The excessive use of chemical fertilizers in cherry cultivation causes environmental problems, including the release of nutrients and soil degradation. These excessive inputs often exceed the actual needs of the trees, causing nutritional imbalances and inefficiencies that do not improve production.
Nutrient leaching, soil degradation, and water contamination are among the environmental repercussions of excessive fertilizer applications, contributing to issues such as biodiversity loss and eutrophication.
Foliar fertilization as an alternative
Foliar fertilization has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional soil-based approaches to address these challenges. This method allows nutrients to be directly absorbed by the canopy, improving absorption efficiency and reducing nutrient waste and environmental impact.
Foliar applications are increasingly used to administer biostimulants, substances that enhance plant growth, nutrient uptake, and stress resistance, further reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
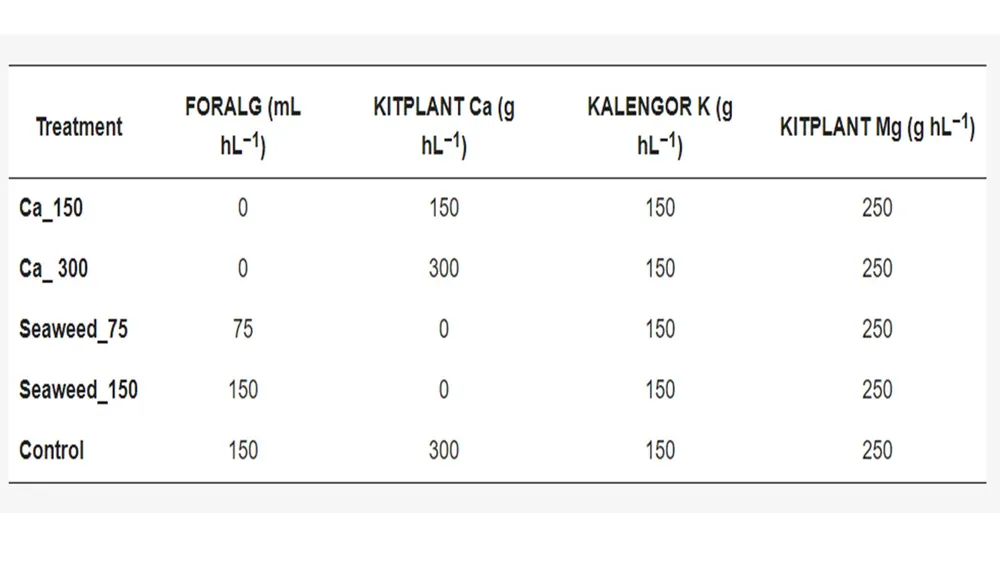 Figure 1. Commercial fertilizers and respective treatment doses applied in the experiment.
Figure 1. Commercial fertilizers and respective treatment doses applied in the experiment.
University study on cherry trees
The objective of the study conducted by the University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro (Portugal) was to assess the physiological and biochemical responses of cherry leaves to pre-harvest foliar applications of calcium (150 and 300 g hL−1) and seaweed extracts (75 and 150 mL hL−1), both individually and in combination.
Through measurements of water status, photosynthetic activity, and metabolite composition on the ‘Burlat’ cultivar, the plant's response to these treatments was observed.
Findings and implications
The results indicate that trees treated with seaweed extracts or a combination of calcium and seaweed had higher levels of sugars, carbohydrates, and proteins, as well as improved hydration status, antioxidant activity, and phenolic content, compared to those treated solely with calcium.
However, the combined treatment did not significantly enhance the overall tree effectiveness compared to the individual applications.
