In recent decades, there has been a notable improvement in yields and one of the cultivation techniques employed relies on the utilisation of polytunnels (i.e. plastic protective covers). Polytunnels have the capacity to mitigate fruit cracking while protecting against other rain-related diseases, hence fruit quality and yield.
However, many sweet cherry varieties in Europe exhibit self-incompatibility, and the presence of pollinating insects plays a crucial role in promoting cross-pollination. Nevertheless, adopting a limited number of species as the primary reliance is highly risky for growers, while the utilisation of controlled pollinators may have adverse effects on the population of wild pollinators.
The presence of varied and heterogeneous wild pollinator groups has the potential to augment the provision of pollination services inside open sweet cherry orchards. Additionally, the implementation of wildflower cultivation in alleyways, along with active management, has the potential to promote the presence of wild pollinators and improve the pollination process.
This is particularly notable due to the superior efficiency of wild visitors in fertilising cherry blooms, surpassing that of managed pollinators. However, the precise impact of wildflower strips on increasing pollinator visits in polytunnel environments remains uncertain.
In 10 commercial cherry orchards located in the West Midlands County (United Kingdom), wildflowers were deliberately cultivated in alleyways situated between rows of trees and protected by polytunnels. The management practises employed in the study consisted of:
a) a solitary cut in September, referred to as Standard Wildflower Strips;
b) regular cutting to maintain a height of 20 cm, known as Actively Managed Wildflower Strips;
c) these practises were compared against Control Strips that were left unsown.
The study involved the collection of data on the floral visitors of cherry and wildflowers over a period of three years (2017-2019). Additionally, the cherry production, including both quantity and quality, was evaluated specifically in the year 2019.
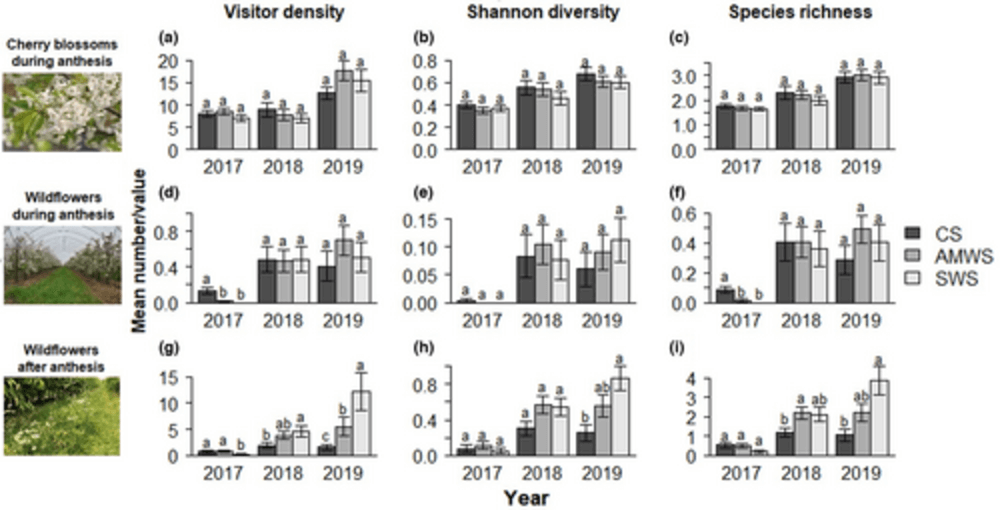 Figure 1: Mean numbers and values (± SE) of visitor density recorded and Shannon diversity and species richness calculated per alleyway treatment visiting (a–c) cherry blossoms and (d–f) wildflowers during anthesis and (g–i) wildflowers after anthesis, respectively, according to year and alleyway treatment
Figure 1: Mean numbers and values (± SE) of visitor density recorded and Shannon diversity and species richness calculated per alleyway treatment visiting (a–c) cherry blossoms and (d–f) wildflowers during anthesis and (g–i) wildflowers after anthesis, respectively, according to year and alleyway treatment
A total of 67 species of visitors were detected, with managed commercial species (Apis mellifera and Bombus terrestris) accounting for approximately 74% of all recorded instances. During the blossom season the visitor density was found to be highest in the Actively Managed Wildflower Strips in comparison to the Control Strips and Standard Wildflower Strips.
