The recent discovery of Leptopilina japonica in the provincial territory offers new opportunities for the biological control of Drosophila suzukii, a fly harmful to small fruits that is causing severe problems for producers, both in Trentino and elsewhere. This parasitoid, native to Asia, was identified in a cherry orchard in the Adige Valley, where it could play a significant role in the natural management of this pest.
The Leptopilina japonica complements Ganaspis brasiliensis, another parasitoid imported from Switzerland and currently undergoing experimentation in quarantine cells at the Edmund Mach Foundation (FEM). Although Ganaspis brasiliensis remains the main candidate for biological control against Drosophila suzukii, it is expected that the two insects could work synergistically to enhance control effectiveness.
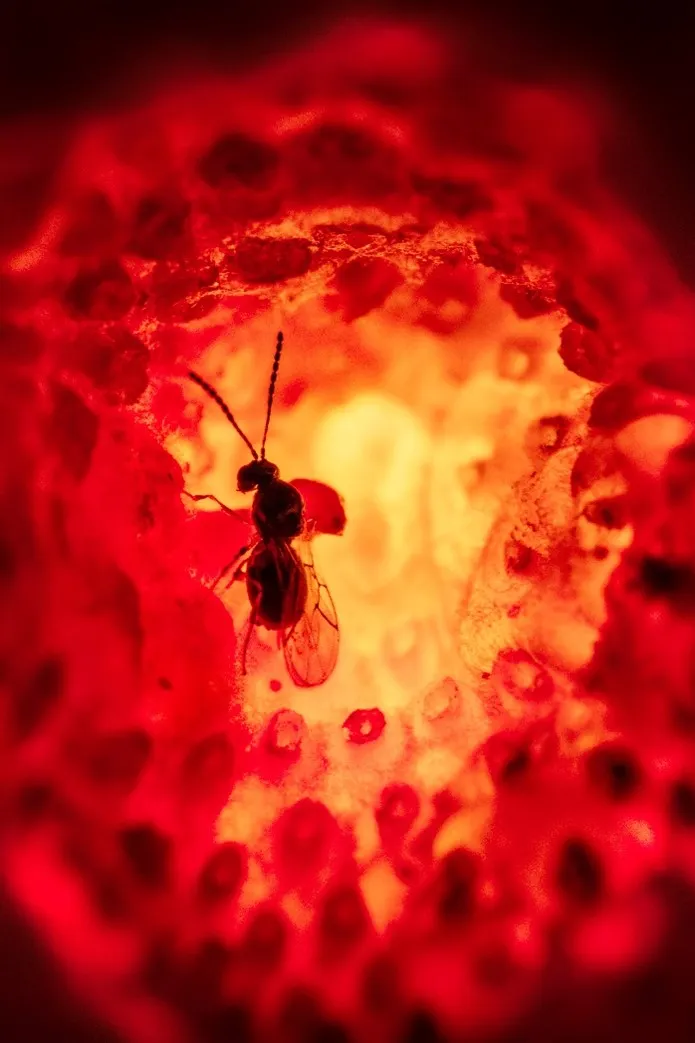 Image 1: These excellent photos by Warren HL Wong @warrenhlwong (Simon Fraser University, BC, Canada) show a female parasitoid wasp Leptopilina japonica extending its ovipositor into a raspberry to parasitize a larva of the spotted-wing fruit fly, Drosophila suzukii, which has become a serious pest of berries worldwide. This is an example of classical biological control, implemented through the introduction of this native Asian species to other parts of the world, thus reducing the need to use insecticides in agroecosystems.
Image 1: These excellent photos by Warren HL Wong @warrenhlwong (Simon Fraser University, BC, Canada) show a female parasitoid wasp Leptopilina japonica extending its ovipositor into a raspberry to parasitize a larva of the spotted-wing fruit fly, Drosophila suzukii, which has become a serious pest of berries worldwide. This is an example of classical biological control, implemented through the introduction of this native Asian species to other parts of the world, thus reducing the need to use insecticides in agroecosystems.
