ollination is a key process in cherry production, as it ensures the formation of high-quality fruit. Below are the main recommendations from a study aimed at increasing pollination efficiency for this variety.
Characteristics of the Areko variety
Areko is a mid-to-late season cultivar originating from Germany, resulting from a cross between Kordia and Regina.
It is notable for combining the best traits of its parent varieties, such as Kordia’s fruit quality and Regina’s productive, consistent tree with a similar growth habit.
Areko is a self-incompatible variety (S1S4), and therefore requires cross-pollination with compatible varieties that bloom at the same time.
Pollination is a crucial step in cherry production to ensure fruit set and quality. The following recommendations are based on a study conducted by agronomist Luis Valenzuela and promoted by ANA Chile®, with the goal of increasing pollination efficiency in the Areko variety.
1. Bloom synchronization
A proper overlap of flowering between Areko and pollinizer varieties is essential for effective pollination. Each cherry blossom remains receptive to pollen for a relatively short window, usually between 12 and 48 hours after opening.
Hot and dry conditions during bloom shorten this period, although treatment with Retain can extend receptivity.
Effect of agroclimatic zones
The behavior of pollinizer varieties, particularly in terms of flowering time, can vary significantly depending on the chosen agroclimatic zone (climate and soil), the season, as well as factors related to rootstock, training systems, and farming practices.
Recommendations for warm zones
These areas include the central valley floor with coastal influence in regions VI and VII of Chile, where seasons are less defined and there are significant climatic variations between years, especially in summer and autumn, with episodes of heat stress in some seasons.
- Recommended pollinizers: Lapins tends to bloom too early, making it ineffective for Areko in these areas. Santina and Skeena are recommended instead.
Recommendations for intermediate zones
These areas include the central parts of regions VI, VII, and part of VIII.
- Recommended pollinizers: Skeena is recommended for its good adaptability to local conditions. Santina is also advised, as it has a prolonged bloom period and can show both open and closed flowers on the same tree.
Recommendations for cold zones
These areas are located in the foothills of regions VI, VII, and VIII.
The annual cycle features well-defined, regular seasons: moderately warm summers, sharply cooling autumns, cold and steady winters, and gradually warming springs.
- Recommended pollinizers: There is good bloom synchronization between Areko and commonly used pollinizer varieties like Kordia and Skeena. Santina also blooms around the same time as Areko, making it a suitable option.
 Figure 1.- We recommend the presence of 2 pollinators in the hot zone, Santina and Skeena, leaving a maximum of 2 rows of the Areko variety together, to ensure sufficient visits by bees carrying compatible pollen.
Figure 1.- We recommend the presence of 2 pollinators in the hot zone, Santina and Skeena, leaving a maximum of 2 rows of the Areko variety together, to ensure sufficient visits by bees carrying compatible pollen.
2. Pollinizer distribution and proportion
Bee flight behavior shows that about 82% of foraging occurs along the same row: bees move back and forth along rows but rarely cross between them (Fig. 1).
- Row placement: No more than 3 consecutive rows of Areko should be planted without the presence of pollinizer varieties.
Pollinizer proportion
- Minimum: at least 10–11% of pollinizer trees, well distributed. This corresponds to one pollinizer every third row and every third tree within pollinizer rows (equal to 11%).
- Commercial: If using commercially valuable pollinizers, entire rows can be planted, increasing the share to up to 25%.
Distribution in warm zones
If commercially viable pollinizers such as Santina (particularly suited to warm zones) are used, entire rows can be planted, comprising 12.5% to 25% of trees in the block (Fig. 2).
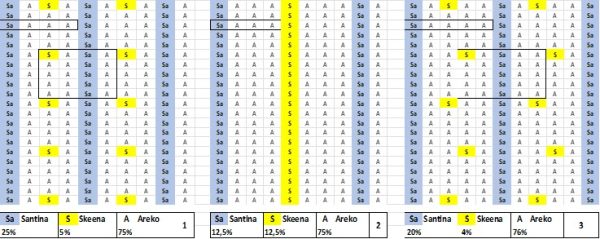 Figure 2.- Proportion and distribution of Santina and Skeena as pollinators of Areko in the warm zone, looking for a dual purpose, both pollination and commercial use of pollinators and their practical management. Placing them in complete rows as the basis for each fourth or fifth row, supplemented with the pollinator Skeena.
Figure 2.- Proportion and distribution of Santina and Skeena as pollinators of Areko in the warm zone, looking for a dual purpose, both pollination and commercial use of pollinators and their practical management. Placing them in complete rows as the basis for each fourth or fifth row, supplemented with the pollinator Skeena.
