Cherry quality after storage is a crucial factor for marketability and for reducing losses, especially in delicate varieties. A recent study conducted on the "Staccato" cultivar in 30 orchards in the Okanagan Valley, Canada, developed an innovative method for predicting post-storage quality by combining soil, leaf, and fruit nutrient analyses.
The goal was to identify pre-harvest and harvest-time factors that most influenced quality after four weeks of storage, using machine learning algorithms, particularly the support vector machine (SVM). The results showed that key parameters such as total soluble solids, firmness, and acidity could be predicted with high accuracy, allowing the supply chain to optimize management and improve final quality.
Key nutritional indicators
The analysis highlighted that calcium content is a key indicator of fruit firmness and soluble solids content after storage, while nitrogen affects firmness, acidity, and the presence of visual disorders such as stem browning.
Zinc content in the leaves showed a correlation with fruit weight and the acidity/soluble solids ratio, while magnesium influenced fruit coloration. Among the various factors analyzed, nutritional measurements in the leaves taken 3–4 weeks before harvest proved to be the most effective in predicting post-storage quality, whereas soil composition was less important compared to data collected directly from the plants.
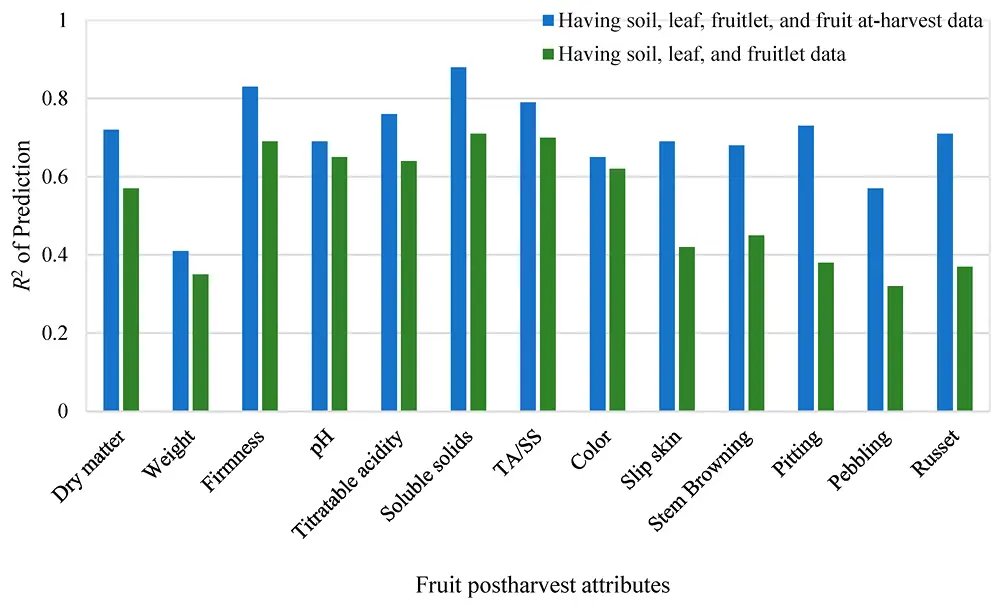 Immagine 1. Prestazioni dell'SVM nella previsione della qualità post-conservazione dei frutti di ciliegia.
Immagine 1. Prestazioni dell'SVM nella previsione della qualità post-conservazione dei frutti di ciliegia.
Predicting visual disorders
A critical aspect is the difficulty of predicting visual disorders based solely on pre-harvest data. However, including data measured at harvest significantly improves predictive capability, suggesting that a combination of pre-harvest and harvest-time information is the optimal approach.
The practical application of these results could help reduce economic losses in the cherry sector, estimated in Canada at between 3 and 10 million Canadian dollars (€2-7 million) per year.
Role of micronutrients in fruit quality
The importance of calcium in fruit firmness is confirmed by numerous previous studies, which highlight its role in cell wall stability, reducing susceptibility to physiological disorders.
Magnesium and iron, on the other hand, have been found to be crucial for maintaining color and sugar content, essential for consumers' perception of quality. Zinc, which is essential for plant metabolism, has shown a direct impact on fruit weight. Therefore, balancing the supply of micronutrients is essential to maximizing final quality.
Pre-harvest data, particularly mid-season leaf nutrients (N, Ca, Mg, Fe, Zn, and B), were reliable predictors of post-storage quality, while fruit nutrient concentrations alone were not sufficient.
