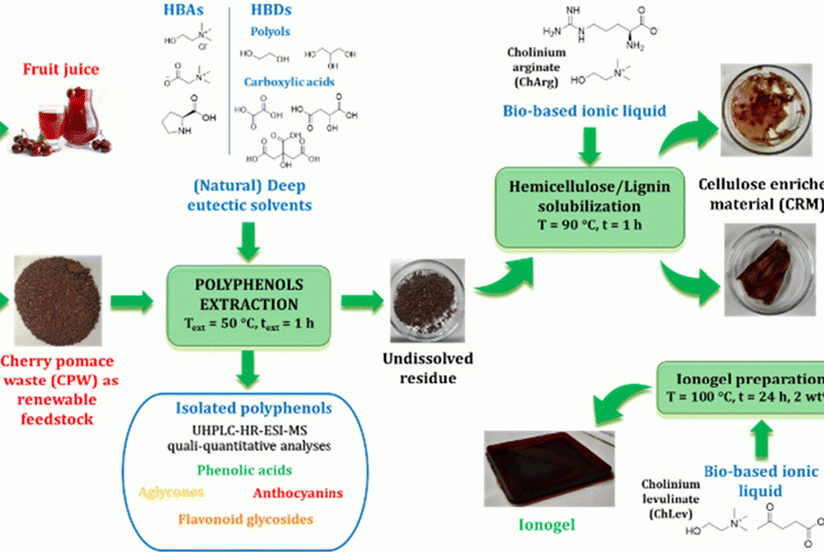
There is a possibility of a breakthrough in the research on controlling Drosophila suzukii. A natural enemy has been found, the parasitic wasp Ganaspis kimorum, which very selectively attacks D. suzukii. This was reported by Wageningen UR researcher Herman Helsen.
Helsen has high hopes for the parasitic wasp that Swiss researchers found in Asia. The researchers have studied the parasitic wasp in the laboratory for years. Earlier this year, they published a study showing that this species very selectively attacks specimens of Drosophila suzukii.
Unlike parasitic wasps native to Europe, this specimen searches for its opponents on trees rather than on the ground. “We hope that the release of Ganaspis can counter the annual explosion of Drosophila suzukii,” he stated.
Before the wasp can be introduced in the Netherlands, there is still much to be done. Helsen: “We need to prove that the introduction of the parasitic wasp will not disrupt the entire native fauna. For such authorization, a dossier is required. The province of Gelderland, through Greenport Gelderland and Fruitpact, has provided the funds to prepare the application dossier."
"We are applying for admission to Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland; the evaluation is under the Ministry of LVVN. We hope to gain admission without issues. Shortly after approval, we hope the research on PPP can begin. The NFO has submitted a research proposal regarding this. This still needs approval. The outcome is expected this year, and the hope is to start research in early 2025.
We need to study Ganaspis, cultivate it, and release it to see the results, its life cycle, and its impact on Drosophila suzukii. The fruit fly will not disappear, but we hope that with the arrival of this parasitic wasp, other management approaches will become more effective and less reliant on chemicals.”
The third step will be to mass-rear the parasitic wasp, creating a product that growers can use in their crops. “We want to introduce it on a large scale: the entire cultivation of red fruits is threatened by Drosophila suzukii. Numerous native species of trees and shrubs with red fruits are also at risk. But all this still requires extensive research.”
Source: Nederlandse Fruttelers Organisatie
Image: Gallardo, F.E., Funes, C.F., Reche, V. et al. First Record and Distribution of Ganaspis brasiliensis (Hymenoptera: Figitidae: Eucoilinae), a Parasitoid of Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Argentina. Neotrop Entomol 51, 164–169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-021-00912-z.
Cherry Times - All rights reserved