There should be no more than 3 consecutive Areko rows. Complete Skeena rows can be used to reach 12.5% of trees (Fig. 2-2), or Skeena trees can be interspersed in the central Areko rows, distant from Santina rows, to total 4–5% of trees (Fig. 2-1 and Fig. 3).
Distribution in intermediate zones
When using commercially valuable pollinizers such as Kordia (well suited for mid to late zones), complete rows can be included, reaching over 12%, up to 25% of total trees (Fig. 3).
Again, do not exceed 3 consecutive Areko rows. Central rows should be integrated with Skeena, reaching 12.5% of trees (Fig. 3-2), or Skeena trees interspersed in central rows far from Kordia rows, totaling 4–5% (Fig. 3-3 and Fig. 1).
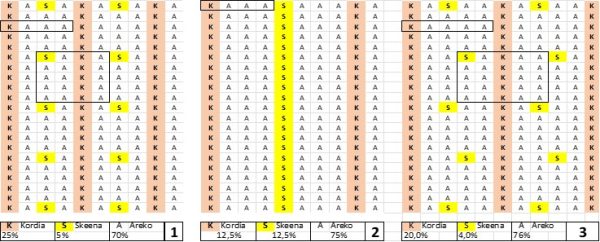 Figure 3.- Proportion and distribution of Kordia and Skeena, as pollinators of Areko in the central zone, with the aim of obtaining adequate pollination, as well as utilising the fruits of the pollinators with practical pollinator management. Kordia and Skeena are placed in alternating complete rows, 1 in every 4, or rows of Kordia integrated with the pollinator Skeena in the middle.
Figure 3.- Proportion and distribution of Kordia and Skeena, as pollinators of Areko in the central zone, with the aim of obtaining adequate pollination, as well as utilising the fruits of the pollinators with practical pollinator management. Kordia and Skeena are placed in alternating complete rows, 1 in every 4, or rows of Kordia integrated with the pollinator Skeena in the middle.
Distribution in cold zones
In these areas, it is advisable to plant complete rows of commercially viable pollinizers, particularly Kordia and Skeena, surpassing 12.5% and reaching up to 25% of pollinizer trees (Fig. 3).
As in other cases, no more than 3 consecutive Areko rows should be without pollinizers. Ideally, alternate with Skeena rows, reaching 12.5% for each pollinizer (Fig. 3-2).
If Skeena has lower commercial value, it can be interspersed in central Areko rows, farther from Kordia, comprising 4–5% of trees (Fig. 3-3 and Fig. 1).
3. Bee management considerations
- Hive placement: 10–15 hives per hectare; place in groups of 4 to 12, in warm, sunny, wind-sheltered areas, on platforms or stands, with access to water.
- Introduction timing: At 5% bloom to pollinate the earliest, highest-quality flowers.
- Optimal temperatures: Bee activity is reduced below 15°C; wind or rain negatively affect activity.
4. High carbon reserves
Maximizing photosynthesis is essential through a combination of factors: well-balanced tree vigor, good canopy light exposure, and stable root moisture.
- Optimal initial tree branching
- Avoid excessive nitrogen via roots
- Prevent over-irrigation in spring
- Avoid water stress in summer and autumn
5. Supplementary pollination
Use of flower jars
A helpful alternative when pollinizer distribution is inadequate. Branches with flowers from compatible varieties are cut at dawn.
Leave some pollinizer trees unpruned in winter to ensure flower availability.
Flowering branches should be placed in plastic bags with water and treated with Retain, then strategically placed along rows distant from pollinizers.
Supplemental pollen at hive entrances
Apply 150 g of pure pollen in 6 doses between 20% and 80% bloom. Two applications per day for 6 consecutive days.
Treatment can be extended in case of bad weather (rain, cold, or cloudy skies).
Electrostatic spraying
Use of Rainier pollen (S1 S4), which is compatible with Areko. Doses: 45–50 g/ha per application. Two applications: at 40% and 70–80% bloom.
Correction of inefficiencies
When needed, it is advisable to review pollinizer distribution based on Figures 2 and 3.
In new orchards, grafting or planting new pollinizer trees may help correct inefficiencies.
In warm zones
Partially replace Lapins with Santina, alternating rows. Skeena can also be added as an effective pollinizer.
Grafting of pollinizers
Entire trees can be grafted. Carefully define:
- which pollinizer varieties to use
- their distribution based on the climate zone
Source: redagricola.com
Image source: Graeb
Luis Valenzuela Medina
Agricultural Engineer M.Sc., Chile
Cherry Times - All rights reserved













