Nitrogen fertilizer application results in increased tree size and leaf area, but limits flowering intensity. Trees grown in nitrogen-limited environments have reduced rates of photosynthesis, resulting in decreased fruit production and size.
This result stems from the fact that photosynthesis is mainly influenced by leaf area rather than leaf mass. Therefore, to ensure quality production, it is important to know the right amount of nitrogen to apply during the growing season.
The objective of the study conducted by researchers at the University of Poznan (Poland) was to evaluate the effects of different levels of nitrogen fertilization on the concentration of the main chemical elements in both soil and leaves, as well as its influence on specific growth parameters of sour cherry plants
In three orchards, leaf chlorophyll and mineral content in two soil layers and their effects on tree growth were examined. Three levels of fertilization were administered to each orchard: 0, 60 and 120 kg of N ha-1 (N0, N60 and N120, respectively). Nitrogen fertilization at the beginning of the growing season affected soil ammonia and nitrate.
Sour cherry plants probably received enough fertilizer with the N60 dose, but only increasing the dose to N120 significantly increased soil nitrogen content. Sampling after the application of ammonium nitrate at the beginning of the growing season recorded the highest soil nitrogen level.
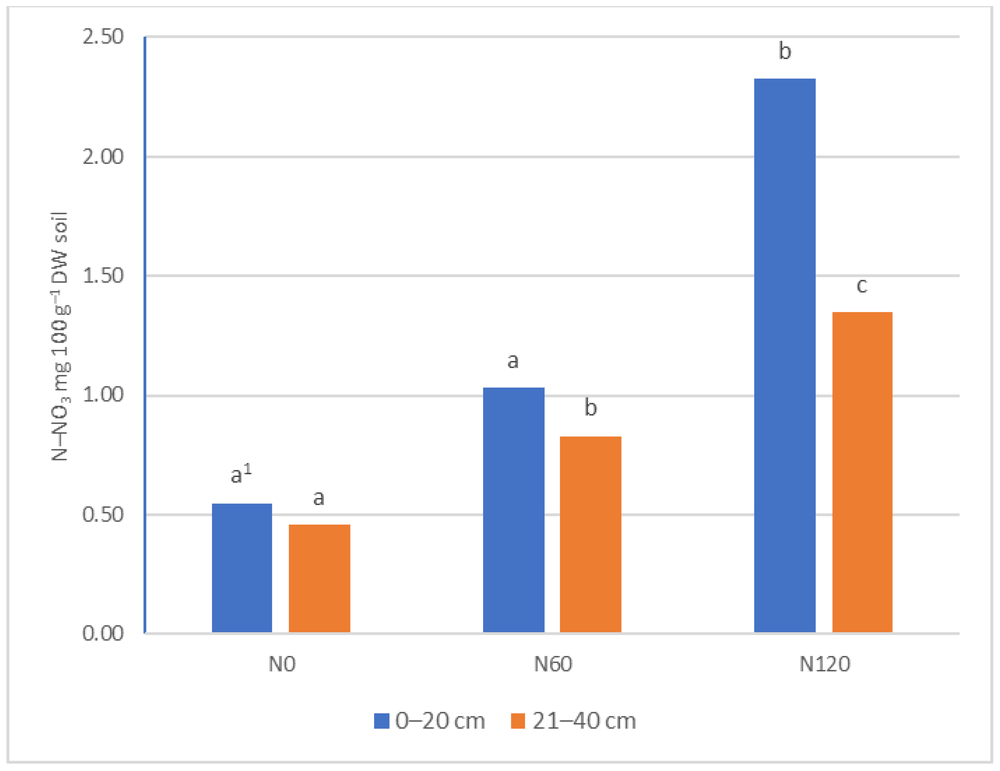 Figure 1: The content of N-NO3 depending on nitrogen fertilization in the soil layer 0–20 cm and- 21–40 cm. Statistical analysis performed separately for each soil level. 1 means that the same letters for each soil level are not significantly different at α = 0.05 (Duncan’s test).
Figure 1: The content of N-NO3 depending on nitrogen fertilization in the soil layer 0–20 cm and- 21–40 cm. Statistical analysis performed separately for each soil level. 1 means that the same letters for each soil level are not significantly different at α = 0.05 (Duncan’s test).
Subsequent sampling dates showed a lower ammonia nitrogen content. The upper soil layer had a similar amount of nitrate in all theses, while the lower layer had a variable nitrate content depending on the sampling date.
