The productivity of small fruits, such as cherries (but not only), is greatly reduced by the insect Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). This pest can be controlled either by chemical insecticides or by the use of entomopathogenic nematodes. These nematodes are easy to apply because they can be mixed in tanks together with other plant protection products (chemical, natural and biological), fertilisers and soil conditioners.
Obviously, the action of pesticides on entomopathogenic organisms varies depending on the species and lineage of the nematodes and the chemical nature and concentrations of the products used. This is why the compatibility of the two methods requires further investigation.
The aim of the study carried out in collaboration between Brazilian and Argentinian research institutes was to assess the compatibility of Steinernema brazilense (IBCBn 06), S. carpocapsae (IBCBn 02), Heterorhabditis amazonensis (IBCBn 24) and H. bacteriophora (HB) with different chemical insecticides for the control of D. suzukii pupae, as well as to monitor the longevity of surviving adult insects.
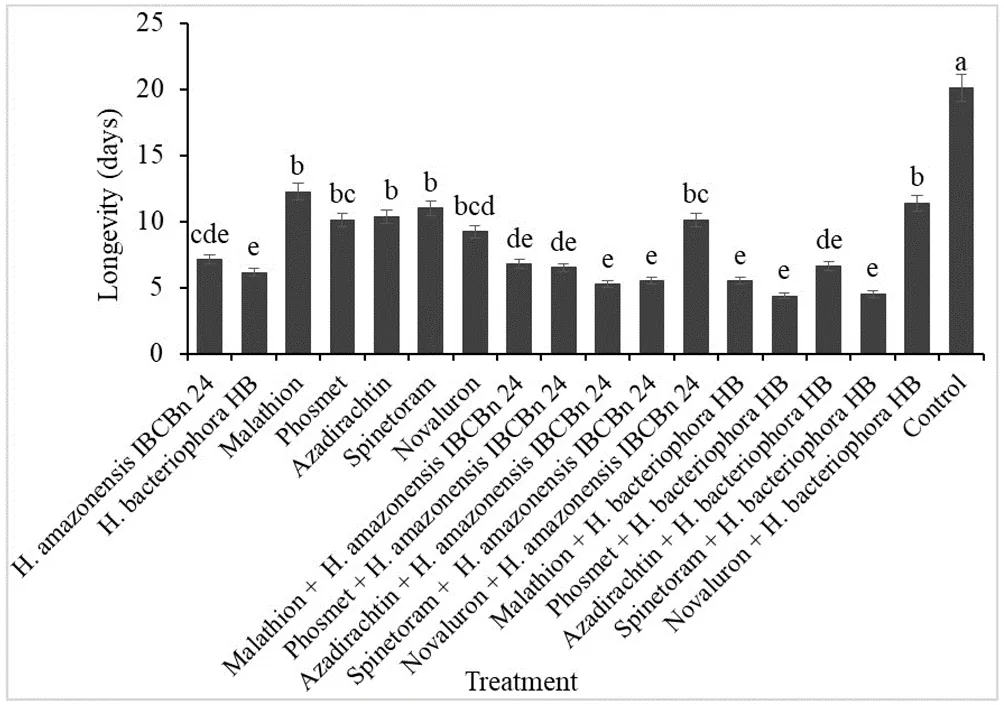 Longevity of Drosophila suzukii adults exposed to a combination of insecticides and H. amazonensis IBCBn 24 or H. bacteriophora HB. Source: Sergio da Costa Dias et al., 2024
Longevity of Drosophila suzukii adults exposed to a combination of insecticides and H. amazonensis IBCBn 24 or H. bacteriophora HB. Source: Sergio da Costa Dias et al., 2024
In contrast, S. carpocapsae was more sensitive to exposure to Malathion, Abamectin, Azadirachtin, Deltamethrin, Lambda-cyhalothrin and Spinetoram. Fosmet was compatible with all nematode species during infectivity bioassays, with minimal changes in infectivity and efficiency compared to treatment with nematodes alone. In contrast, Lambda-cyhalothrin generally reduced nematode infectivity on D. suzukii pupae, with a reduction in efficiency of up to 75 %.
The second study compared pupae mortality induced by the two most compatible nematode species and five insecticides in different combinations. When used alone, both Heterorhabditis species caused 78-79% mortality of D. suzukii pupae. They were also tested in combination with Spinetoram, Malathion, Azadirachtin, Fosmet or Novaluron at a dose of one quarter. Importantly, H. bacteriophora showed an additive effect on D. suzukii pupae, resulting in a 79% mortality rate when used alone and 89% when combined with Spinetoram.
Combined with Novaluron, however, the number of infectious nematodes was significantly reduced to 270 in H. amazonensis and 218 with H. bacteriophora. The lifespan of adult flies emerging from pupae treated with entomopathogenic nematodes was significantly shorter than that of untreated pupae. The combined use of Heterorhabditis and compatible chemical insecticides was promising, with the exception of Novaluron.
In conclusion, most of the nematode-insecticide combinations evaluated did not compromise the viability of the nematodes, which remained viable with high infectivity rates. In an integrated pest management approach, the use of insecticides in combination with some Brazilian entomopathogenic nematode isolates is promising against D. suzukii.
Sourcee: Dias, S.d.C.; de Brida, A.L.; Jean-Baptiste, M.C.; Leite, L.G.; Ovruski, S.M.; Lee, J.C.; Garcia, F.R.M. Compatibility of Entomopathogenic Nematodes with Chemical Insecticides for the Control of Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Plants 2024, 13, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13050632
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











