The systematic Sweet Cherry Breeding in Germany dates to the first work of R. Nebel and C.F. Rudloff in Müncheberg in 1928. After the Second World War, this work was continued by M. Schmidt in Müncheberg until 1955.
In 1953 E.L. Loewel, E.v. Vahl and F.-G. Zahn started a new breeding program in Jork. As a result, the cultivars 'Alma', 'Annabella', 'Bianca', 'Erika', 'Oktavia', 'Regina', 'Valeska', and 'Viola' were selected. From 1985 to 1999 the program was continued by H. Schmidt in Ahrensburg.
A second breeding programme was started in Naumburg by H. Mihatsch and M. Fischer in 1958 and continued in Dresden-Kauscha from 1971 to 1990. The released cultivars from this program are 'Namare', 'Namosa', 'Naprumi', 'Namati', and 'Nadino'. After both breeding programs were terminated, the plant material was transferred to Dresden-Pillnitz, where sweet cherry breeding has been continued by M. Schuster since 2001.
Seven new cultivars have already been released: 'Narana', Swing® 'PiSue 192', 'Habunt', 'Areko', 'Polka', Aria® 'PiSue 161', and 'PiSue 177'. Nineteen new promising breeding clones are currently under multi-site testing and approximately 100 clones are in stage II evaluation. The main breeding objectives are fruit quality, like size, firmness, sugar content, high productivity, self-fertility, and high resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
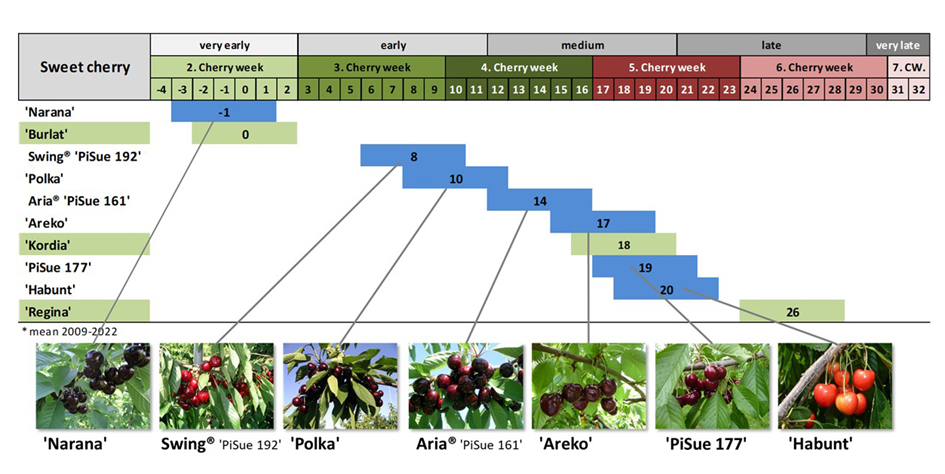 Image 1: Ripening time - JKI sweet cherry cultivars in comparison to cultivars 'Burlat', 'Kordia', and 'Regina'.
Image 1: Ripening time - JKI sweet cherry cultivars in comparison to cultivars 'Burlat', 'Kordia', and 'Regina'.
Mirko Schuster
Institute for Breeding Research on Fruit Crops, Julius Kühn-Institut (JKI) – Federal Research Centre for Cultivated Plants, D-01326 Dresden (DE)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











