Pruning is normally carried out during the winter period, when the trees are in dormancy. In cherry trees, however, pruning the trees in early autumn, specifically during the first ten days of September, could be a method to improve the balance between fruit quantity and plant development.
It has been observed that pruning trees during the vegetative phase of plant development leads to an increase in fruit size and a change in fruit colour, as well as a reduction in the incidence of brown rot.
From 2018 to 2020, researchers from Moldova State University of Agriculture conducted a study aimed at assessing the impact of pruning on both the resting and developmental stages of cherry trees of the ‘Regina’ variety, grafted onto the MaxMa 14 rootstock. Pruning was carried out in the following order: during the resting period (control group), during the flowering period, after harvest (in July) and at the beginning of autumn (in the first ten days of September).
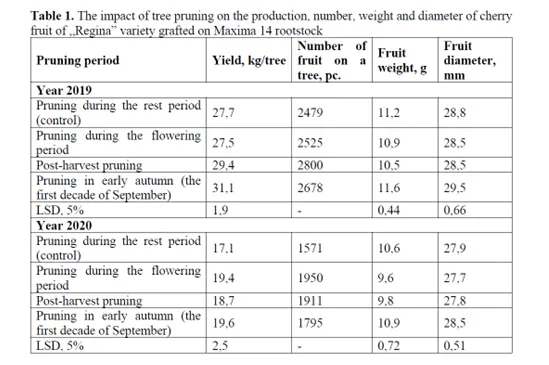 Table 1: The impact of pruning in Regina/MaxMa 14 on production per tree, number of fruits per tree, average weight and average fruit size per tree.
Table 1: The impact of pruning in Regina/MaxMa 14 on production per tree, number of fruits per tree, average weight and average fruit size per tree.
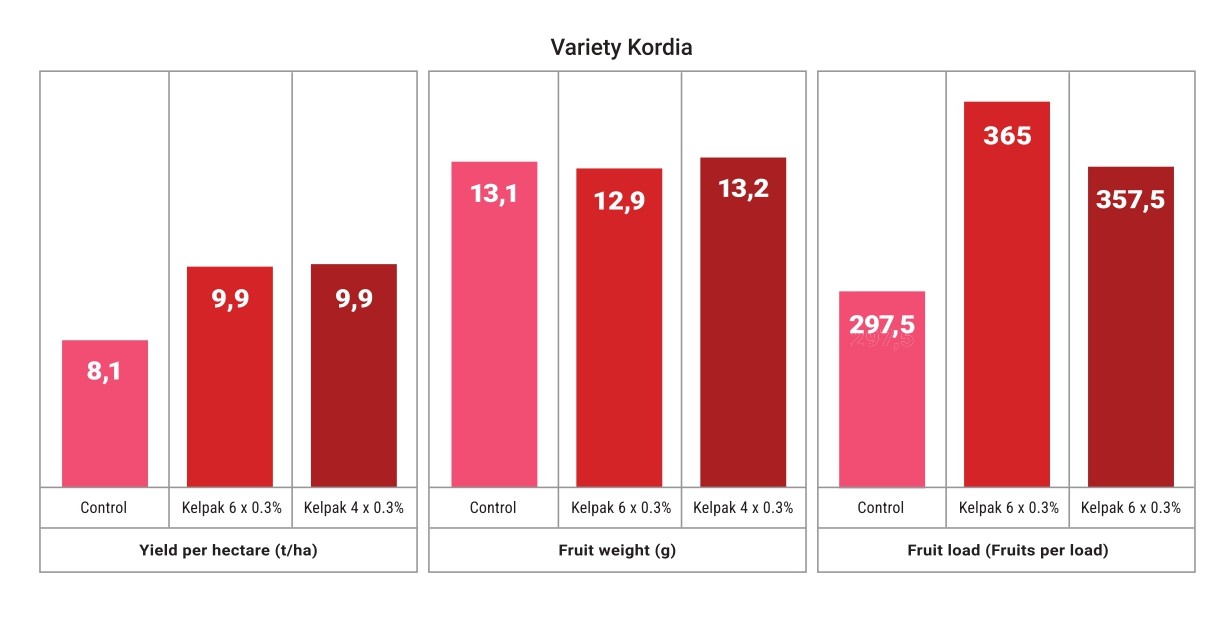
In general, the production load of the plants in the two test years was strongly influenced by the climatic conditions, characterised by late spring frost during flowering and high temperatures during the vegetative phase. However, the yield and fruit quality were also influenced by the pruning time of the trees.
