In vitro cultivation and cryopreservation techniques are fundamental tools for preserving biodiversity and producing healthy, pathogen-free plant material.
However, the impact of these techniques on the plant-associated microbiome remains not fully understood.
A recent study focused on this aspect, analyzing how the diversity of endophytic bacteria is influenced by in vitro culture and cryogenic freezing procedures in sweet cherry, and evaluating whether the inoculation of specific bacterial strains can improve the plants’ regenerative capacity after such treatments.
Sweet cherry responses
The sweet cherry cultivars used in the study were “Sunburst” and “Mindaugė”. The results showed differences between the two varieties in response to cryogenic freezing: while “Sunburst” benefited from pre-conditioning, achieving survival and regeneration rates of 69% and 43% respectively, “Mindaugė” showed weaker responses, with regeneration limited to 12% even after pretreatment.
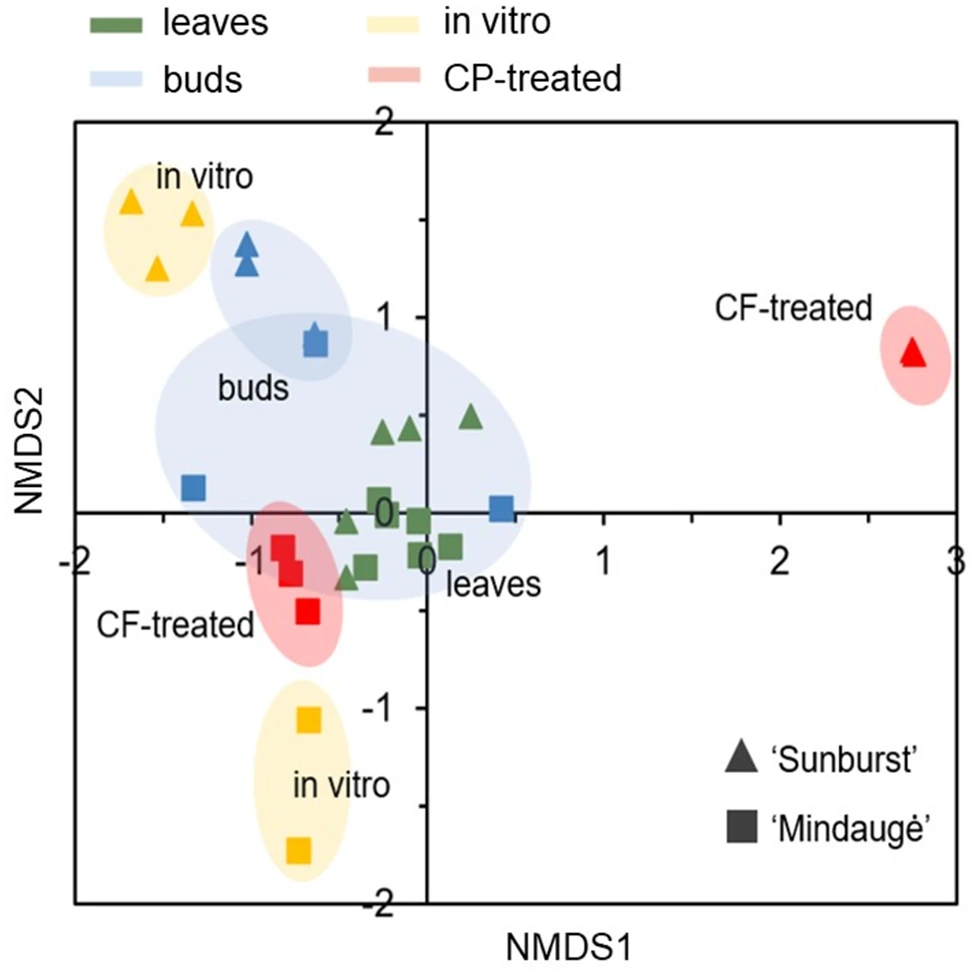 Figure 1. Bacterial diversity variation in sweet cherry leaf, bud, in vitro control, and CF-treated shoot samples. The nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis of the OTU datasets generated using metataxonomic sequencing of 16 S rRNA variable region V4 of cvs. Sunburst and Mindaugė samples was carried out using the Bray‒Curtis dissimilarity matrix.
