In today’s global context, water availability is decreasing while food demand continues to rise. For these reasons, optimizing water use efficiency (WUE) has become a key priority for sustainable agricultural production.
With this objective, a recent study examined the impact of various irrigation strategies on yield and WUE in three major fruit species: apple, peach, and sweet cherry.
Through a meta-analysis of existing literature, the study assessed six alternative irrigation strategies: Moderate Deficit Irrigation (MDI), Severe Deficit Irrigation (SDI), Regulated Deficit Irrigation (RDI), Partial Rootzone Drying Irrigation (PRDI), Farmer Practiced Irrigation (FPI), and Over-Irrigation (OI).
Strategies and results for sweet cherry
The control treatment in these studies was either the absence of any water deficit or full irrigation (FI), restoring 100% of evapotranspiration (ET).
Among the various irrigation strategies, RDI emerged as the most promising approach for sweet cherry, showing a 56% improvement in WUE without a significant reduction in yield.
MDI and SDI also demonstrated WUE increases of 42% and 14%, respectively, while maintaining overall productivity. Conversely, FPI and OI led to a decline in both yield (–10%) and WUE (–14%), highlighting the negative impact of excessive irrigation.
Environmental and soil factors
Overall, the implementation of any irrigation strategy improved WUE by 14% with only a 1% decrease in yield for sweet cherry.
By contrast, while apple and peach also showed improvements in WUE, their yields decreased, suggesting that sweet cherry is particularly well-suited to water-saving strategies.
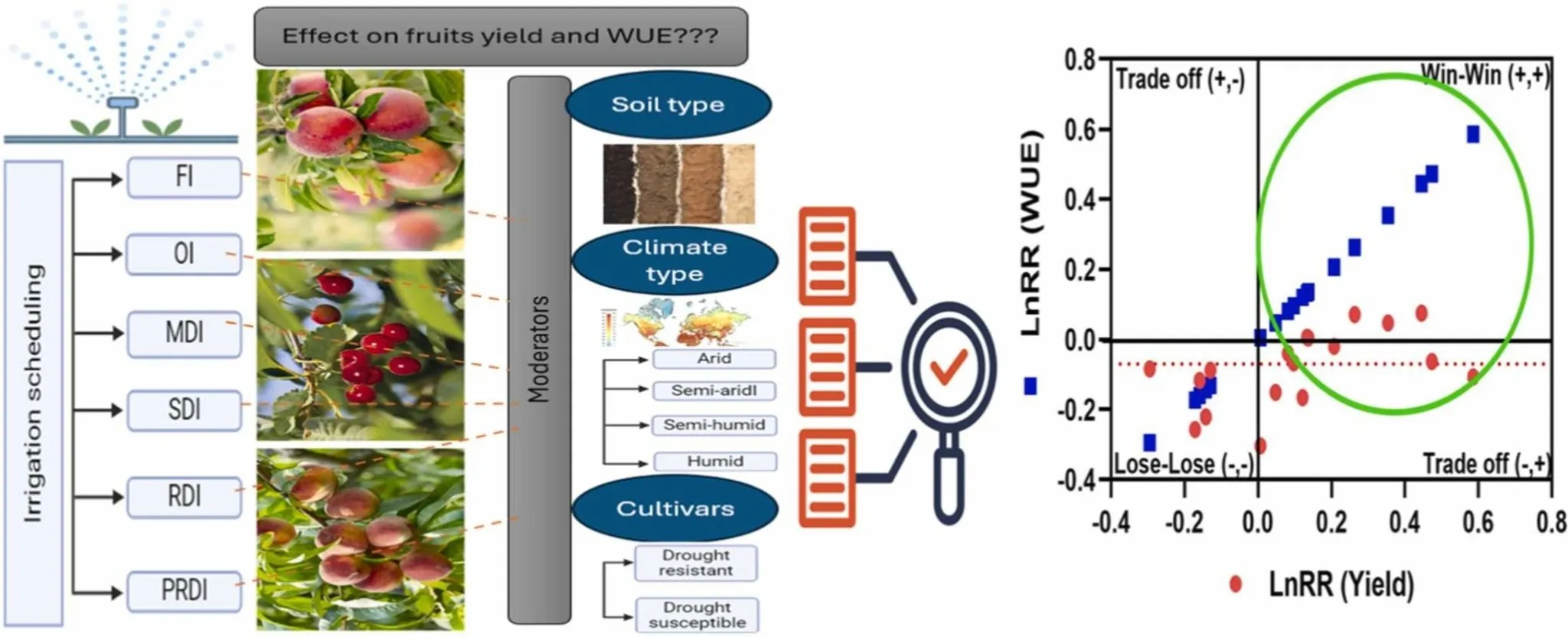 Figure 1. Summary graph of the experimental test. Full irrigation (FI), over irrigation (OI), moderate deficit irrigation (MDI), severe deficit irrigation (SDI), regulated deficit irrigation (RDI) and partial rootzone drying irrigation (PRDI).
Figure 1. Summary graph of the experimental test. Full irrigation (FI), over irrigation (OI), moderate deficit irrigation (MDI), severe deficit irrigation (SDI), regulated deficit irrigation (RDI) and partial rootzone drying irrigation (PRDI).
The effectiveness of these irrigation strategies is modulated by environmental and soil factors.
In semi-humid climates, adopting RDI resulted in a yield increase of up to 13% and a WUE gain of up to 54% in sweet cherry, while in semi-arid climates the benefits were more limited.
Soil type and cultivar response
Soil type also plays a significant role: in clay soils, RDI improved both yield and WUE due to the higher water retention capacity.
In sandy soils, however, there was a greater risk of yield reduction, making more frequent and targeted irrigation necessary.
Different sweet cherry cultivars respond differently to irrigation, but overall, the species has shown strong yield stability under water deficit conditions, along with improvements in WUE, indicating high drought tolerance.
This confirms the potential of sweet cherry as a fruit species suitable for water-saving irrigation strategies.
Conclusions and future perspectives
However, it is crucial to carefully calibrate the intensity and timing of water deficit according to the plant’s phenological stage, soil type, and local climate, in order to avoid negative effects on flowering and fruit set.
Integrating RDI with soil moisture monitoring and plant physiological indicators can enable precision irrigation management tailored to specific conditions and crop requirements.
In summary, optimizing irrigation management through approaches like RDI offers a promising strategy to enhance the sustainable productivity of sweet cherry, maximizing yield per unit of water used and ensuring agricultural system resilience amid declining water availability.
Source: Ali, N., Dong, Y., & Lavely, E. (2024). Impact of irrigation scheduling on yield and water use efficiency of apples, peaches, and sweet cherries: A global meta-analysis. Agricultural Water Management, 306, 109148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2024.109148
Source images: Ali et al., 2024; Omeg Family
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (ITA)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