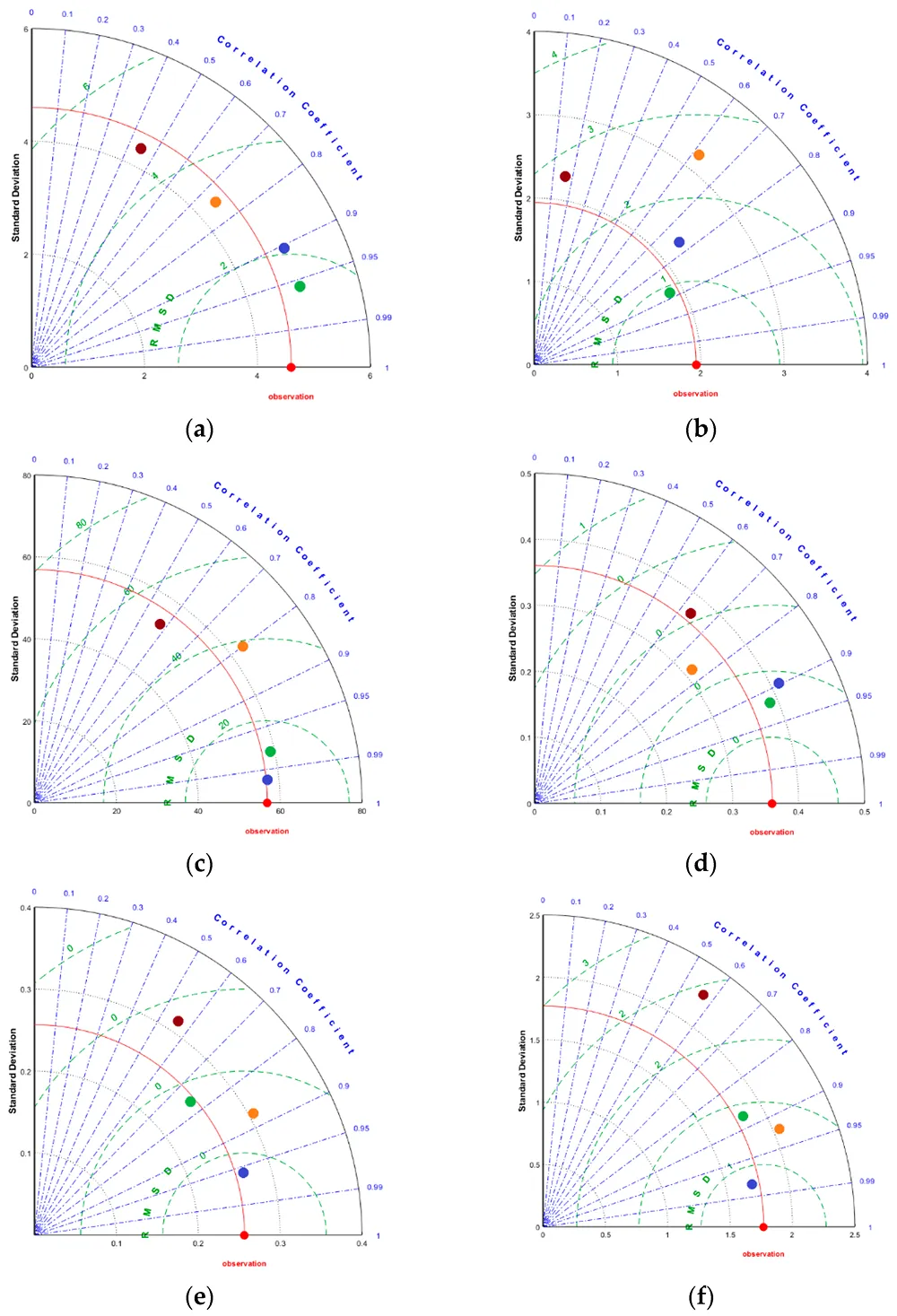 Image 2. Taylor diagrams for the prediction of post-harvest fruit attributes. The points coloured red are the actual attribute values, while the other points belong to the predicted values using the attributes of the fruit (orange), leaves (green), harvested fruit (blue) and soil (crimson). ( a ) dry matter, ( b ) weight, ( c ) firmness, ( d ) pH, ( e ) titratable acidity, ( f ) total soluble solids, ( g ) TA/TSS ratio, ( h ) slippery skins, ( i ) stem browning, ( j ) pitting, ( k ) gravel and ( l ) rust.
Image 2. Taylor diagrams for the prediction of post-harvest fruit attributes. The points coloured red are the actual attribute values, while the other points belong to the predicted values using the attributes of the fruit (orange), leaves (green), harvested fruit (blue) and soil (crimson). ( a ) dry matter, ( b ) weight, ( c ) firmness, ( d ) pH, ( e ) titratable acidity, ( f ) total soluble solids, ( g ) TA/TSS ratio, ( h ) slippery skins, ( i ) stem browning, ( j ) pitting, ( k ) gravel and ( l ) rust.
Future perspectives
Future studies should focus on refining sampling strategies (timing, location, and leaf type). Additionally, it would be useful to develop technologies for rapid in situ measurement of nutrients (such as portable X-ray fluorescence) to further simplify and speed up analyses.
In conclusion, these findings provide new perspectives on managing the cherry supply chain. The use of predictive models based on machine learning offers a concrete opportunity to improve the sustainability of cherry production by optimizing fertilizer use and reducing losses throughout the supply chain.
Images: Sharifi et al., 2024; SL Fruit Service
Source: Sharifi, M., Wolk, W., Asefpour Vakilian, K., Xu, H., Slamka, S., & Fong, K. (2024). Integrating Soil, Leaf, Fruitlet, and Fruit Nutrients, Along with Fruit Quality, to Predict Post-Storage Quality of Staccato Sweet Cherries. Horticulturae, 10(11), 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10111230
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