Figure 1. Bacterial diversity variation in sweet cherry leaf, bud, in vitro control, and CF-treated shoot samples. The nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis of the OTU datasets generated using metataxonomic sequencing of 16 S rRNA variable region V4 of cvs. Sunburst and Mindaugė samples was carried out using the Bray‒Curtis dissimilarity matrix.
The core of the study was a metataxonomic analysis of the bacterial microbiome associated with leaf tissues, dormant buds, in vitro shoots, and shoots after cryopreservation.
The findings highlighted a drastic reduction in microbial diversity under in vitro conditions, along with the predominance of a single bacterial family, which differed depending on the genotype: Sphingomonadaceae for “Sunburst” and Mycobacteriaceae for “Mindaugė”.
Microbial shifts after freezing
After cryogenic treatment, further changes were observed: in “Sunburst” tissues, Burkholderiaceae became dominant, a bacterial family known for its positive interactions with plants and resilience in extreme conditions.
In “Mindaugė” tissues, Mycobacteriaceae were replaced by Bacillaceae and Enterobacteriaceae, which are also commonly found in the leaves of field-grown plants.
The study also explored co-cultivation experiments: cryopreserved “Mindaugė” shoots were inoculated with growth-promoting bacterial isolates (Brevibacterium sp., Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus toyonensis).
The results were notable: leaf area increased by up to 75% and shoot biomass by 37% compared to the uninoculated control.
Microbiome restoration benefits
This demonstrates that targeted integration of beneficial endophytes can mitigate the negative effects of cryopreservation and enhance the performance of in vitro cultures.
Furthermore, the combined inoculation of four bacterial strains did not produce additive effects, suggesting possible antagonistic interactions between the microorganisms.
