In August 2022, a new pathogen affecting cherry trees was reported in Turkey. The fungus Paecilomyces maximus, already known in other parts of the world, causes dieback and canker in cherry trees, which is one of Turkey's most important crops. Therefore, controlling this pathogen will be crucial to avoid significant production losses.
The first case of infection was detected in an orchard located in the Çınar region, in Diyarbakır province. Symptoms observed in the plants included branch wilting, wood canker, discoloration of the bark and internal parts of the trunk, which eventually led to plant death. The incidence of the disease was estimated at around 5% in the orchard, a figure that, although limited, immediately raised concerns due to the rapid spread and severity of the symptoms.
To precisely identify the responsible pathogen, researchers collected wood samples from infected trees. The samples were superficially disinfected and cultured on potato dextrose agar (PDA) to observe the fungus's growth. The colonies initially developed in white but over time turned yellow or brown, indicating the presence of Paecilomyces maximus.
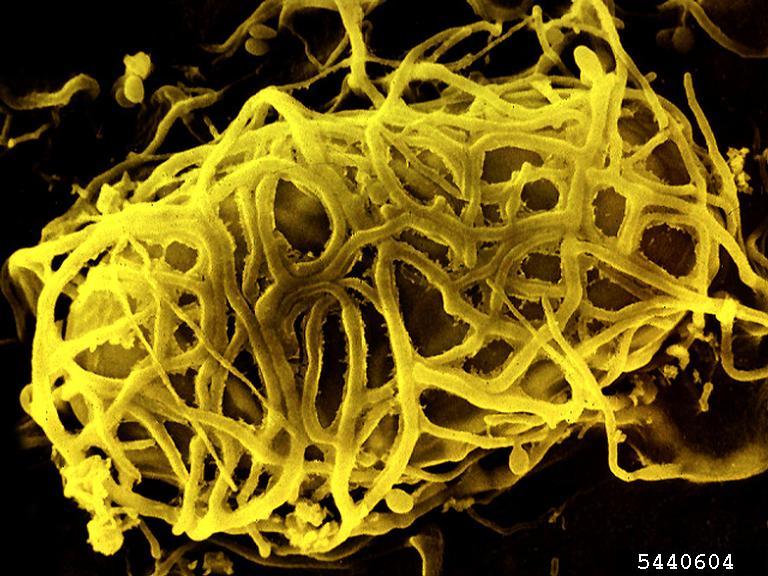
Microscopic observation revealed the presence of branched conidiophores, with phialides arranged in divergent whorls and ellipsoidal or cylindrical conidia with truncated ends. These morphological characteristics were consistent with those reported in the literature for P. maximus.
However, to definitively confirm the identity of the pathogen, a molecular analysis was performed. Sequencing of the ITS region and the beta-tubulin gene showed a very high degree of similarity (99.6% for ITS and 100% for beta-tubulin) with a known strain of Paecilomyces maximus, thus confirming the fungus's identification.
To further verify the pathogenic role of P. maximus in cherry trees, experimental tests were carried out following Koch's postulates. Branch segments, previously wounded, were inoculated with the fungus grown in the laboratory.
After five weeks of incubation under controlled conditions, brown necrotic lesions appeared on the inoculated branches, while control branches, treated with sterile agar, showed no symptoms. This experiment confirmed that Paecilomyces maximus is indeed responsible for the dieback and canker observed in cherry trees in Diyarbakır.
In conclusion, the discovery of Paecilomyces maximus on cherry trees in Turkey highlights the importance of early diagnosis and collaboration to effectively address new phyto-pathological threats. Further research will be necessary to develop effective and sustainable protocols and solutions to protect cherry trees, one of Turkey’s most vital crops.
Source: Ozan, G. N., Çaplık, D., & Bayraktar, H. (2024). First report of Paecilomyces maximus causing dieback on cherry in Türkiye. Journal of Plant Pathology, 1-2. https://doi-org/10.1007/s42161-024-01717-w.
Image: IPM Images
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











