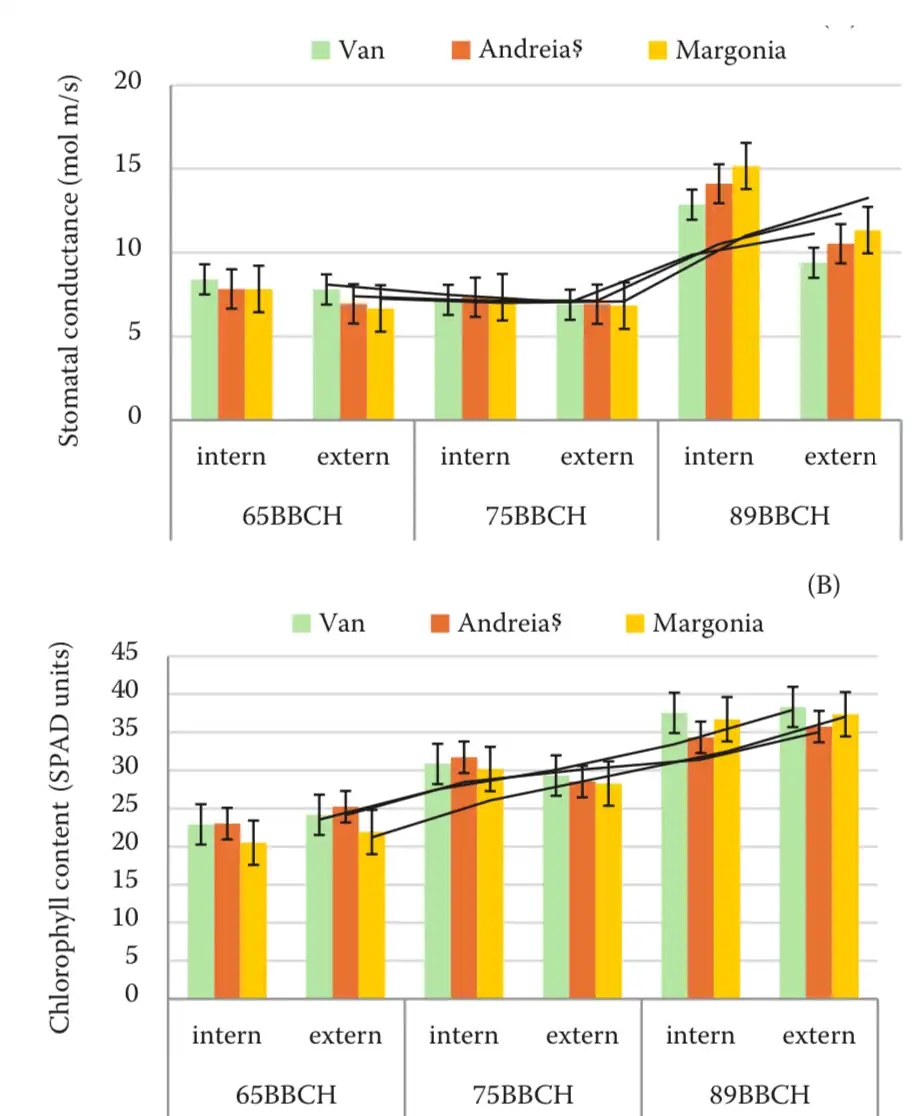 Figure 1. Stomatal conductance (A) and chlorophyll content (B) in the studied sweet cherry cultivars (2022–2023).
Figure 1. Stomatal conductance (A) and chlorophyll content (B) in the studied sweet cherry cultivars (2022–2023).
The study measured stomatal conductance, the relative water content (RWC) of the leaves, and their ability to retain water over time (dehydration after 24 hours), across three key phenological stages: full bloom (65 BBCH), fruit at 80% of its final size (75 BBCH), and fruit ripening (89 BBCH).
Ecophysiological measurements and findings
Measurements were carried out on both the inner and outer parts of the canopy to assess the physiological differences related to leaf position. Results showed significant variability not only among the cultivars but also between the internal and external canopy zones.
The “Andreiaș” cultivar stood out for its strong ability to retain water in the leaves and lower dehydration over time, suggesting a higher resistance to water stress. Particularly, leaves located in the inner canopy showed higher stomatal conductance and chlorophyll content, indicators of more intense photosynthetic activity and a better water status, compared to those exposed on the outer part of the tree.