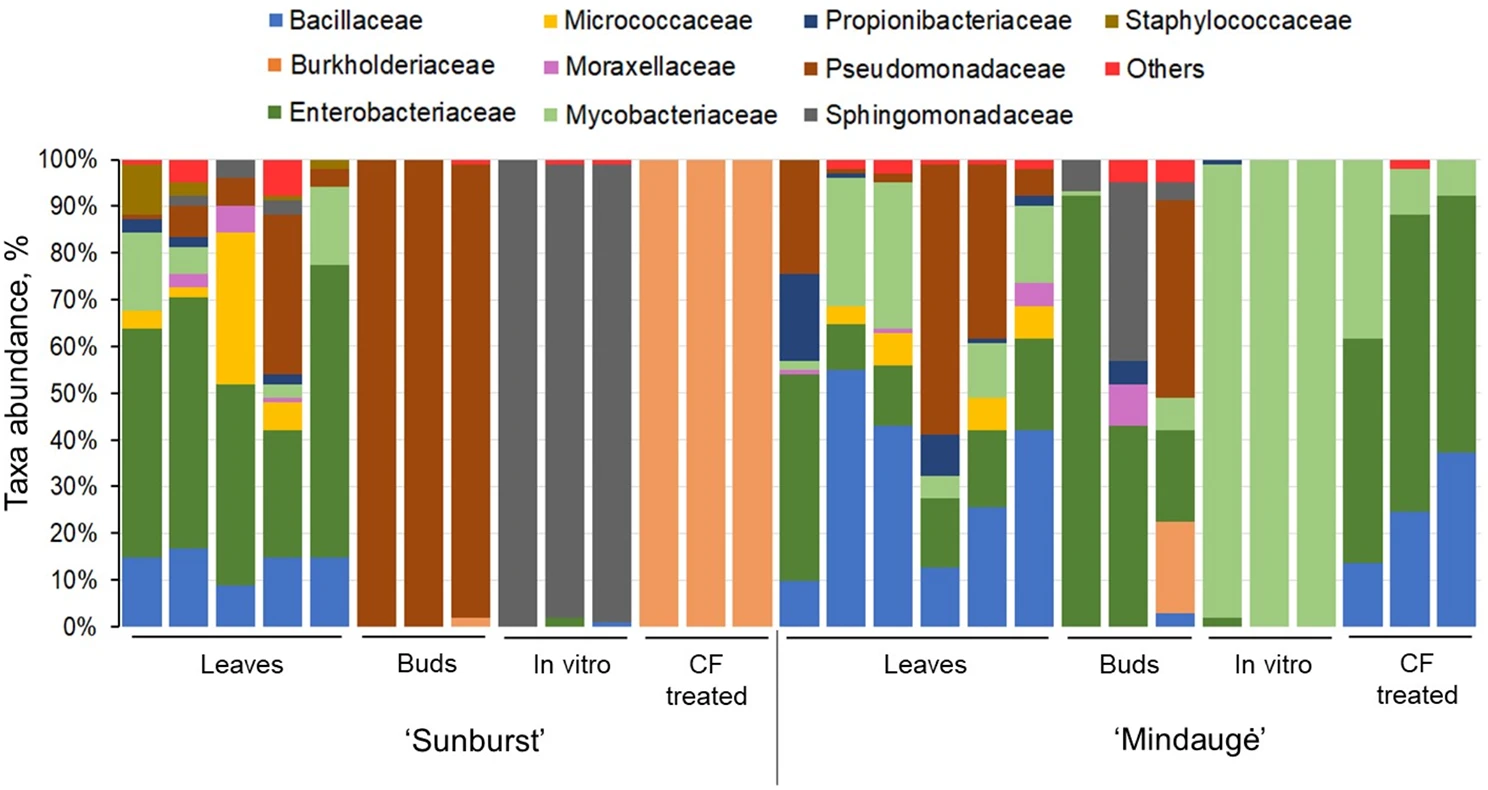 Figure 2. Abundance of endophytic bacterial taxa in leaf, dormant bud, in vitro shoot control, and cryogenic freezing-treated sweet cherry samples. Endophytic bacteria whose abundance did not exceed the 5% level were assigned to others.
Figure 2. Abundance of endophytic bacterial taxa in leaf, dormant bud, in vitro shoot control, and cryogenic freezing-treated sweet cherry samples. Endophytic bacteria whose abundance did not exceed the 5% level were assigned to others.
The study confirms that the composition of the endophytic microbiome is strongly influenced by propagation and preservation techniques, and that such alterations can negatively impact plant physiology by increasing oxidative stress and reducing growth.
Conversely, the controlled restoration of the microbiome can be an effective strategy to support vitality and regeneration of plant cultures after cryopreservation.
Conclusions and outlook
In conclusion, the study shows that endophytic bacterial diversity is significantly reduced under in vitro conditions, often leading to a genotype-specific dominance of bacteria from a single family.
Moreover, co-cultivation experiments with pure endophytic bacterial isolates demonstrated the benefits of applying plant growth-promoting bacterial inoculum to improve the recovery of shoots after cryopreservation.
These findings open new possibilities for enhancing the propagation and cryopreservation of clonally propagated plants using in vitro and cryogenic freezing techniques.
Fonte: Vinskienė, J., Tamošiūnė, I., Rugienius, R., Andriūnaitė, E., Stanys, V., & Baniulis, D. (2024). Endophytic bacterial community dynamics in sweet cherry in vitro shoot culture and their role in shoot adaptation after cryopreservation. BMC Plant Biology, 24(1), 1145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-024-05866-z
Fonte immagini: Vinskienė et al, 2024; VitroLeaf
Andrea Giovannini
Università di Bologna
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











