Controlling species like Drosophila suzukii requires innovative approaches that reduce reliance on synthetic chemical pesticides. Among advanced biocontrol techniques, the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) has proven to be an effective method. By sterilizing male insects, it is possible to gradually decrease harmful insect populations.
Traditionally, the SIT technique is applied to the same target species (homospecific), avoiding risks related to the introduction of new species. However, a recent Italian study analyzed the use of cross-species SIT, which leverages reproductive interference between different species to enhance effectiveness. The goal was to combat Drosophila suzukii, a pest that poses a threat to fleshy fruits such as cherries.
The study examined the use of sterilized Drosophila melanogaster males to interfere with the reproduction of Drosophila suzukii. The concept involves exploiting competition between males of these two species for the same females, taking advantage of incomplete mating barriers.
Experiments showed that male Drosophila melanogaster irradiated with gamma radiation doses between 60 and 80 Gy maintain high sterility without significant reductions in longevity compared to non-irradiated males, making them suitable for field use. Additionally, the sterilized males actively court Drosophila suzukii females with behaviors comparable to non-sterilized ones and successfully mate with them, though without producing offspring.
Tests showed that the number of new Drosophila suzukii individuals significantly decreases in the presence of sterilized Drosophila melanogaster males, regardless of the population ratio between the two species. This suggests that the reproductive interference exerted by sterilized males not only causes unfruitful matings but also produces additional effects that further limit the reproduction of Drosophila suzukii.
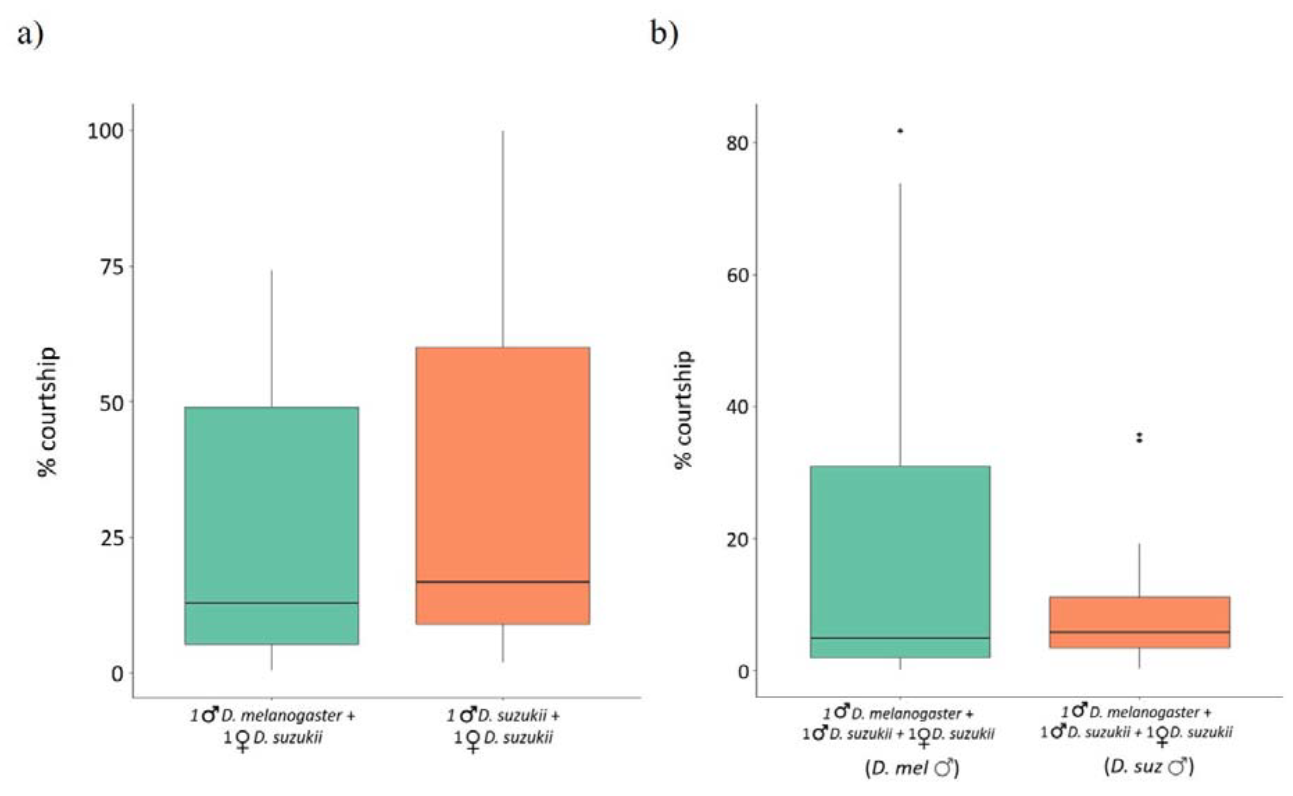 Image 1: Time spent in courting Drosophila suzukii females by D. suzukii and irradiated D. 589 melanogaster males. (a) Percentage of the total time spent courting D. suzukii females by D. 590 melanogaster and D. suzukii males when alone (green and orange column, respectively) 591 Wilcoxon Mann–Whitney test p-value > 0.05. (b) Percentage of the total time spent courting D. 592 suzukii females by D. melanogaster and males D. suzukii when placed together (green and 593 orange columns, respectively) Wilcoxon Mann–Whitney test p-value > 0.05. Source: Cerasti et al., 2024.
Image 1: Time spent in courting Drosophila suzukii females by D. suzukii and irradiated D. 589 melanogaster males. (a) Percentage of the total time spent courting D. suzukii females by D. 590 melanogaster and D. suzukii males when alone (green and orange column, respectively) 591 Wilcoxon Mann–Whitney test p-value > 0.05. (b) Percentage of the total time spent courting D. 592 suzukii females by D. melanogaster and males D. suzukii when placed together (green and 593 orange columns, respectively) Wilcoxon Mann–Whitney test p-value > 0.05. Source: Cerasti et al., 2024.
Among these factors, it is hypothesized that Drosophila melanogaster males release repellent substances during courtship, such as cis-vaccenyl acetate, which deters Drosophila suzukii females from laying eggs. Furthermore, during mating, Drosophila melanogaster males may introduce substances in their seminal fluid that reduce the females' tendency to remate with other males of their own species.
This study demonstrates how sterilized Drosophila melanogaster males can induce effective reproductive interference in Drosophila suzukii without the risks associated with introducing foreign species. Drosophila melanogaster does not pose a threat to crops, as it only lays eggs on decaying fruit.
Additionally, using Drosophila melanogaster in a cross-species SIT technique offers practical advantages; indeed, the extensive biological knowledge of this species, as a model organism, could enable further optimization of SIT programs.
In conclusion, the adoption of systems like cross-species SIT represents a new paradigm of integrated biological control that could change the management of invasive species such as Drosophila suzukii, with promising applications on a broader scale.
Source: Cerasti, F., Cristofaro, M., Mastrantonio, V., Scifo, J., Verna, A., Canestrelli, D., & Porretta, D. (2024). Can reproductive interference be integrated into the Sterile Insect Technique for pest control? Insights from the spotted wing fly Drosophila suzukii. bioRxiv, 2024-09. PREPRINT. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.05.611447.
Images: EPPO gd; Cerasti et al., 2024.
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