Trees that were pruned in the first ten days of September showed an average yield of 31 kg/tree in 2019, and 19.6 kg/tree in 2020, making them the most productive. The average fruit size was not influenced by the pruning time. In fact, the average values calculated are in the range of 27.7-29.8 mm.
However, it is interesting to note that pruning in the first ten days of September led to a significant reduction in the percentage of fruits with a diameter of 24 mm or less (1.6-2.9%) and at the same time increased the number of fruits with a diameter of 28 mm or more (18.3-36.1%), without influencing the total yield.
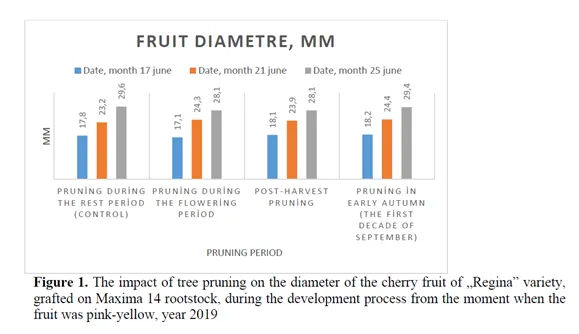 Image 1: The impact of pruning on fruit diameter of the cherry variety Regina, grafted on MaxMa 14 rootstock, during the development process from the time the fruit was at veraison (year 2019). Source: Balan and Servan, 2024.
Image 1: The impact of pruning on fruit diameter of the cherry variety Regina, grafted on MaxMa 14 rootstock, during the development process from the time the fruit was at veraison (year 2019). Source: Balan and Servan, 2024.
The soluble solids content (mean values between 17.29 and 19.27 °Brix) and the titratable acidity in the fruit (0.65-0.78 mg malic acid per 100 g of fruit) presented similar values, regardless of the pruning time. The results indicate that the pruning time can be used as a strategy to maintain the physiological balance between growth and fruiting and to manage the number of fruits of the ‘Regina’ variety grafted onto the Maxma 14 rootstock.
Pruning during the flowering period can be carried out when the buds have overwintered well and the climatic conditions are favourable for fruiting, especially in self-fertile varieties.
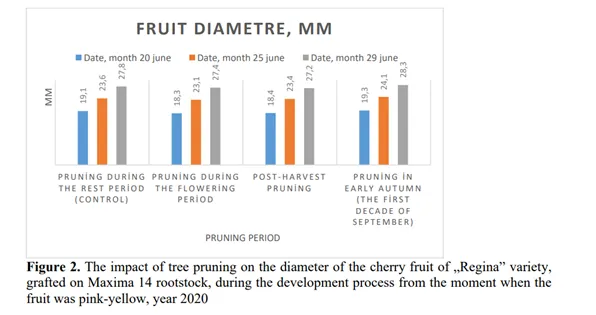 Image 2: The impact of pruning on fruit diameter of the cherry variety Regina, grafted on MaxMa 14 rootstock, during the development process from the time the fruit was at veraison (year 2020). Source: Balan and Servan, 2024.
Image 2: The impact of pruning on fruit diameter of the cherry variety Regina, grafted on MaxMa 14 rootstock, during the development process from the time the fruit was at veraison (year 2020). Source: Balan and Servan, 2024.
Post-harvest pruning, on the other hand, can reduce the assimilation of organic substances necessary for the formation of fruit buds in the following year. Finally, pruning in early autumn showed positive effects in terms of average fruit weight and a more uniform fruit distribution, with a higher prevalence of fruit size above 28 mm. In addition, the number of fruits per tree was reduced, but without reducing the total yield.
These results are encouraging, but it remains to be studied what the effects are in the long run, to assess the influence of the pruning time on the quantity and quality of the cherries.
Source: BALAN V., ȘARBAN V., The Impact of The Cherry Tree Pruning Period on The Production and Quality of Fruit in an Intensive Cultivation System, State Agricultural University of Moldova, Faculty of Horticulture, Department of Horticulture
Images: SL Fruit Service; Balan e Servan, 2024
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved