Within the framework of the multidisciplinary FAR Mission Oriented project 'Process and product innovations in the sour cherry chain: an integrated approach for the valorisation of a typical Modenese production', financed by the Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Modena, at the laboratories of the Department of Life Sciences of UNIMORE, research was carried out with the aim of assessing the effectiveness of a treatment with high hydrostatic pressure (HPP, high pressure processing) for the quality preservation of fresh sour cherries.
The HPP process involves pressurising the product, already packed in flexible packaging, to between 300 and 600 MPa, for a time ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes. The effectiveness of HPP treatments depends on various factors, such as product acidity, applied pressure, holding time, temperature, food matrix characteristics and target microorganism. Similar treatments have been shown to inactivate moulds, yeasts and vegetative cells, while they are not sufficient to destroy bacterial spores, which are highly baro-resistant.
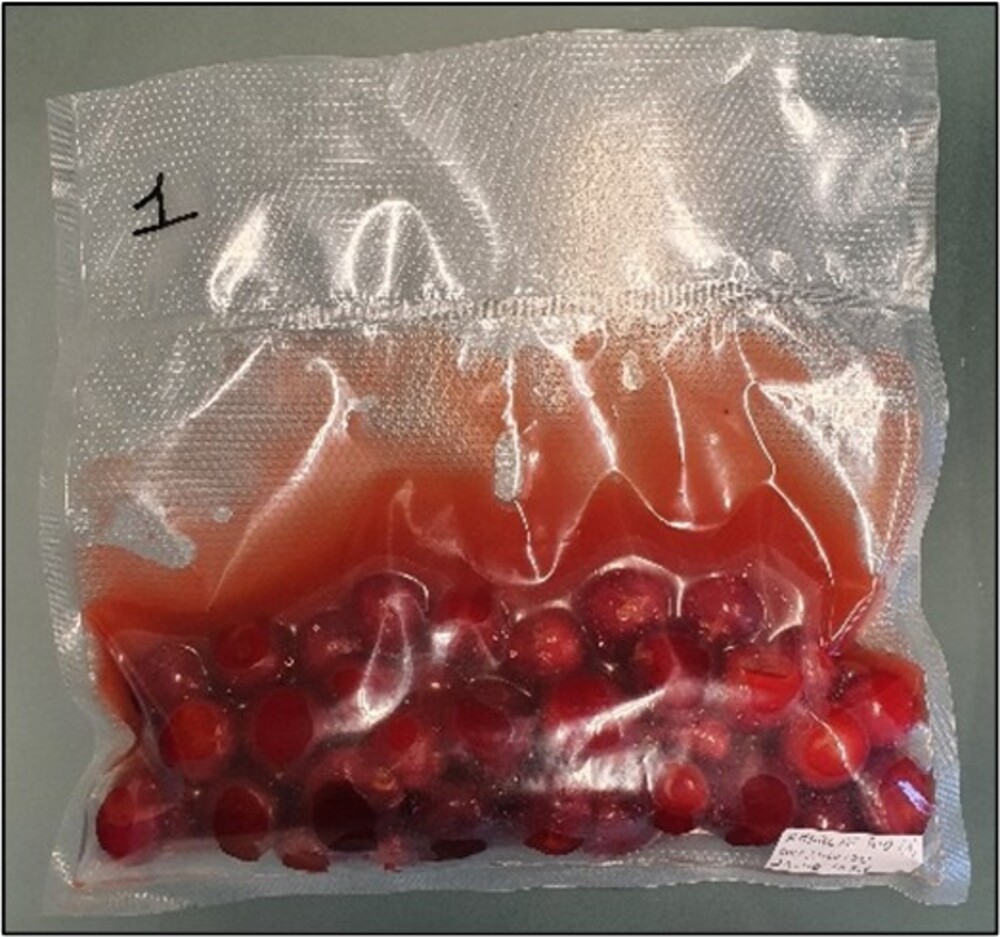 Image 1. Sample of HPP sour cherries.
Image 1. Sample of HPP sour cherries.
Due to the very short spoilage time, 'amarena brusche di Modena' cherries have a reduced shelf life and limited availability on the market as a fresh product. Conventional processing technologies, while on the one hand guaranteeing food safety and a long shelf life, on the other hand modify the sensory and nutritional characteristics, leading in particular to the loss of thermolabile constituents and alteration of colour, flavour and aroma.
Samples of stoned Amarena del Rio, supplied by the company Piombini (Casinalbo di Formigine), packed in flexible packaging, were subjected to an HPP cycle at 600 MPa for 3 minutes (at HPP Italia, Traversetolo, PR). The efficacy of the HPP treatment was evaluated through the study of microbiological stability, colour monitoring, pH, antioxidant activity and content in bioactive constituents (polyphenols, flavonoids and anthocyanins) during 5 months of refrigerated storage.
The results obtained confirmed the effectiveness of the HPP treatment in reducing the total aerobic mesophilic load and the load of yeasts and moulds below the detection threshold of the plate count method. In addition, the treated samples remained microbiologically stable throughout the storage period (5 months). The colorimetric evaluation, using a* and b* values with the evaluation of hue and saturation, showed substantial colour stability up to 3 months of cold storage, after which a colour change towards yellow shades was observed, with a change in colour intensity. No change was recorded in the pH value (3.2), which, in addition to acting in synergy with the high hydrostatic pressures in microbial inactivation, determines an unfavourable environment for the growth of any cells that may have survived the treatment.
The biological activity of fruit and vegetables depends on the content of bioactive compounds. Polyphenols represent the largest group of plant secondary metabolites, with proven action in the prevention of oxidative stress-related diseases. The quantification of phytochemicals in plant products is of fundamental importance for understanding their contribution in promoting health through diet. The content of bioactive components was found to be unaffected by processing, but variations during storage were observed in particular for total anthocyanins, which can be correlated with the changes in colour parameters recorded. A similar trend was found for the total antioxidant capacity: indeed, the HPP treatment did not significantly influence the antioxidant activity, which remained at high levels during storage.
