The post-harvest storage of cherries as well as their appearance is significantly influenced by several factors, including surface disorders and cracking. Besides physiological disorders, the quality of cherries is significantly influenced by the firmness and flavour of the flesh, which are two of the main factors determining consumer acceptability.
The firmness of the pulp naturally decreases during the development of the fruit on the tree and in the subsequent post-harvest period. The activation of enzymes associated with the degradation of pectin, the main stabilising factor of the fruit's primary cell walls, is responsible for this loss of firmness. However, it has been reported that sweet cherries with a firmer pulp at harvest are more successful in retaining this pulp during the cold storage phase than those harvested with a softer pulp.
In general, the normalised strain force expressed in Newtons per millimetre is used to ascertain the firmness of the pulp of sweet cherries. This measurement can be performed either by the force required to move the cherries by a distance expressed in % of their diameter per millimetre, or by applying a force over a defined distance (which is simpler and more suitable for user-friendly applications).
In recent years, numerous instruments have been put on the market, but an unambiguous method for assessing flesh firmness has not yet been found. The Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (Greece) conducted a study on two cherry cultivars, Regina and Canada Giant.
In addition to a fixed compression distance of 0.16 mm in the shortest fruit thickness dimension, the experiments included the application of variable compression levels (1%, 5% and 10%) according to fruit size. In addition to the evaluation of flesh firmness, several fruit quality attributes, sensory evaluations of firmness and primary fruit metabolites were assessed.
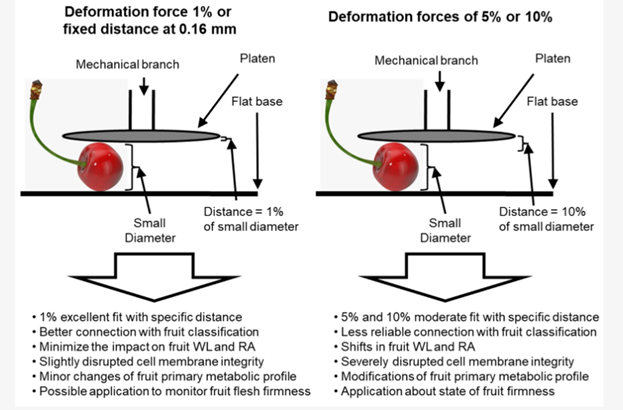
The researchers noted that fruits subjected to a 1 per cent strain force and a fixed distance of 0.16 mm within each cultivar showed a strong correlation with the panelists' preferences. Further analysis of the collected data showed that the control (0%) or the 1% strain force did not influence the metabolome, membrane integrity or physiological characteristics of the fruits in these categories, while the groups with 5% and 10% strain force showed clearly distinct and deteriorating quality values.
Compared to 5% or 10% strain forces, the impact of a 1% strain force on physiological attributes, including weight loss, respiration activity and membrane integrity, and also in metabolic analysis, was minimal. The results of this study suggest a potential future direction for monitoring sweet cherries during post-harvest storage, both during cold storage and shelf-life, with minimal impact on fruit physiology.
Does the research stop here? Absolutely not, extensive testing is needed to apply the proposed compression distance to the determination of sweet cherry firmness on a large scale.
Source: Karageorgiadou, M.; Rodovitou, M.; Nasiopoulou, E.; Titeli, V.S.; Michailidis, M. Sweet Cherry Fruit Firmness Evaluation Using Compression Distance Methods. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050435.
Image: Karageorgiadou ET AL., 2024
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