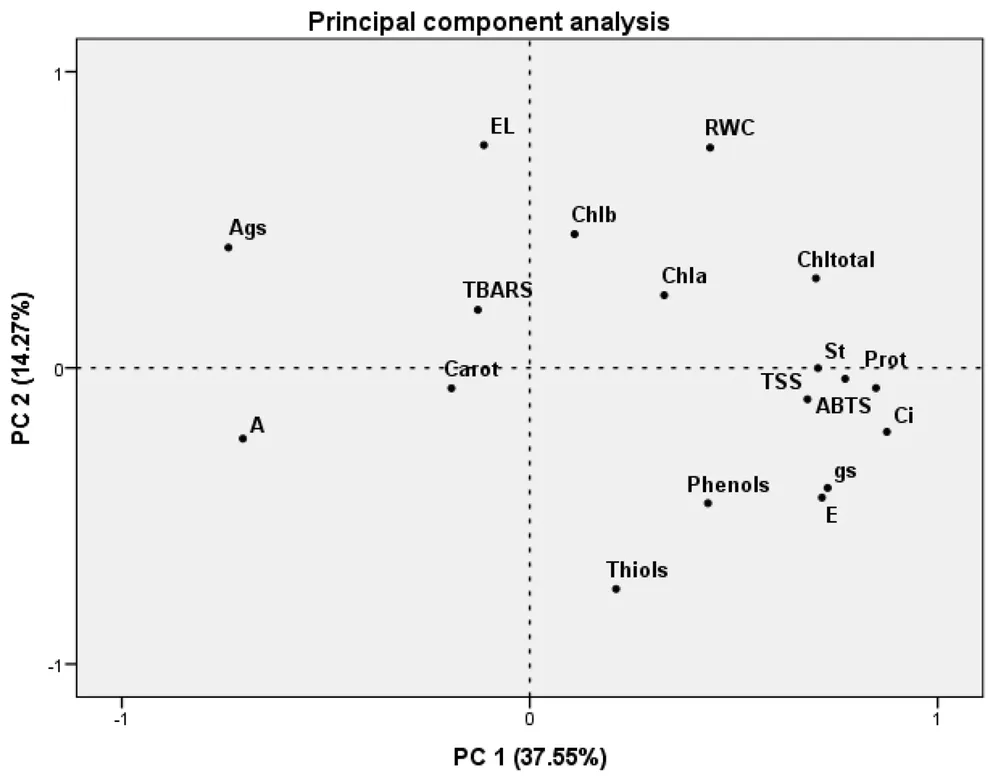 Figure 2. Figure 10. Principal component analysis using the whole dataset of all applied treatments (n = 5). Analyzed parameters: E—transpiration rate; A—net CO2 assimilation rate; gs—stomatal conductance; Ci—intercellular CO2 concentration; A/gs—intrinsic water use efficiency; Chla—chlorophyll a; Chlb—chlorophyll b; Chltotal—chlorophyll total; Carot—carotenoids; RWC—relative water content; EL—electrolyte leakage; TSS—total soluble sugars; St—starch; Prot—protein content; TBARS—lipid peroxidation; ABTS—antioxidant activity; Phenols—total phenols; and Thiols—thiol content.
Figure 2. Figure 10. Principal component analysis using the whole dataset of all applied treatments (n = 5). Analyzed parameters: E—transpiration rate; A—net CO2 assimilation rate; gs—stomatal conductance; Ci—intercellular CO2 concentration; A/gs—intrinsic water use efficiency; Chla—chlorophyll a; Chlb—chlorophyll b; Chltotal—chlorophyll total; Carot—carotenoids; RWC—relative water content; EL—electrolyte leakage; TSS—total soluble sugars; St—starch; Prot—protein content; TBARS—lipid peroxidation; ABTS—antioxidant activity; Phenols—total phenols; and Thiols—thiol content.
Seaweed extracts, both alone and in combination with calcium, influenced several important parameters related to plant health and stress resilience.
Previous research and conclusions
Previous research has shown that seaweed extracts can improve crop performance, increase resistance to both biotic and abiotic stresses, and extend the post-harvest shelf life of perishable fruits, such as cherries. The results obtained in this study are therefore consistent with previous findings.
The low stomatal conductance observed in trees treated with calcium in terms of gas exchange suggests a potential reduction in stomatal opening, which is likely a mechanism to prevent excessive water loss under certain conditions.
The positive control, which contained increased concentrations of calcium and seaweed, served as a benchmark to evaluate the relative effectiveness of each treatment, despite the absence of a negative control.
Although calcium improved specific photosynthetic parameters, seaweed extracts significantly increased antioxidant activity, improved water retention, and increased sugar and protein levels, thus demonstrating better plant health and resilience.
Interestingly, the combination of calcium and seaweed did not generate synergistic effects, indicating that each treatment might optimize plant responses through different mechanisms.
Source: Pereira, S.; Silva, V.; Guedes, F.; Raimundo, F.; Sousa, J.R.; Silva, A.P.; Gonçalves, B. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of ‘Burlat’ Sweet Cherry to Pre-Harvest Foliar Application of Calcium and Seaweed Extracts. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10111173
Images: Pereira et al., 2024; SL Fruit Service
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