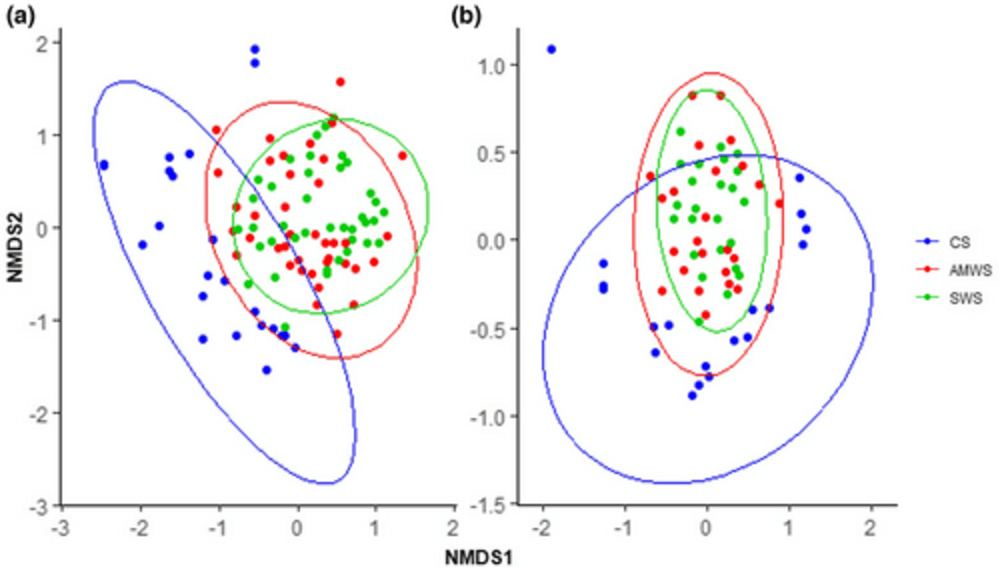 Figure 2: Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots of the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity for floral communities according to alleyway treatment after cherry anthesis in (a) 2018 and (b) 2019
Figure 2: Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots of the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity for floral communities according to alleyway treatment after cherry anthesis in (a) 2018 and (b) 2019
However, no statistically significant difference was seen in the yield of harvestable fruit among these areas. During the rest of the season, it was noted that there was a higher density, diversity, and richness of visitors in the wildflower treatments as compared to the Control Strips, especially in the Standard Wildflower Strips treatment, which aligns with the differences in floral communities observed between the treatments.
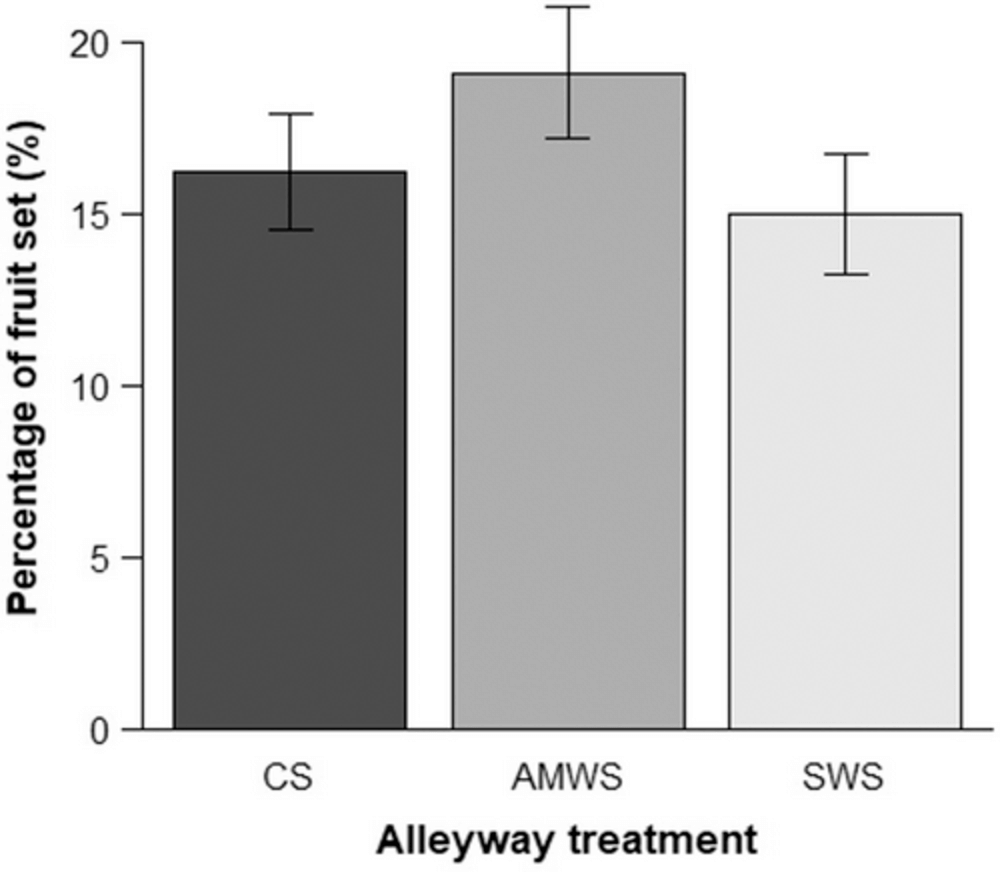 Figure 3: Mean percentage (± SE) of fruit set recorded on open-pollinated blossoms in 2019 according to alleyway treatment
Figure 3: Mean percentage (± SE) of fruit set recorded on open-pollinated blossoms in 2019 according to alleyway treatment
