The phenological phases characteristic of sweet cherry depend on both the environmental conditions and the growth conditions, which are in turn influenced by the cultivar/rootstock combination. Knowing them is an important factor for the correct varietal choice in the establishment of new cherry orchards.
Four cherry varieties (Ferrovia, Regina, Kordia, and Skeena) grafted onto two rootstocks (Gisela 6 and MaxMa 14) were the subject of a study conducted at the Fruit Growing Institute in Plovdiv (Bulgaria). The monitored phenological development phases included, among others, bud swelling, full flowering dates, anthesis duration, fruit ripening date, and the overall vegetation period.
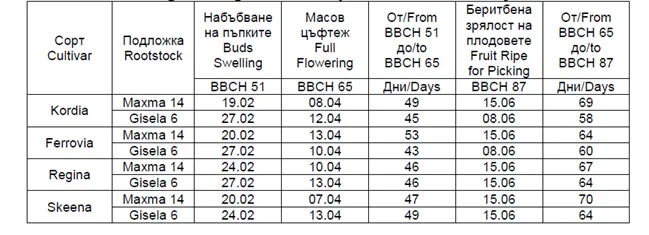 Image 1: Phenological phases and average development dates in stages BBCH 51, 65, and 87.
Image 1: Phenological phases and average development dates in stages BBCH 51, 65, and 87.
In the Plovdiv region, in the studied cultivar/rootstock combinations, the first bud swelling phase (BBCH 51) occurred with the Kordia cultivar on MaxMa 14 on February 19, and the last with cv Regina on MaxMa 14 on February 24.
In the sweet cherry varieties grafted onto Gisela 6, a delay in the vegetation period was observed, ranging from 3 to 8 days. In trees grafted onto Gisela 6, a flowering delay of 2 days (Regina and Ferrovia) to 5 days (Kordia) was observed compared to those grafted onto MaxMa 14 rootstock.
The period from bud swelling (BBCH 51) to full flowering (BBCH 65) ranged from 43 to 53 days for the different cultivar/rootstock combinations.
From full flowering (BBCH 65) to fruit ripening (BBCH 87), the shortest period was reported for the varieties grafted onto rootstock Gisela 6, ranging from 3 to 11 days shorter compared to the same varieties grafted onto MaxMa 14 rootstock.
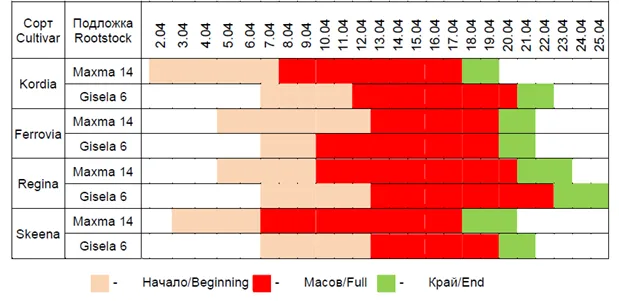 Image 2: Phenogram of the start, full, and end phenological phases.
Image 2: Phenogram of the start, full, and end phenological phases.
The longest vegetative period, in both rootstocks, was recorded in the Skeena variety, with 289 days in trees grafted onto MaxMa 14 and 277 days in trees grafted onto Gisela 6, respectively. The shortest period was observed in the Kordia cultivar, with 276 and 270 days, respectively.
Source: Penka Filyova, Fruit Growing Institute – Plovdiv, 4000, Agricultural Academy – Sofia, Bulgaria, Study of the Influence of the Rootstock on the Phenological Development of the Sweet Cherry. Journal of Mountain Agriculture on the Balkans, Research Institute of Mountain Stockbreeding and Agriculture, Troyan 2024, 27 (6), 295-307. ISSN1311-0489.
Images: Penka Filyova; SL Fruit Service
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