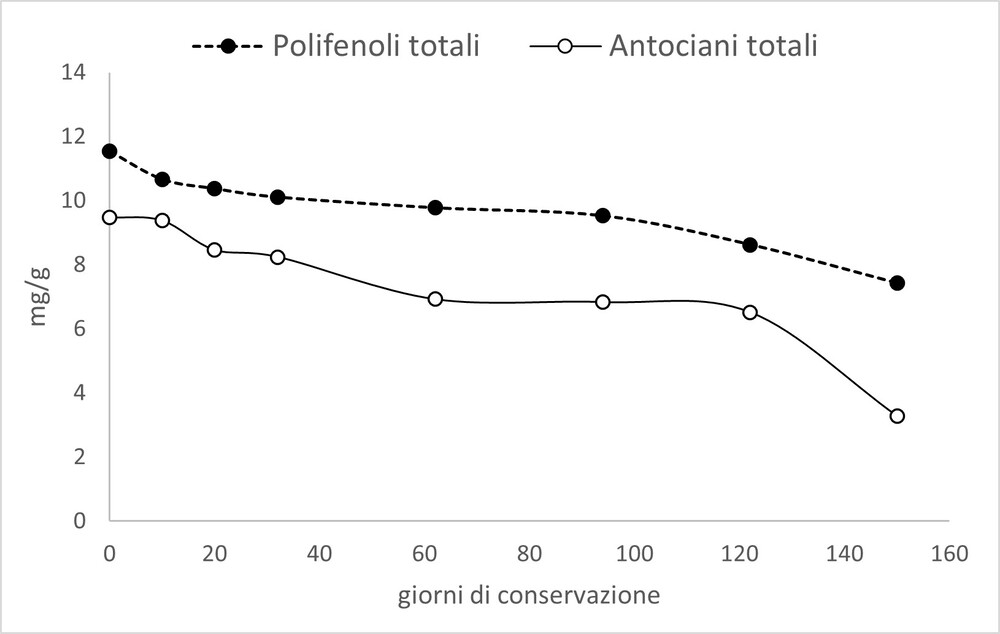 Image 2. Development of total polyphenol and total anthocyanin levels in cold-pasteurised sour cherries using HPP technology.
Image 2. Development of total polyphenol and total anthocyanin levels in cold-pasteurised sour cherries using HPP technology.
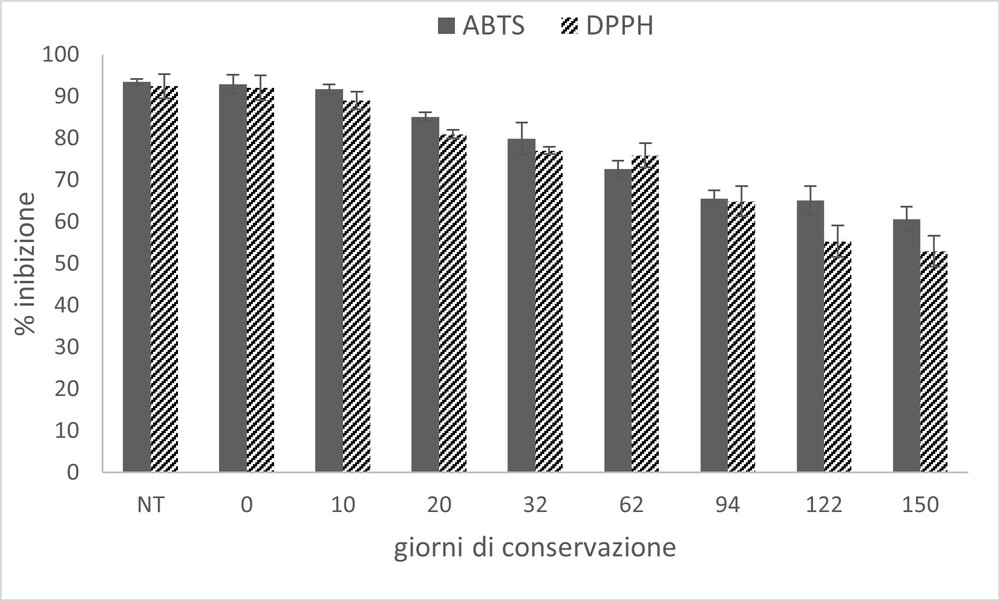 Image 3. Antioxidant capacity, measured by ABTS and DPPH tests, in cold pasteurised sour cherries using HPP technology.
Image 3. Antioxidant capacity, measured by ABTS and DPPH tests, in cold pasteurised sour cherries using HPP technology.
Overall, results allow us to state that the HPP treatment is able to preserve the quality characteristics of fresh stoned black cherries for at least 3 months under refrigerated conditions. After this period, the product may present variations in instrumental colour parameters and a decrease in anthocyanin content, without however compromising the hygienic safety of the product.
The HPP treatment therefore represents an interesting strategy for the valorisation of the fresh sour cherry fruit, with potential for the development of fresh-like ready-to-eat products and semi-finished products (for sectors such as confectionery, ice-cream parlours, etc.) able to compete on the markets for superior sensory and health qualities
The full study has been published in the scientific journal Foods, and is available in open access:
Tenuta, M.C.; Artoni, E.; Fava, P.; Bignami, C.; Licciardello, F. (2023). Shelf Life Extension and Nutritional Quality Preservation of Sour Cherries through High Pressure Processing. Foods, 12, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020342
Fabio Licciardello
University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved