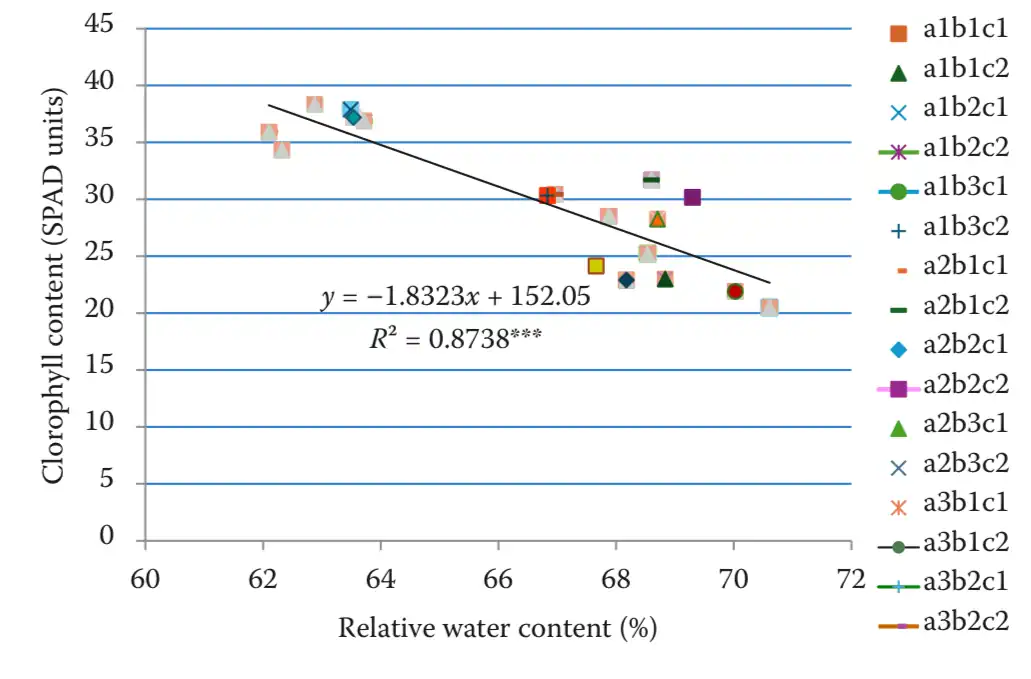 Figure 2. Dependence of the chlorophyll content to the relative water content. (a1 – 65BBCH; a2 – 75BBCH; a3 – 89BBCH; b1 – ‘Van’; b2 – ‘Andreiaș’; b3 – ‘Margonia’; c1 – canopy interior; c2 – canopy exterior; **positive correlation – distinctly significant n = 18, P5% = 0.47)
Figure 2. Dependence of the chlorophyll content to the relative water content. (a1 – 65BBCH; a2 – 75BBCH; a3 – 89BBCH; b1 – ‘Van’; b2 – ‘Andreiaș’; b3 – ‘Margonia’; c1 – canopy interior; c2 – canopy exterior; **positive correlation – distinctly significant n = 18, P5% = 0.47)
During the fruit ripening stage, which is characterized by a high evapotranspiration demand, maximum stomatal conductance values were recorded in the internal leaves of the cultivar “Margonia” (up to 17.84 mol m−2 s−1).
Correlations and adaptive mechanisms
A positive correlation between stomatal conductance and chlorophyll content (R² = 0.686) suggests that leaves with higher stomatal opening also have higher photosynthetic activity. Conversely, a negative correlation was observed between leaf water content and SPAD values (R² = –0.874), indicating that physiologically more active leaves tend to dehydrate faster.
Nonetheless, despite the overall decrease in leaf water content during the ripening stage, the rate of dehydration was significantly reduced. This represents an effective adaptation mechanism that allows the plant to limit water loss and preserve vital functions during a critical phase for fruit development.
This water-retaining ability was particularly evident in the cultivar “Andreiaș”, which showed a better overall water balance.
