The progress in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) breeding has been marked by the identification of molecular markers for crucial traits, utilizing genome sequencing for marker-assisted selection (MAS). Despite these achievements, quantitative trait locus (QTL) analyses have often lacked resolution, leading to missed gene associations.
Traditional breeding methods face challenges related to low efficiency and high costs. Recent developments in whole-genome sequencing have uncovered nearly 2 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), promising higher marker density for genome-wide association studies (GWAS). However, uneven SNP distribution remains an obstacle, hindering the identification of candidate genes. The current hurdle is to leverage GWAS potential for high-resolution mapping to expedite the breeding of improved sweet cherry varieties.
Researchers employed paired-end sequencing on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform, generating a 4.15-Tb sequence with samples contributing 7.6–36.8 Gb each. The extensive genome coverage allowed the identification of 1,767,106 high-quality SNPs distributed across the accessions. Principal component analysis (PCA) and Bayesian information criterion (BIC) indicated a homogeneous population without distinct genetic subgroups.
Phenotypic diversity assessed from 2012 to 2020 revealed significant variability across traits, with Collection of Genetic Resources (CGR) accessions displaying more pronounced diversity than breeding materials (BM). Notable differences in color traits and fruit size were observed, aligning with the goals of selective breeding.
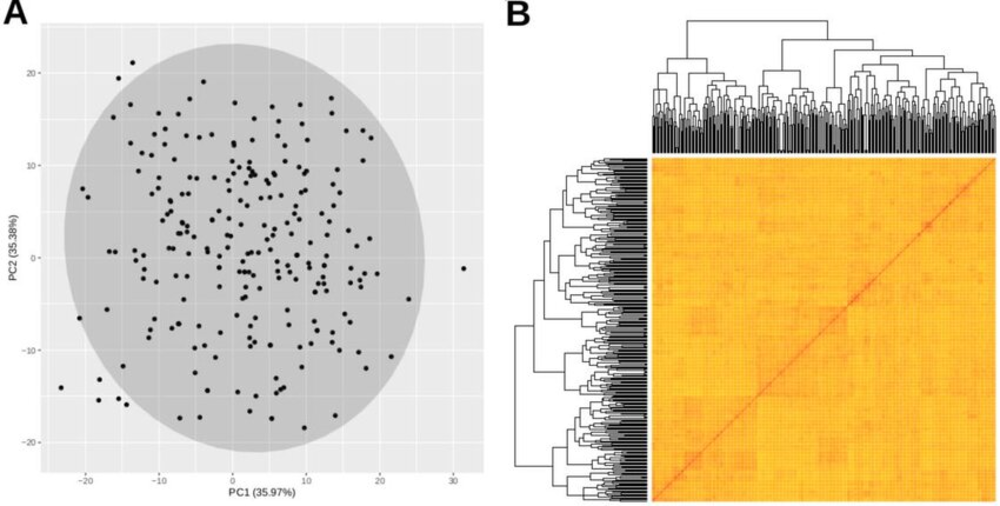 Collection of Genetic Resources population structure analysis. A) Principal component (PC) analysis plot of the first two PCs identified from 235 accessions based on 1,767,106 single nucleotide polymorphisms. B) Heat map of a kinship matrix estimated using the VanRaden algorithm. Both plots were generated with GAPIT.
Collection of Genetic Resources population structure analysis. A) Principal component (PC) analysis plot of the first two PCs identified from 235 accessions based on 1,767,106 single nucleotide polymorphisms. B) Heat map of a kinship matrix estimated using the VanRaden algorithm. Both plots were generated with GAPIT.
Source: EurekAlert!
Image: High-resolution genome-wide association study of a large Czech collection of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) on fruit maturity and quality traits - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Collection-of-Genetic-Resources-population-structure-analysis-A-Principal-component_fig1_364394570.
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











