The loss of genetic diversity in cherry cultivars in recent decades has led to a lower reduced adaptability to changes of growing and climatic conditions. In many breeding programs. interspecific crosses have been used to increase genetic diversity and to achieve new characteristics in fruit crops
In the case of sour cherry, Prunus cerasus, the first interspecific crosses with P. maackii and P. fruticosa were made in the first half of the 20th century by I. V. Michurin in Russia and L. Kerr in Canada to increase winter hardness.
In the cherry breeding program at Dresden-Pillnitz various interspecific crosses and backcrosses have been carried out over the last 20 years. In sweet cherry, P. avium, crosses were made with P. canescens, P. armeniaca, and P. tomentosa and in sour cherry, P. cerasus, with P. maackii, P. padus, P. serotina, and P. spinosa.
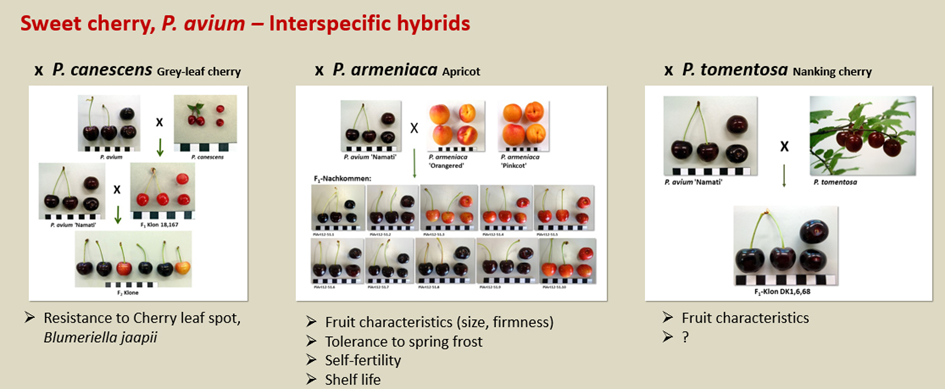 Image 1: Released interspecific crosses with Sweet cherry, P. avium (2x)
Image 1: Released interspecific crosses with Sweet cherry, P. avium (2x)
The aims of this breeding program are to develop of genotypes with new fruit and tree characteristics and a higher level of resistance to biotic and abiotic stress. The diploid Prunus species P. canescens, the tetraploid species P. maackii, and P. serotina have proven to be promising resistance donors for cherry breeding.
 Image 2: Released interspecific crosses with Sour cherry, P. cerasus (4x)
Image 2: Released interspecific crosses with Sour cherry, P. cerasus (4x)
The F1 progeny of the crosses between sweet cherry and apricot showed a high tolerance of flowers to spring frost and interesting fruit characteristics such as size, firmness, and shelf life in the first years of growth. The obtained plant material will be characterized in further studies. Interesting genotypes will be used as new starting material for the breeding process.
Mirko Schuster, Susan Schröpfer, Henryk Flachowsky
Institute for Breeding Research on Fruit Crops, Julius Kühn-Institut (DE)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