This discovery was made as part of a doctoral research program jointly conducted by FEM and the University of Molise, supported by contributions from the Sant’Orsola cooperative and funded by the Autonomous Province of Trento through the project “Biological control of alien species.”
The monitoring conducted by FEM made it possible to observe the population trends of Drosophila suzukii, the level of infestation on cultivated and wild fruits, and the presence of natural antagonists. During these activities, it was possible to capture, for the first time in Europe, an alien parasitoid outside its native range. The Leptopilina japonica has shown great effectiveness in its native areas in parasitizing the larvae of D. suzukii.
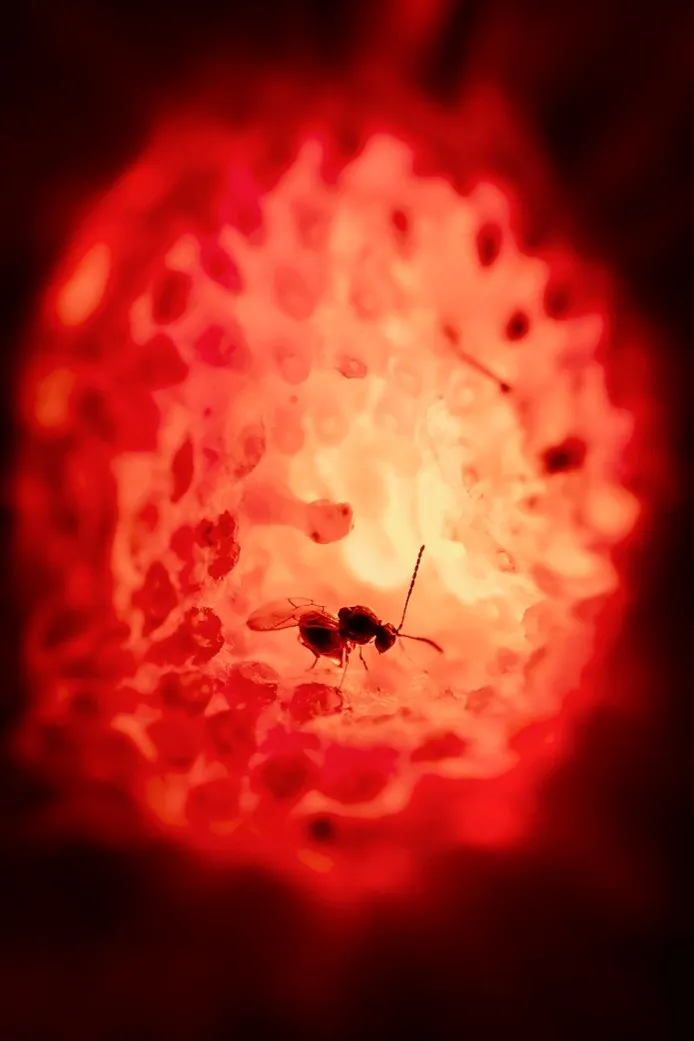 Image 2.
Image 2.
The initial identification, based on morphological characteristics, was later confirmed through molecular analysis, which validated the presence of the species in the province. "After the first discovery," explain Alberto Grassi and Simone Puppato from the FEM Technology Transfer Center, "we initiated a targeted study with sampling of cultivated and wild fruits, stored in a climatic chamber, to verify the presence of other alien parasitoids."
Preliminary results suggest that Leptopilina japonica is already widely distributed in the province of Trento: it has been found in five different sites, located up to 20 km apart and at altitudes ranging between 211 and 685 meters. The investigation is still ongoing, but this discovery represents an important step forward in the sustainable management of one of the greatest threats to red pulp fruits.
Source: La Busa
Images: La Busa; Warren H. L. Wong, S. Fraser - University, BC, Canada.
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












