In recent years, the introduction of advanced biotechnological technologies has led to numerous advancements in the control of Drosophila suzukii, a pest insect that attacks fleshy fruits, causing significant economic losses. Native to East Asia, this species has quickly colonized America and Europe, laying eggs inside the fruits, damaging the flesh and accelerating the decay process.
Traditional management methods have proven insufficient in fully controlling this insect, thus there is a need to develop and adopt innovative strategies, such as those based on genetic manipulation.
One of the most widely studied methods is the “Sterile Insect Technique” (SIT), which involves releasing males sterilized through radiation that are incapable of producing offspring when mating with wild females.
The effectiveness of this technique, which has already been successfully tested on other insects, has been improved through the use of fluorescent markers to monitor competition and sperm transfer. However, sterilization by radiation can reduce insect vitality, thus requiring further refinements for sustainable, long-term control.
Another promising strategy is “X-shredding”, which selectively destroys the X chromosome during spermatogenesis, using CRISPR with a DNA-specific cutting system. This results in a progeny with a strong male bias, which could, over time, reduce the overall population.
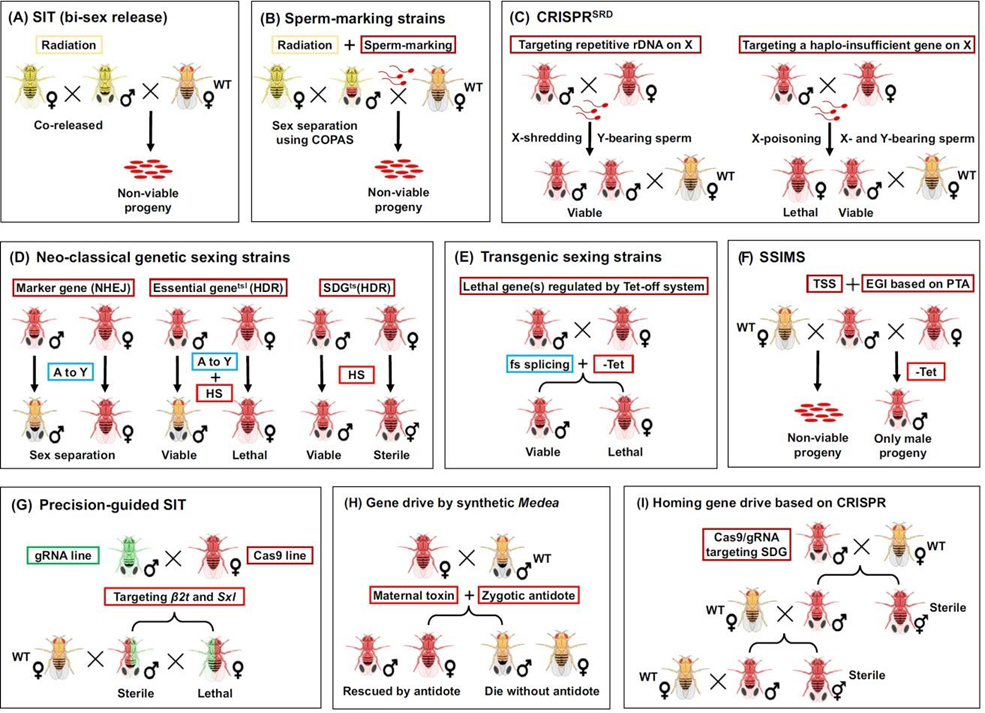 Genetic control strategies for spotted wing Drosophila (SWD). Source: Ying Yan et al., 2024
Genetic control strategies for spotted wing Drosophila (SWD). Source: Ying Yan et al., 2024
Other approaches include the “Transgenic Sexing Strains” (TSSs), which eliminate females through lethal genes activated in the absence of antibiotics like tetracycline. This technique eliminates the need for irradiation and allows the release of exclusively sterile or incompatible males, reducing the presence of egg-laying females.
The “Genetic Sexing Strains” (GSSs) technique, also using CRISPR, enables sex selection and male sterility by manipulating rearing temperatures.
The “gene drive” approach has been proposed for pest control for decades. However, the discovery of new genetic systems has significantly advanced the development of these strategies in parasitic insects like Drosophila suzukii.
These systems promote the spread of specific modified genes, inducing lethality in individuals not carrying the gene. For example, the “Medea” system uses synthetic microRNAs that act at the embryonic level, leading to the death of descendants that do not inherit the resistant version of the gene. Despite its laboratory efficacy, the practical application of this approach requires caution to avoid unwanted ecological effects.
Finally, the “Precision-guided SIT” (pgSIT) leverages CRISPR to eliminate females and sterilize males. Laboratory studies have shown that the continuous release of such insects can lead to a population collapse of Drosophila suzukii in just a few generations, highlighting the potential of this technology. However, the field integration of these genetic solutions requires tools to reduce costs.
The adoption of these innovative strategies will require careful and rigorous assessments to foresee the impact on ecosystems and human health, yet the potential for specific control of Drosophila suzukii is promising. Furthermore, these biotechnological solutions could become a powerful tool for global pest management.
Source: Yan, Y., Ahmed, H. M., Wimmer, E. A., & Schetelig, M. F. (2024). Biotechnology-enhanced genetic controls of the global pest Drosophila suzukii. Trends in Biotechnology.
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











