Washington State University's economic analysis reveals that managing and controlling disease X requires a considerable commitment of time and financial resources. However, a lack of response can have even higher costs for farmers, as pointed out by Welcome Sauer, an orchard analyst with the university. His economic model shows that mitigation practices, such as removal of infected trees and locust control, generate a significant return on investment.
The model, comprising seven treatment scenarios and dozens of variables over a 60-year period, provides a detailed view of the economic realities faced by farmers. The ideal approach is to prevent the disease from the outset by investing in protective nets to defend the orchard. Even if infection does occur, investment in vector control can extend the profitability of the orchard by nine years compared to situations where no preventive measures are taken.
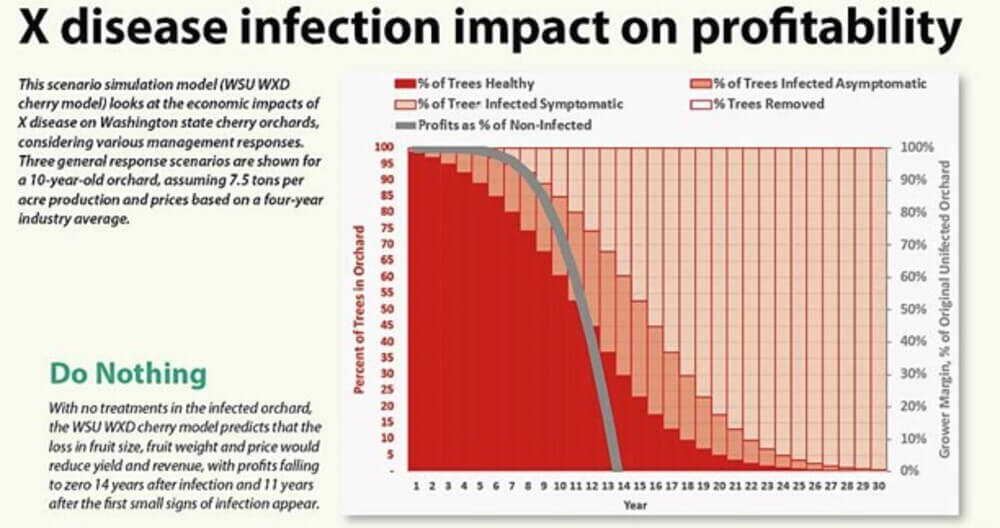
Aggressive removal of infected trees and replanting can stabilise profitability, albeit with lower margins than with a block that has never been infected. The model takes into account that the disease can spread invisibly for years before it becomes evident, causing significant financial losses. The disease also affects the size and quality of the fruit, with complex effects on prices.
The ultimate goal is to make the model accessible to farmers as a practical tool to adapt operational costs, cherry prices and infection rates to their farms. The analysis aims to fill information gaps in the sector, providing an in-depth understanding of the economics and challenges of managing disease X.
Read the full article: Good Fruit Grower
Images: Good Fruit Grower
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











