Traditional vigorous rootstocks such as Mazzard F 12/1 (Prunus avium L.) and Mahaleb (P. mahaleb L.) produce the first harvest between the fourth and sixth year and reach full production between the eighth and twelfth year, resulting in delayed investment returns.
The cultivation of sweet cherry cultivars on the next generations of semi-dwarfing and dwarfing rootstocks will allow orchards to bear fruit earlier compared to traditional rootstocks.
Early and consistent production of high-quality fruit for fresh consumption. Good flavor and significantly higher income for the new organic cherry orchards.
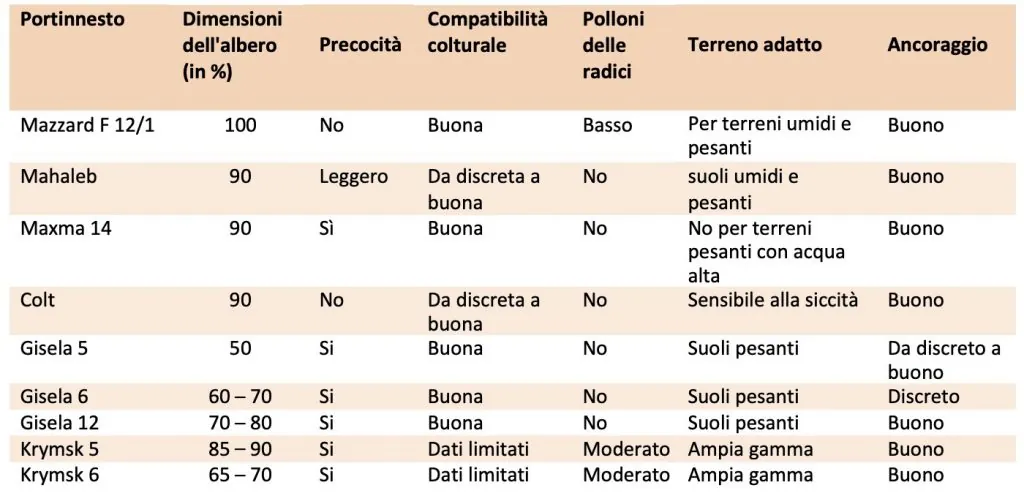 Table 1: Characteristics of traditional and size-controlling cherry rootstocks widely used in organic orchards
Table 1: Characteristics of traditional and size-controlling cherry rootstocks widely used in organic orchards
Practical recommendations
Dwarfing and semi-dwarfing rootstocks reduce tree vigor, induce precocity, improve disease resistance, and allow growers to harvest higher-quality fruit from high-density orchards (Figure 1).
 Figure 1: Rootstock selection focuses on reducing tree size, precocity, and compatibility with the cultivar (Tamara cultivar). Photo: R. Vávra (VSUO).
Figure 1: Rootstock selection focuses on reducing tree size, precocity, and compatibility with the cultivar (Tamara cultivar). Photo: R. Vávra (VSUO).
Dwarfing and semi-dwarfing rootstocks can reach full production in 5–6 years (Figure 2) compared to 8–12 years with traditional rootstocks (Mazzard F 12/1, Mahaleb).
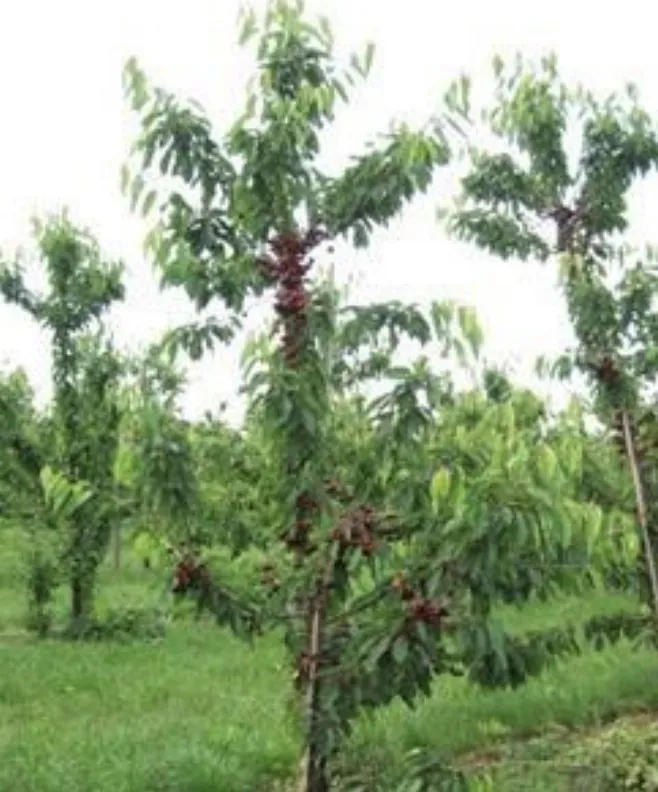 Figure 2: Trees on dwarfing rootstocks begin to bear fruit from the third year. Photo: R. Vávra (VSUO).
Figure 2: Trees on dwarfing rootstocks begin to bear fruit from the third year. Photo: R. Vávra (VSUO).
Tree size depends on soil fertility, selected cultivar, irrigation, site, and pruning.
Support the trees when using Gisela 6 and Gisela 5 rootstocks with stakes to prevent leaning due to weak anchorage (Figure 3).
 Figure 3: Trees on Gisela 5 rootstock require stake support. Photo: R. Vávra (VSUO).
Figure 3: Trees on Gisela 5 rootstock require stake support. Photo: R. Vávra (VSUO).
Management and recommendations
Self-fertile cherry cultivars combined with dwarfing rootstocks result in more regular yields and improved cash flow for newly established orchards.
Avoid the most dwarfing rootstocks (Gisela 5 and Krymsk 6) in shallow and low-fertility soils.
Consult advisors to ensure the size-controlling rootstocks chosen for new plantings are suited to the tree density, soil, and desired climate conditions.
Size-controlling rootstocks make it possible to establish pedestrian orchards with easier and safer management and a more favorable working environment.
Image source: SL Fruit Service
Radek Vávra, Jiří Kaplan, Tomáš Jan
Biofruitnet
Cherry Times – All rights reserved