High pressure processing to preserve
In the last decade, the need for new fruit product preservation technologies has increased, with the aim to improve and maintain food quality, particularly fresh juices and beverages.
Cherry, thanks to its organoleptic characteristics such as taste, softness, aroma, nutritional value, and health benefits, is a highly appreciated fruit, being also rich in metabolites like polyphenols and anthocyanins.
The weakness of this fruit lies in its high perishability, which is addressed through processing techniques. Generally, products are subjected to thermal pasteurization, but this can reduce its nutritional composition.
On the other hand, high pressure processing (HPP) has emerged as a non-thermal technique that uses hydrostatic pressure (ranging from 100 to 1,000 MPa) to inactivate microorganisms while preserving nutrients, offering a more effective alternative to extend the shelf life of fruit juice.
Cherry juice and its bioactive properties
Its low caloric content, nutrient density, and rich source of antioxidants classify this fruit among so-called superfoods.
Anthocyanins, such as cyanidin-3-glucoside and cyanidin-3-rutinoside, are mainly responsible for the antioxidant activity and have a capacity four times higher than vitamin E, even surpassing the effectiveness of vitamin C in promoting human health.
Therefore, it is important to ensure that preservation treatments protect these beneficial compounds.
The study conducted at the Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, in collaboration with the Department of Physiology and the Department of Applied Chemistry, all located in Lahore (Pakistan), evaluated the impact of high pressure processing and thermal pasteurization on phytochemicals, antioxidant activity, microbial, and sensory characteristics of cherry juice during storage.
Method and results of the study
For the study, cherry juice was subjected to two different high-pressure treatment levels (400 and 600 MPa) for 5 minutes or thermal pasteurization (95 °C) for 30 seconds, followed by storage (60 days at 4 °C).
Results showed that both high pressure and thermal pasteurization had a significant impact on phenolics, flavonoids, and antioxidants compared to the untreated control.
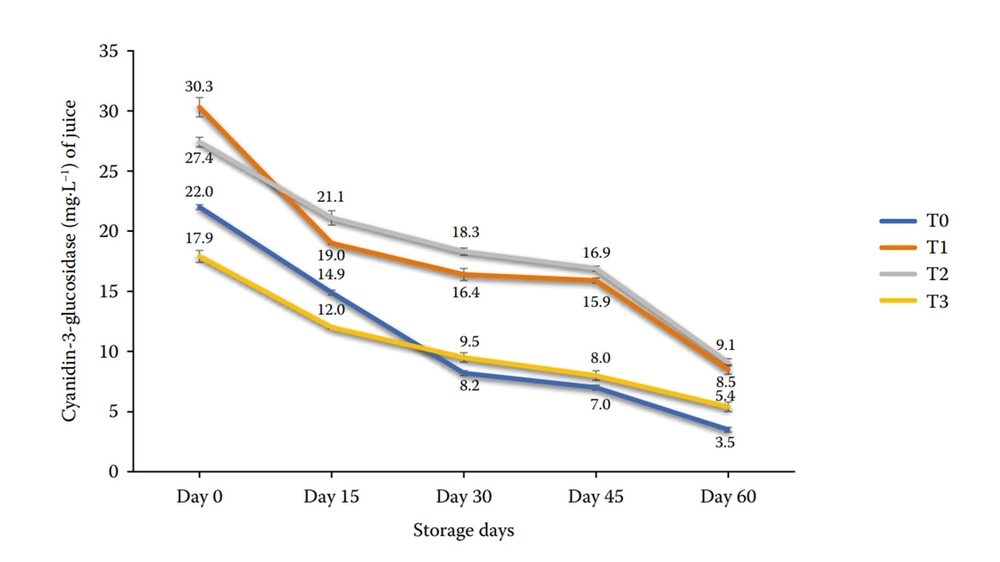 Figure 1. Cyanidin-3-glucosidase (mg·L–1) of sweet cherry juice subjected to high pressure processing and thermal treatment stored at (4 °C) for 60 days.
Figure 1. Cyanidin-3-glucosidase (mg·L–1) of sweet cherry juice subjected to high pressure processing and thermal treatment stored at (4 °C) for 60 days.
However, the thermally pasteurized juice showed rapid deterioration compared to the high-pressure juice, while the levels of anthocyanins and cyanidin-3-glucoside were significantly different between the two groups.
Microbial findings revealed the safety of the high-pressure treated juice with a shelf life of 45 days.
Conclusions and implications
Interestingly, the high-pressure treated juice had better sensory acceptability from consumers.
Ensuring the microbial safety of juices is essential to prevent foodborne illnesses caused by pathogenic microorganisms contaminating products.
This study suggested that both high pressure and thermal pasteurization reduced the initial microbial load to undetectable levels.
Sweet cherry is a rich source of flavonoids like quercetin, which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential.
The study reported an anthocyanin range of 227 to 268 mg per liter as a baseline value.
Furthermore, high pressure at 600 MPa was found to be the most efficient in retaining phenols, flavonoids, and the antioxidant potential of the juice compared to thermal treatment, which is why not only the bioactive profile of the juice was maintained, but also better sensory attributes compared to the thermally treated group.
Source: agriculturejournals.cz
Image Source: Ahamad et al., 2024; Sleep Foundation
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (ITA)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