Conclusions and implications
In conclusion, the study demonstrates that even in the absence of irrigation, certain sweet cherry cultivars can maintain efficient physiological activity thanks to adaptive strategies involving stomatal conductance regulation, leaf distribution within the canopy, and specific biochemical traits.
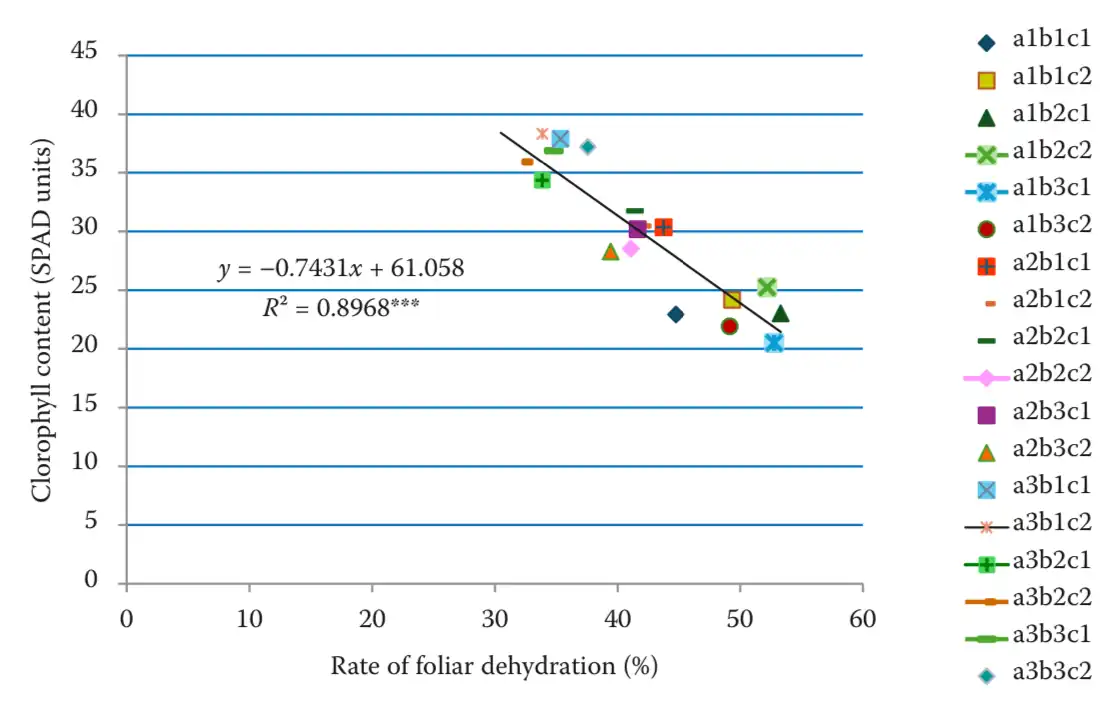 Figure 3. Dependence of the chlorophyll content to rate of foliar dehydration. (a1 – 65BBCH; a2 – 75BBCH; a3 – 89BBCH; b1 – ‘Van’; b2 – ‘Andreiaș’; b3 – ‘Margonia’; c1 – canopy interior; c2 – canopy exterior; ***positive correlation – high significant (n = 18, P5% = 0.47)
Figure 3. Dependence of the chlorophyll content to rate of foliar dehydration. (a1 – 65BBCH; a2 – 75BBCH; a3 – 89BBCH; b1 – ‘Van’; b2 – ‘Andreiaș’; b3 – ‘Margonia’; c1 – canopy interior; c2 – canopy exterior; ***positive correlation – high significant (n = 18, P5% = 0.47)
The data collected may support the development of predictive models for cultivar selection and crop management in drought-prone areas, contributing to more climate-resilient agriculture.
Further research will be essential to deepen our understanding of the physiological and molecular responses of these cultivars under increasingly extreme environmental conditions.
Source: Mineață, I., Perju, I., Sîrbu, S., Golache, I. E., Ungureanu, I. V., Ostaci, S., & Jităreanu, C. D. (2024). Ecophysiological aspects of some sweet cherry cultivars from the North-East of Romania. Hort. Sci. (Prague), 51, 305-313. https://doi.org/10.17221/113/2023-HORTSCI
Source images: Sirbu et al., 2024; SL Fruit Service
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna
Cherry Times - All rights reserved