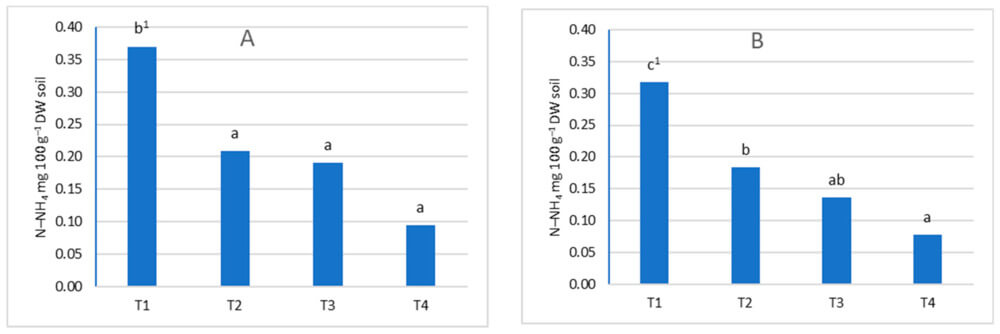 Figure 2: The content of N-NH4 depends on the date of sampling (A)—in the soil layer 0–20 cm, (B)—in the soil layer 21–40 cm. The nitrogen determination: T1—term after flowering trees, T2—term during the intensive fruit growth, T3—term after fruit harvest in August, T4—term after the end of vegetation. 1 means that the same letters are not significantly different at α = 0.05 (Duncan’s test).
Figure 2: The content of N-NH4 depends on the date of sampling (A)—in the soil layer 0–20 cm, (B)—in the soil layer 21–40 cm. The nitrogen determination: T1—term after flowering trees, T2—term during the intensive fruit growth, T3—term after fruit harvest in August, T4—term after the end of vegetation. 1 means that the same letters are not significantly different at α = 0.05 (Duncan’s test).
In addition, soil nitrogen was not affected by orchard age. The arable soil layer had higher nitrogen, but the difference was significant only for ammonium. The K/Mg ratio increased due to high nitrogen fertilization, which increased phosphorus and potassium and lowered magnesium in the upper soil layer.
It also slightly (but not significantly) lowered the pH of the upper soil layer. The lower layer showed similar changes for phosphorus and magnesium. Moreover, soil pH slightly increased after nitrogen fertilization. Nitrogen fertilization increased leaf and trunk cross-sectional area.
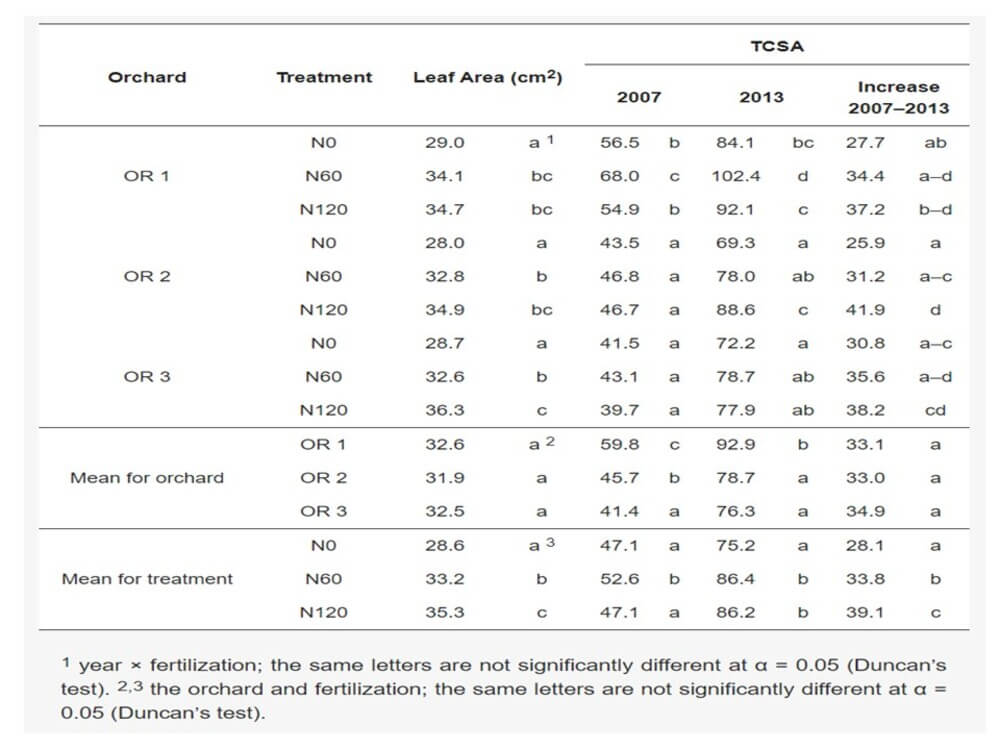 Table 1: The influence of nitrogen fertilization on cherry growth in 2007–2013.
Table 1: The influence of nitrogen fertilization on cherry growth in 2007–2013.
However, nitrogen fertilization did not affect chlorophyll content. In conclusion, the results indicate that 60 kg of nitrogen per hectare is the best dose to provide adequate nutrition for sour cherry trees. Nitrogen supply increased its presence in leaves, while it decreased phosphorus and potassium concentrations. N60 fertilization recorded the highest concentration of magnesium and calcium, while N120 fertilization lowered them due to increased vegetative growth.
Weather conditions, particularly precipitation, which is responsible for leaf growth, influenced chlorophyll content the most. Thus, these results reaffirm that nitrogen fertilization is undoubtedly necessary for good production performance, but it should not exceed in the application.
Source: Rutkowski, K.; Łysiak, G.P. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilization on Tree Growth and Nutrient Content in Soil and Cherry Leaves (Prunus cerasus L.). Agriculture 2023, 13, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030578.
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved













