Fruit cracking is a common physiological disorder in many sweet cherry-growing regions. It occurs when rain and/or high humidity concentrate in the period leading up to harvest, wetting the fruit’s surface. Water from rain, fog, cold exposure, or dew formation can cause the pericarp to split, damaging the fruit and leading to significant production losses.
With ongoing climate change, the risk of cracking is further amplified, making it increasingly necessary to find solutions to monitor and prevent this occurrence.
A recent study by German researchers introduces a new methodology based on the use of close-range remote sensing (CRRS) to monitor the temperature of sweet cherry fruit. Using LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, combined with thermal imaging, they were able to create 4D point clouds representing the fruit with temperature annotations.
This approach allowed the researchers to study the temperature distribution in sweet cherry orchards and model the formation and persistence of wetness on the fruit's surface. Surface wetness is, in fact, one of the main factors contributing to cracking, and understanding its spatial and temporal distribution is essential for developing mitigation strategies.
The study’s results show that cracking is not necessarily linked to water absorption but rather to the duration of wetness presence on the fruit surface. Temperature models obtained through LiDAR 4D revealed that sweet cherry tree canopy density has a marginal impact on wetness formation.
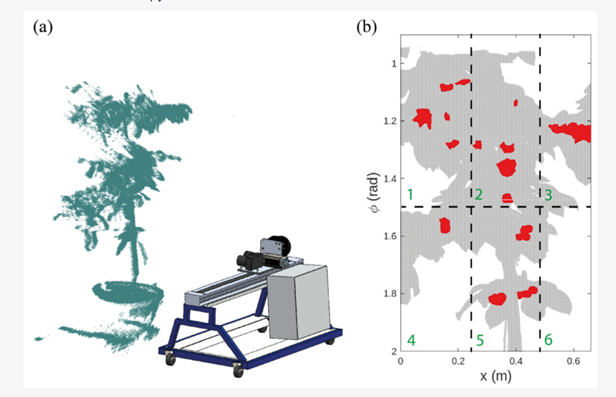 Image 1: (a) Multisensor platform and example raw 3D point cloud of a cherry canopy. (b) Example of a scanned cherry tree (T5) with delimited spatial locations (1 to 6). ϕ is the polar angle with respect to the LiDAR position, ranging from 0 to π from the top to the bottom of the canopy. Fruit clusters marked in red were distributed in the six locations. Source: Tapia-Zapata et al., 2024.
Image 1: (a) Multisensor platform and example raw 3D point cloud of a cherry canopy. (b) Example of a scanned cherry tree (T5) with delimited spatial locations (1 to 6). ϕ is the polar angle with respect to the LiDAR position, ranging from 0 to π from the top to the bottom of the canopy. Fruit clusters marked in red were distributed in the six locations. Source: Tapia-Zapata et al., 2024.
However, monitoring surface temperatures made it possible to identify when the fruit approaches or exceeds the dew point, a key indicator of potential wetness formation. The study found that when the dew point threshold index (Ydew) exceeds a value of 1.17, no wetness forms on the fruit’s surface.
Temperature monitoring using this technology allowed the development of a predictive model for wetness formation, which can be applied in ecological studies to improve plant resilience to climate change. Furthermore, the ability to collect spatially precise data at the fruit level offers new opportunities to predict and consequently reduce sweet cherry cracking damage, improving production quality and minimizing losses.
In conclusion, the application of techniques like CRRS and LiDAR for temperature modeling in sweet cherry orchards represents an interesting development in cracking control solutions. This technology enables real-time fruit surface monitoring, identifying wetness formation risks, and potentially contributing to the development of integrated models to reduce cracking damage across the entire orchard.
Source: Tapia-Zapata, N., Winkler, A., & Zude-Sasse, M. (2024). Occurrence of Wetness on the Fruit Surface Modeled Using Spatio-Temporal Temperature Data from Sweet Cherry Tree Canopies. Horticulturae, 10(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070757.
Image: SL Fruit Service
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











