The benefits of calcium in the cultivation of cherries are well known. Its effects on the quality and post-harvest of this prized fruit make it an essential element for production orchards and export companies. However, this element presents some very specific challenges. First of all, it is not very mobile throughout the plant. The lack of calcium transport capacity within the plant makes it difficult to reach the growing fruits.
The second issue is that calcium follows the water flow through the xylem, which means that its absorption is closely tied to the plant's transpiration capacity. This, in turn, is conditioned by climatic factors, such as humidity or temperature, which prevent the correct absorption of calcium by the plant, even when high levels of this element are present in the soil.
These two circumstances (low calcium mobility and its dependence on the plant's transpiration flow) make it really difficult to translocate this nutrient to the fruits. Traditionally, treatment has been carried out with numerous foliar applications of calcium-containing products throughout fruit development, with very irregular and generally insufficient results.

For this reason, the Manvert strategy includes:
- Applying a solution that mobilizes calcium, specifically formulated for this purpose, to give this nutrient the ability to move through the plant and reach the fruits, along with a solution that provides easily assimilable calcium.
- Applying through the roots, so that calcium is transported through the xylem. Foliar applications should be complementary.
- Applying at the right time, in an early phase, at the beginning of cell division or, in other words, at the time of petal drop, which coincides with the peak calcium absorption by the crop.
In summary, the strategy involves applying a calcium mobilizer along with an assimilable calcium source, through the roots and during the petal drop stage.
This solution consists of only two products:
- Movili-Ca by Manvert is a biostimulant that moves calcium within the plant. Its formulation with the PACaR (Promoter of Root Calcium Absorption) molecule makes this product a valuable and unrivaled mobilizer on the market.
- Manvert win-Ca, which is a solution with calcium fulvates that provides available and easily assimilable calcium, as well as unlocking calcium fixed in the soil. Manvert win-Ca is the calcium source that will mobilize Manvert Movili-Ca within the plant, reaching the fruits.
This treatment maximizes the use of calcium when it is most needed, reducing negative physiopathies for cherries such as lizard skin, pitting, or rot. This Manvert calcium solution has been demonstrated in the field and through numerous trials conducted by us and others, such as the one carried out in a Santina cherry orchard on Colt rootstock in Comalle, Chile, between October 2022 and February 2023.
The Manvert calcium treatment (a single application of Manvert Movili-Ca + Manvert win-Ca) was compared to a control. Evaluations were made at the time of harvest and 45 days after harvest.
These are the results obtained at harvest with the application of the Manvert calcium treatment:
- An increase of 23.6% in cherry production.
- An increase in cherry size and average weight by 2.1% and 6.1%, respectively.
- An increase in soluble solids content by 4.8%.
- An increase in total calcium by 12.2%.
- An increase in bound calcium by 30.2%.
These are the results obtained in post-harvest (after 45 days of cold storage):
- Reduction of cherries affected by lizard skin by 9.3%.
- Reduction of pitting in cherries by 56%.
- Absence of rot.
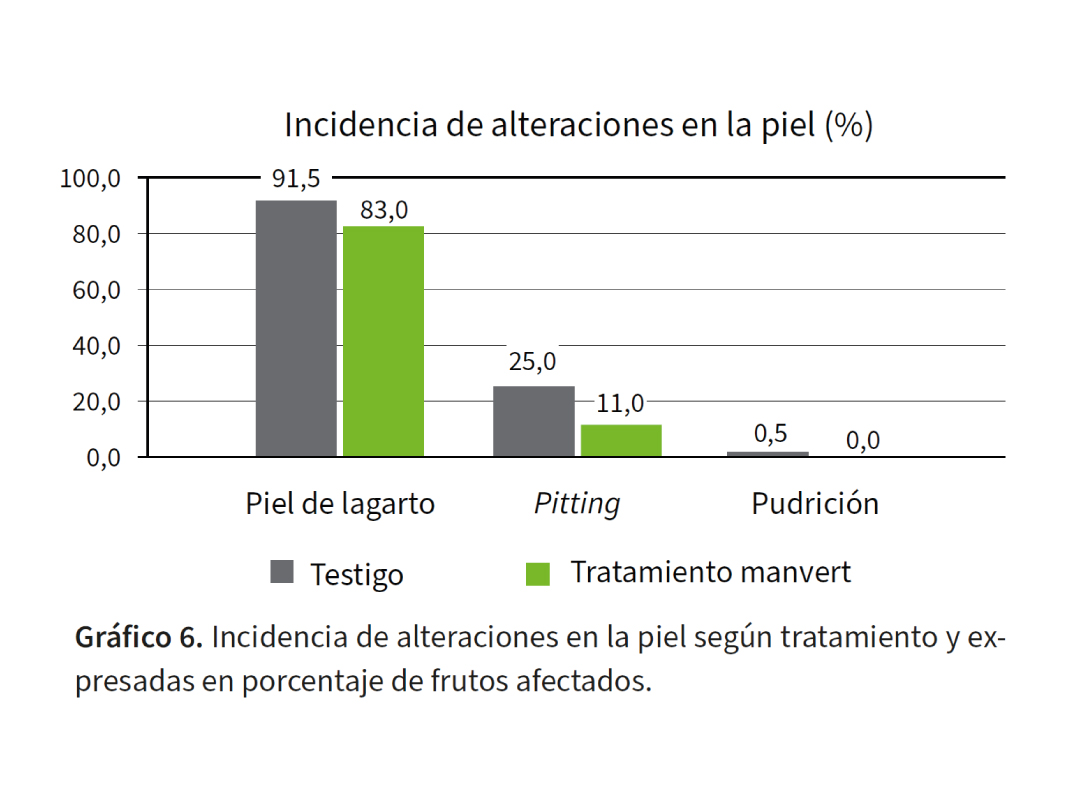 Image 1: Incidence of skin disorders based on treatment, expressed as a percentage of affected fruits.
Image 1: Incidence of skin disorders based on treatment, expressed as a percentage of affected fruits.
With the Manvert treatment, a profit of nearly €12,000 per hectare was achieved, equivalent to a return rate of €64.6 in profit for every euro invested in the products compared to untreated areas. This calculation was made based on economic and statistical data related to the area and year of the experiment.
Source: Mundoagro
Images: SL Fruit Service; Mundoagro.
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












