Stefano Lugli, SL Fruit Service
Chair of Cherry Times technical-scientific committee
In the experimental field of Fragsburg, near Merano (Italy), the Small Fruits and Stone Fruits working group of the Laimburg Research Center has been conducting scientific experiments on cherry trees for over 30 years.
On Thursday, June 20, a well-attended training meeting was held for farmers and technicians, during which the experts from CS Laimburg, led by Massimo Zago and Giacomo Gatti, presented the results of the latest ongoing trials, mostly focused on planting systems and cherry orchard management techniques. Here is a brief summary for the readers of Cherry Times.
Towards HDP and 2D Training Systems
 Photo 1: Bibaum cv Kordia on Gisela 5. Source: SL Fruit Service.
Photo 1: Bibaum cv Kordia on Gisela 5. Source: SL Fruit Service.
The classic spindle used for over 20 years in South Tyrolean cherry orchards could soon be replaced by more productive narrow wall training systems, which offer higher yields per hectare, earlier fruiting, better fruit size, and improved economic performance due to better agronomic efficiency and lower pruning and harvesting costs.
"Among the six training systems tested," Gatti explains, "the best were the double axis or Bibaum at 2140 trees/ha and the Super Spindle at 2570 trees/ha, while other 2D systems (UFO and Drapeau) were less suited to the vegetative-productive habits of varieties such as Kordia and Regina, although they remain very interesting and efficient models under different conditions and with other varieties."
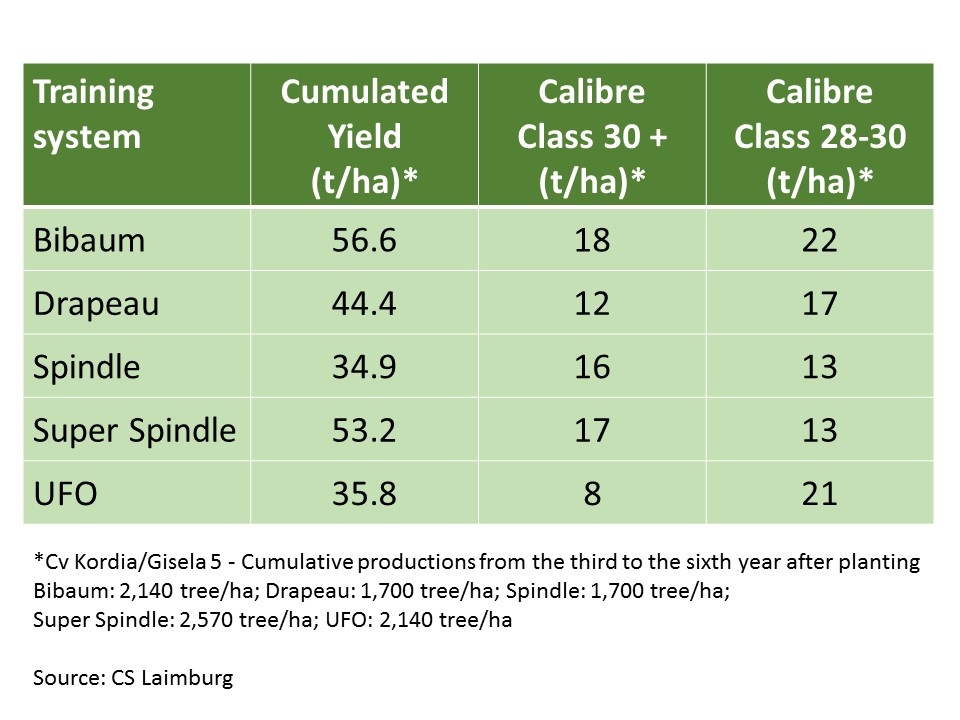 Table 1: Experimental results on training systems.
Table 1: Experimental results on training systems.
Cherry Tree Pruning Can Be Mechanized
 Photo 2: Row of Kordia on Piku 1 pruned mechanically. Source: SL Fruit Service.
Photo 2: Row of Kordia on Piku 1 pruned mechanically. Source: SL Fruit Service.
Profit margins for cherry producers in South Tyrol can be improved by reducing certain costs in orchard management wherever possible, through mechanizable interventions such as pruning. In a six-year trial on cv Kordia/Piku 1 trained as a spindle, three pruning techniques were compared: classic manual pruning at the end of winter, a single mechanical pruning intervention in September without subsequent corrective pruning.