Despite the lack of correlation between visitor density and fruit set, the presence of pollinating insects had a crucial role in determining both fruit yields and quality. The fruit set seen in blossoms that were exposed to visitors was approximately 17%, whereas the fruit set was less than 1% when the blossoms were excluded from visitors..
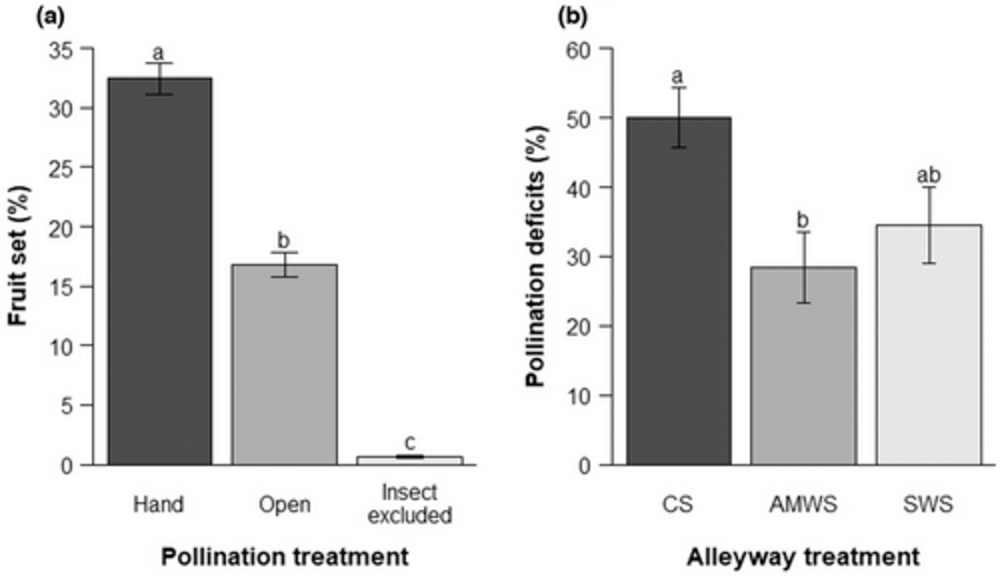 Figure 4: Mean percentages (± SE) of (a) fruit set according to pollination treatment and (b) pollination deficits according to alleyway treatment in 2019.
Figure 4: Mean percentages (± SE) of (a) fruit set according to pollination treatment and (b) pollination deficits according to alleyway treatment in 2019.
The findings of this research indicate that the implementation of wildflower alleyways in commercial sweet cherry orchards has a positive impact on both visitor density and richness. This active inter-row management has the potential to increase production and simultaneously mitigate problems associated with pollination deficit conditions.
Source: Mateos-Fierro, Z., Garratt, M. P. D., Fountain, M. T., Ashbrook, K., & Westbury, D. B. (2023). The potential of wildflower strips to enhance pollination services in sweet cherry orchards grown under polytunnels. Journal of Applied Ecology, 60, 1044–1055. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.14394.
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved














