The Drosophila suzukii, a parasitic insect of fruit crops, stands out for its ability to feed on a wide variety of fruits. A recent study conducted by researchers at INRAE reveals that this fly accumulates chemical compounds from fruits without metabolizing them, a tolerance that may allow it to adapt to different environments. The results of this study, published in the journal eLife, could help develop innovative strategies to protect crops from this pest.
Plant-eating insects generally focus on one or a few specific plants. However, some insect species are exceptions and feed on a wide variety of plants. This is the case of Drosophila suzukii, a formidable small fly that attacks many fruit crops, including cherries, grapes, strawberries, and raspberries. Capable of feeding on many fruit varieties, this species is considered a generalist.
A research group, composed of INRAE scientists from the CBGP (Centre de Biologie pour la gestion des populations) and SVQV (Santé de la vigne et qualité du vin) units, sought to understand how these insects manage to digest and utilize such a wide range of chemical compounds present in their different foods.
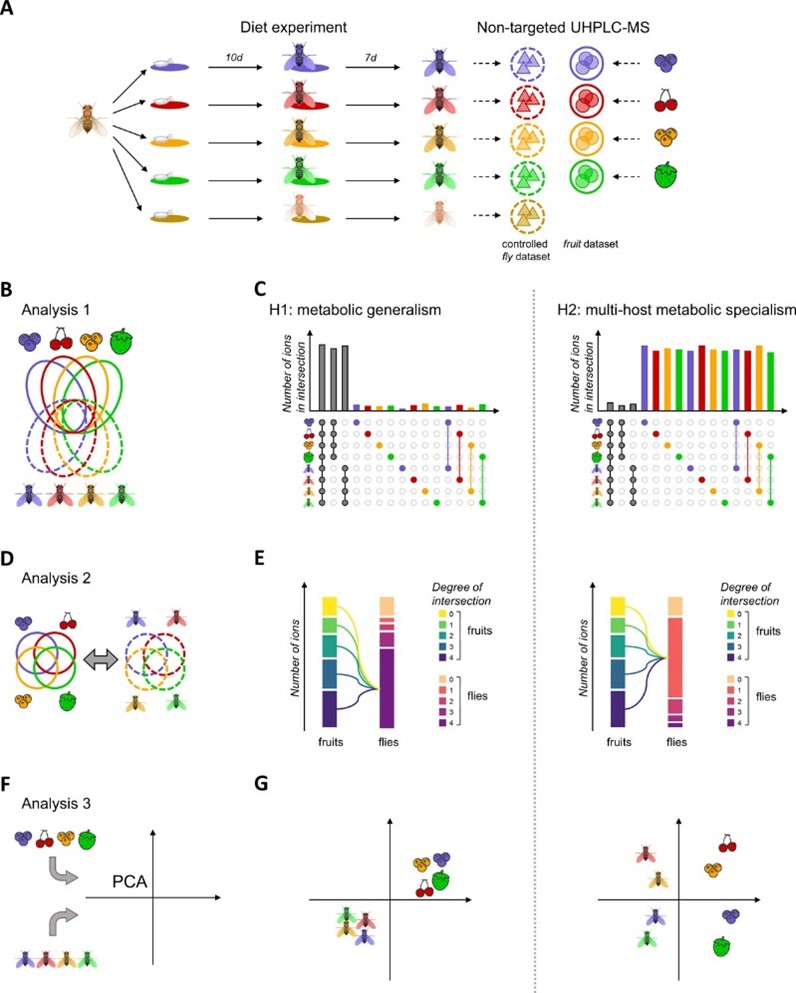 Image 1: Schematic overview of the experimental design, host-use analyses, and expectations according to the hypotheses of "metabolic generalism" and "multihost metabolic specialism." Source: Olazcuaga et al., 2024.
Image 1: Schematic overview of the experimental design, host-use analyses, and expectations according to the hypotheses of "metabolic generalism" and "multihost metabolic specialism." Source: Olazcuaga et al., 2024.
The scientists compared the chemical composition of different fruits with that of the fruit flies that had consumed them. The results, obtained using an advanced technique known as high-performance chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry, are particularly intriguing.
The fruit flies passively accumulate many specific compounds from the fruits without metabolizing them. This means that D. suzukii is not particularly adapted to each fruit it consumes; instead, it seems to tolerate a diversity of chemical compounds.
This tolerance could give D. suzukii significant flexibility, an important advantage in exploiting different environments. Researchers believe that this ability to utilize a variety of fruits could be crucial for the survival of populations during winter, finding refuge fruits.
The study published in the journal eLife, which combines evolutionary biology and chemical ecology, provides a better understanding of the relationships between plants and insects. It could contribute to the development of new strategies for managing this pest, which is a real scourge for cherry growers, particularly by identifying refuge fruits.
Source: INRAE
Image: Reussir
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