The results presented during the visit are surprising. "Mechanical pruning," commented Gatti, "allowed for an average yield of 19t/ha, good-sized cherries, and could potentially save producers around 20,000 euros per year."
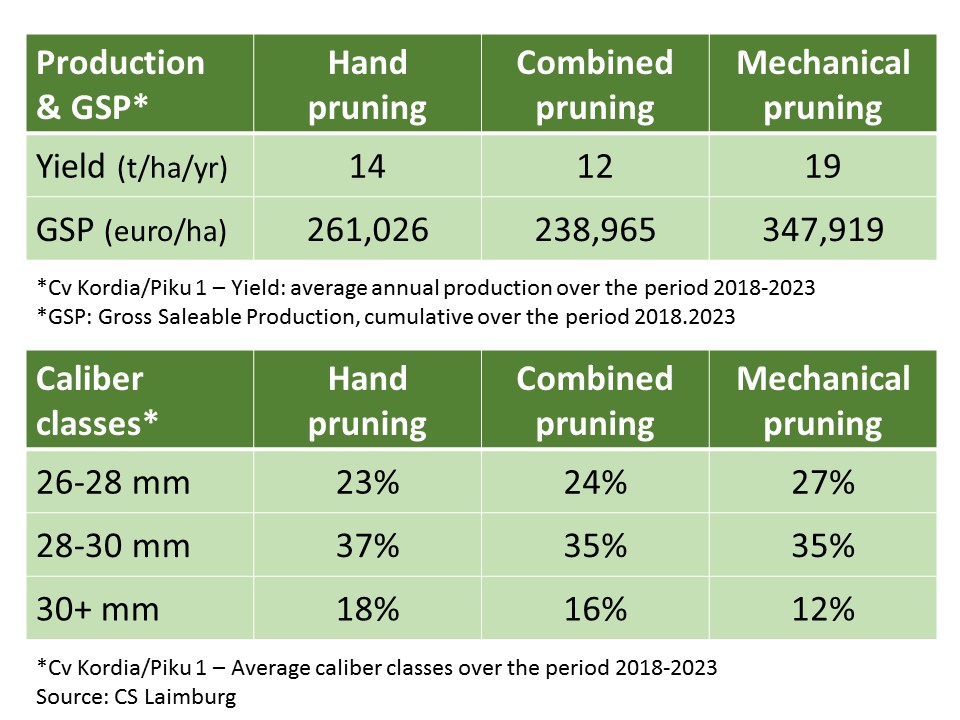 Table 2: Experimental results on pruning trials.
Table 2: Experimental results on pruning trials.
Choosing the Rootstock and Replanting Issues
 Photo 3: Cherry trees on Gisela 6 in replanted soil. Source: SL Fruit Service.
Photo 3: Cherry trees on Gisela 6 in replanted soil. Source: SL Fruit Service.
The development of cherry growing in South Tyrol can be considered relatively recent, at least compared to other Italian growing areas where cherry trees have been cultivated for almost two centuries.
Researchers at CS Laimburg were forward-thinking, setting up a 17-year trial on replanted cherry soil with cv Kordia grafted onto various rootstocks (Colt, MM14, Piku 1, Gisela 6, and Gisela 5) to find solutions to issues related to soil fatigue and replanting diseases in cherry trees.
"The results from this trial," Zago explains, "show that the Gisela 6 rootstock is the most suitable for countering soil fatigue, making it a priority choice for renewing an orchard on the same land. Conversely, Gisela 5 proved too weak for replanting, while Colt and MM14 were too vigorous and inefficient under our conditions."
Varietal Innovation Is Not a Priority
 Photo 4: Areko, a new variety, offspring of Kordia and Regina. Source: SL Fruit Service.
Photo 4: Areko, a new variety, offspring of Kordia and Regina. Source: SL Fruit Service.
Accustomed to off-season productions and yields of 20-25 t/ha with high-quality late varieties such as Kordia and Regina, the need to expand a limited but strongly consolidated and profitable varietal offering is not a priority for the South Tyrolean production chain.
The technical day organized by CS Laimburg could have been a good opportunity for discussion and analysis on the topic of genetic improvement and expanding production calendars before Kordia and after Regina. The timing and cherries probably aren't ripe yet to tackle these topics. Maybe next time.
Congratulations to the entire Laimburg research center staff for organizing the visit, for the investments made in cherry experimentation, and for the excellent results achieved.
Cherry Times - All rights reserved

















