Drosophila suzukii, one of the main pests of the cherry tree, is capable of causing considerable damage every year and needs to be controlled as effectively as possible. To achieve this, it is useful to start with the basics: knowing and understanding its behaviour.
We can compare D. suzukii to a tourist, moving from field to field in response to the supply of fruit and energy available to survive the winter. The key factors influencing the intensity of the attack are therefore two: the availability of fruit throughout the year and the conditions for hibernation.
Numerous studies in the USA and Argentina have shown that the insect tends to abandon orchards during certain times of the year, taking refuge in non-cultivated areas and then returning in the following spring. This behaviour has also been confirmed in Chile, thanks to data collected with monitoring traps in the Maule area and other cherry-growing areas.
It was also found that in the 2023-2024 season, cherry orchards located near water sources and surrounded by hills faced increased pressure from this insect. To predict and manage the intensity with which this insect may attack, early detection of population fluctuations is necessary.
It is therefore with monitoring that the pressure of Drosophila suzukii can be anticipated, as it provides valid data on the presence and evolution of the insect. Cherry producers must therefore participate in monitoring networks or, alternatively, install trap systems themselves.
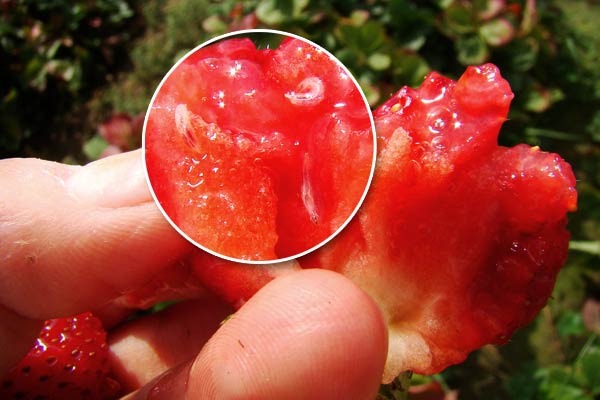
Indeed, the return of the insect during the following year depends on:
- the number of overwintering insects and
- the availability of food sources during the winter.
When the presence of the insect is detected, action must then be taken to control it. The control of D. suzukii requires a multifactorial strategy that combines insecticide application with cultural management practices. In general, at least 4 applications of specific insecticide from veraison to harvest are recommended.
The Agricultural and Livestock Service of Chile has authorised a wide range of insecticides valid for Drosophila control, offering various options of different chemical groups to avoid the emergence of resistance phenomena. The effectiveness of control techniques depends on various factors, including the application of the correct dose of product and proper orchard management. Some factors that may compromise fruit protection are:
- Presence of pollinators: they normally ripen earlier and affect the effectiveness of treatments.
- Insect phenology: it is essential to plan chemical interventions on the basis of the insect's actual stage of development.
- Training of operators and good condition of treatment machinery.
- Variations in harvesting: possible variations in ripening and harvesting must be considered.
The management of Drosophila suzukii in cherry trees requires the combination of knowledge of the insect's behaviour with the implementation of control tools that are adapted to local conditions. Anticipation, constant monitoring and flexibility in adjusting control techniques are essential to protect crops and ensure quality at harvest. With a proactive and data-driven approach, producers can effectively tackle this persistent threat, ensuring sustainability and profitability of their cherry production.
Fonte: Cherry Magazine
Immagine: WSU
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











