Cherries are highly valued for their sweet flesh. Undoubtedly, this attribute and the particular characteristics of this fruit make it one of the most susceptible fruits to cracking due to rainfall. In the following paragraphs, researchers from the Universidad de Talca address the causes of this issue and some prevention strategies.
Each season, cracking poses a threat to the harvest, potentially leading to complete production loss if rains occur during the advanced stages of fruit ripening. According to Fedefruta estimates, the October and November rains of the 2023/24 season caused a 50% reduction in early cherry varieties' production, particularly affecting the O'Higgins region and the province of Curicó. Damaged fruits cannot be marketed due to their rapid susceptibility to developing diseases, resulting in significant reductions in orchard income.
Physiological aspects
The specific mechanisms involved in cherry cracking are still under discussion. Currently, one of the most accepted hypotheses is that proposed by the Agricultural Production Systems Institute at the University of Hannover in Germany, which suggests a “zipper model”, where fruit cracking occurs similarly to the opening of a zipper on clothing (Figure 2).
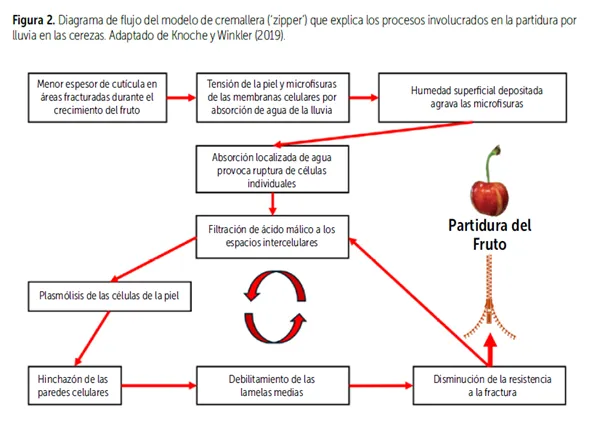 Figure 2: Flow diagram of the zipper model explaining the processes involved in rain-induced cracking in cherries. Adapted from Knoche and Winkler (2019).
Figure 2: Flow diagram of the zipper model explaining the processes involved in rain-induced cracking in cherries. Adapted from Knoche and Winkler (2019).
During rainfall, deposited water moves toward the fruit through microfractures in the cuticle generated during growth. Absorption occurs due to the high osmotic potential difference between the flesh and rainwater. This leads to a rapid volume increase in some epidermal cells, causing various tensions within the fruit structure. When rainfall is heavy, water absorption in the cells can lead to membrane rupture, releasing malic acid into the apoplast, which solubilizes calcium bound to cell walls, weakening their integrity and adhesion between cells.
This causes tissue separation between cell walls, prolonging the partitioning as water absorption continues. Studies conducted by the Pomáceas Center have established that a fruit volume increase between 2.0% and 2.5% is sufficient to cause fruit cracking...
Want to read the full article? Sign up for our free Cherry Times newsletter! This is the only way to receive each new article directly in your inbox and stay updated with high-quality advice and analysis. Don't miss this unique opportunity!
Sign up for the Cherry Times newsletter for free!
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











