Frost represents an abiotic climatic factor that can harm both plants and animals. The ability to withstand frost is influenced by several variables, including the plant type, the plant health status, and the phenological phase in which the plant is during the frost event.
In almost all temperate fruit-growing locations, spring frost poses a serious threat to productivity. As one of the first fruit varieties to begin growing in the spring, sweet cherry is particularly vulnerable to late frost, with the risk of decreased fruit yield.
Normally, plants are able to survive during the winter season unless extremely harsh frosts occur below their frost resistance limit. The critical temperature, or fatal temperature, which results in the death of plant tissues, is used to characterise damage caused by winter and spring frost.
Due to recent changes in the climate, it has been observed a modification in the normal seasonality of temperature, leading to a shift in plant phenology.
This study investigated the timing of the cherry tree's onset of flowering, completion of flowering, and length of flowering in the Czech Republic under various climatic circumstances. Available data were from 1924 up to 2012. The minimum air temperature and frequency of frost event occurrence were compared with the phenological data. Looking at the overall picture, it has been observed an advancement both for the beginning and the end of flowering (of 13.9 and 8.1 days, respectively).
In addition, also the flowering period increased up to 4.1 days. It has to be noted that at higher elevations the alterations were more pronounced. The trend in the number of frost days changed negatively at the lowland station (0.3 day) and positively at the highland station (+1.2 day) during the cherry tree blossoming season.
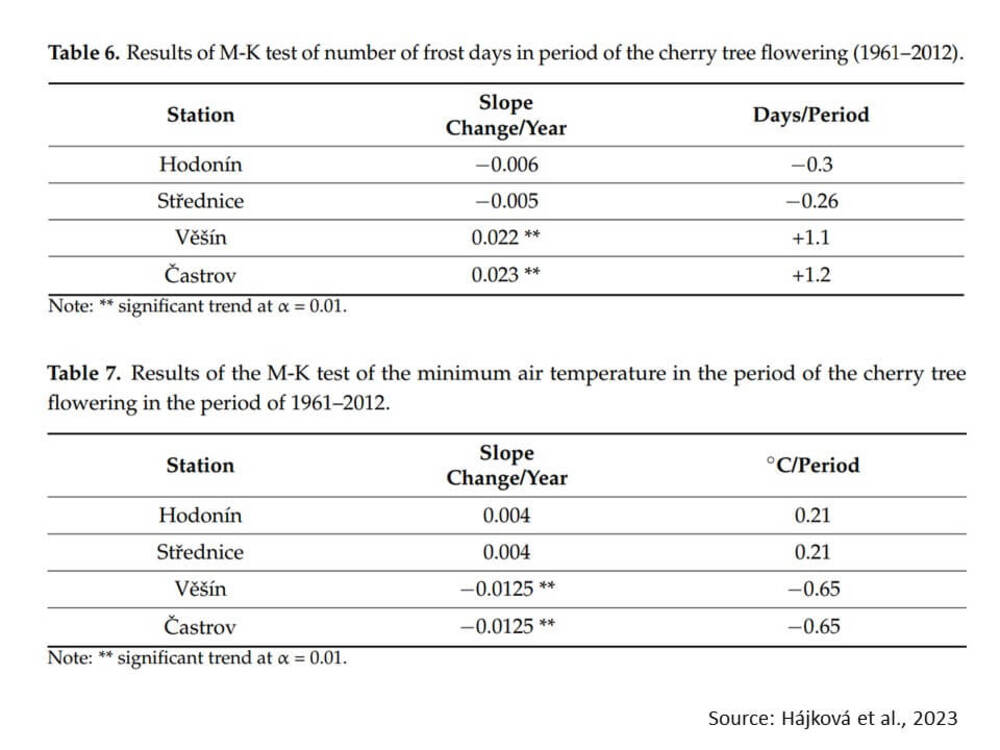
Cherry tree blossoms are more vulnerable at higher elevations, according to the positive trend of frost-day incidence and the negative trend of minimum air temperature during cherry tree blossoming. The largest number of days with minimum air temperatures below 1.1 °C during the flowering period varied between 4 and 6 days, with lowland stations seeing a negative trend in the number of frost days and highland stations experiencing a positive trend.
To ensure a plentiful harvest, it is crucial to protect the orchards from damaging spring frosts when establishing fruit trees. One approach that researchers suggest to safeguarding fruit trees is the use of artificial fog, but there are other methods as well. Additionally, there is indirect protection provided both by the accurate choice of the most suitable cultivar and the altitude of the orchard.
According to this study, the Czech Republic's highlands are more endangered than its lowlands when it comes to cherry tree flowering. In order to further enhance risk management in fruit producing, regional studies with forecasts based on climate models that take into account changes in circulation conditions are crucial.
Source: Hájková, Lenka, Martin Možný, Veronika Oušková, Lenka Bartošová, Petra Dížková, and Zdeněk Žalud. 2023. "Increasing Risk of Spring Frost Occurrence during the Cherry Tree Flowering in Times of Climate Change" Water 15, no. 3: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030497
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











