Drosophila suzukii lays eggs in fresh mature fruits, compromising their quality and promoting secondary infections, making it a major threat to fruit cultivation. Traditional control methods include low-temperature treatments and insecticide fumigation, but their effectiveness and mechanisms of action are not yet fully understood.
A recent study from Korea analyzed the combined effect of ethyl formate (EF) and cold treatment on this invasive species, focusing on metabolic alterations to better understand their impact on insect physiology.
Ethyl formate is a naturally occurring volatile compound with insecticidal properties that acts quickly and leaves no residues. However, its effectiveness is limited by its low tissue penetration and the need for high concentrations.
On the other hand, low-temperature treatments are commonly used in fruit export and quarantine processes, proving effective in pest control without compromising fruit quality. The combination of these two approaches appears to enhance insecticidal effects, but the biochemical mechanisms underlying this synergy had not been clarified.
Through a comparative metabolomic analysis, researchers identified the main metabolic pathways altered by the combined treatment. A significant impact was observed on the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, which is involved in energy production, and on purine and pyrimidine synthesis, essential for nucleic acid metabolism.
Additionally, detoxification-related metabolites such as cytochrome P450 and glutathione underwent significant variations, indicating an intense stress response.
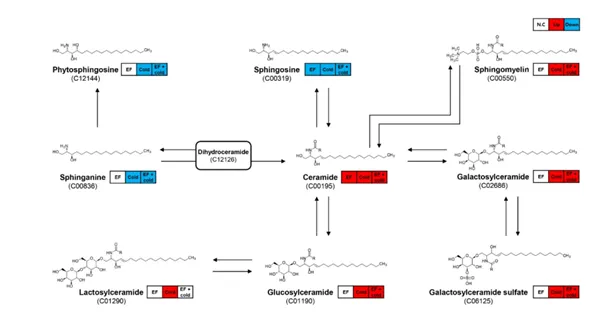 Image 1: Pathway analysis of sphingolipid metabolism. Overregulated and underregulated lipids are indicated by red and blue lines, respectively. The numbers represent KEGG IDs. Source: Junbeom Lee et al., 2024.
Image 1: Pathway analysis of sphingolipid metabolism. Overregulated and underregulated lipids are indicated by red and blue lines, respectively. The numbers represent KEGG IDs. Source: Junbeom Lee et al., 2024.
Ethyl formate treatment showed clear inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase, the final enzyme in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, leading to the accumulation of Krebs cycle intermediates and a reduction in Drosophila’s energy efficiency.
Conversely, cold exposure stimulated glycolytic metabolism, enhancing energy production in response to thermal stress. Moreover, the combined treatment increased sphingolipid synthesis, which is crucial for cell membrane integrity and the insect's immune response.
A reduction in flavin mononucleotide (FMN), an essential cofactor for P450 oxidoreductase, a key enzyme in detoxification processes, was also observed. This reduction could compromise Drosophila’s ability to withstand environmental and chemical stresses, increasing the lethality of the combined treatment.
Finally, a significant alteration in glutathione disulfide (GSSG) levels, a marker of oxidative stress, was detected, suggesting that the joint action of ethyl formate and cold generates a strong redox imbalance in the insect’s cells.
These findings open new perspectives for the eco-friendly management of Drosophila suzukii. The combination of ethyl formate and low temperatures has proven to be an effective and sustainable strategy for controlling this harmful insect.
A deeper understanding of the metabolic mechanisms involved allows not only the optimization of current treatments but also the development of new targeted strategies, minimizing environmental impact. Finally, this study provides valuable data for improving quarantine practices and identifying biomarkers useful in evaluating treatment efficacy.
Source: Lee, J., Kim, H. K., Jeon, J. C., Seok, S. J., Kim, G. H., Koo, H. N., & Lee, D. W. (2024). Metabolite changes by combined treatment, ethyl formate and low temperature, in Drosophila suzukii. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 25948. https://doi-org/10.1038/s41598-024-77436-0.
Images: Entomology Today; Junbeom Lee et al., 2024.
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











