Fruit firmness is a highly valued characteristic among sweet cherry consumers, as it is associated with freshness.
Additionally, greater firmness leads to better shelf life and resistance to handling.
One of the most common strategies to enhance this trait is the use of gibberellic acid (GA), a phytohormone that influences the growth and development of plant tissues.
Study on “Bing” and “Lapins” cultivars
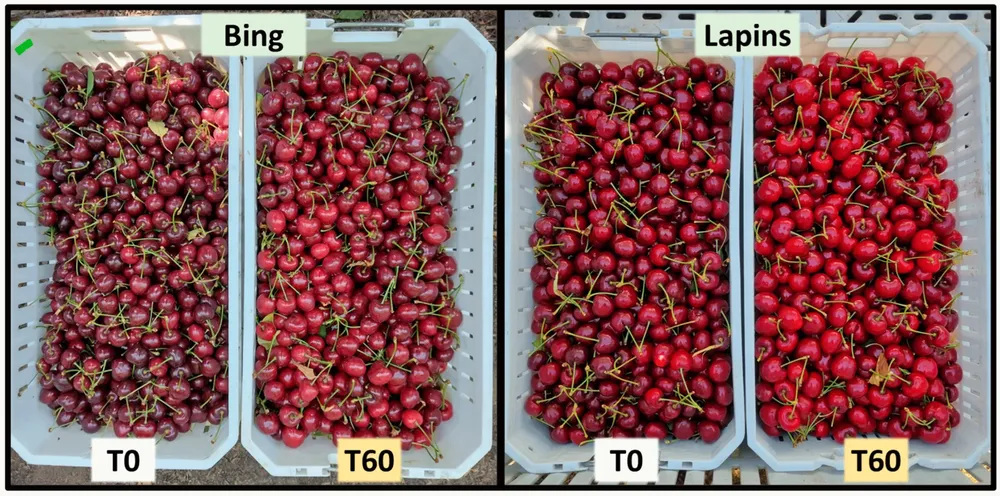 Figure 1. Colour expression of sweet cherry, cv. ‘Bing’ and ‘Lapins’, at 77 and 79 days after full bloom, respectively, for fruit treated with GA. T0: control and T60: GA at 30 ppm applied at pit-hardening and straw-colour stages.
Figure 1. Colour expression of sweet cherry, cv. ‘Bing’ and ‘Lapins’, at 77 and 79 days after full bloom, respectively, for fruit treated with GA. T0: control and T60: GA at 30 ppm applied at pit-hardening and straw-colour stages.
A recent study analyzed the effects of gibberellic acid on the rheological properties of sweet cherries, particularly in “Bing” and “Lapins” cultivars, both at harvest and after 35 days of storage at 0°C, evaluating resistance to mechanical damage during handling and storage.
The study tested different application rates (15, 20, 25, 30 ppm) and timing.
The application of gibberellic acid resulted in a 2–4 days delay in fruit ripening compared to untreated cherries and led to a significant increase in fruit size and weight in “Lapins,” thereby enhancing yield, while no appreciable differences were observed in “Bing.”
Effects on fruit structure and resistance
The use of gibberellic acid also affected the mechanical characteristics of the sweet cherries: regardless of the applied concentration, it increased the modulus of elasticity and fruit resistance both at harvest and after storage.
This means that treated cherries were firmer and more resistant, a feature that can reduce the risk of bruising and damage during transport and sale.
The beneficial effects of gibberellic acid on fruit structure were maintained even after a long period of cold storage and three days of exposure to 15°C, simulating commercial conditions.
Pros and cons of gibberellic acid
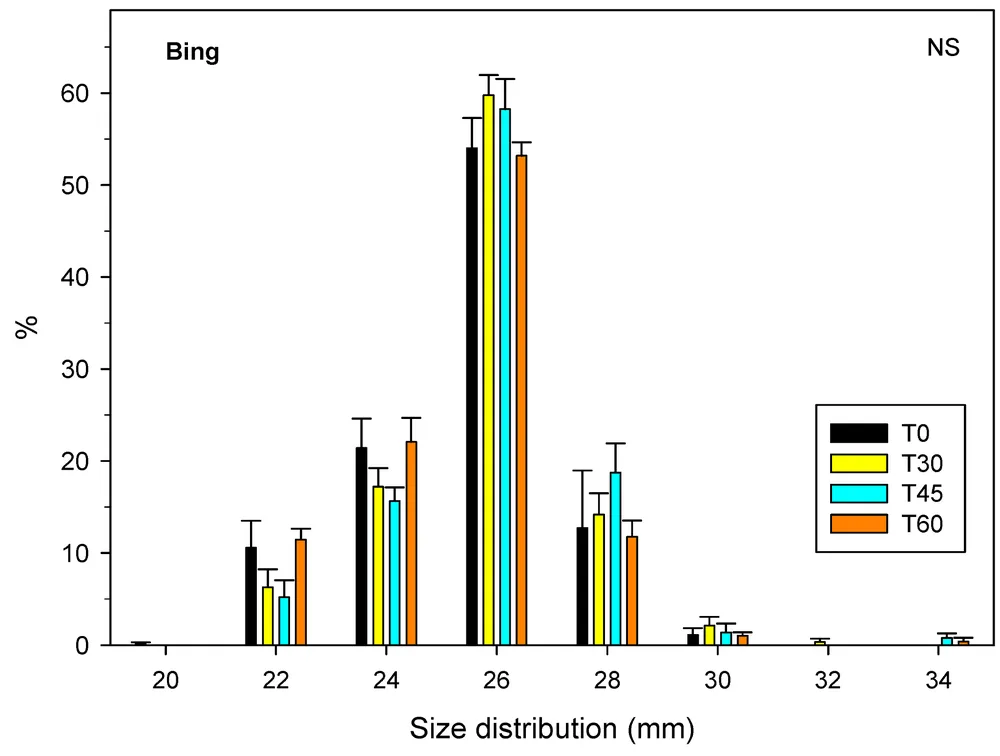
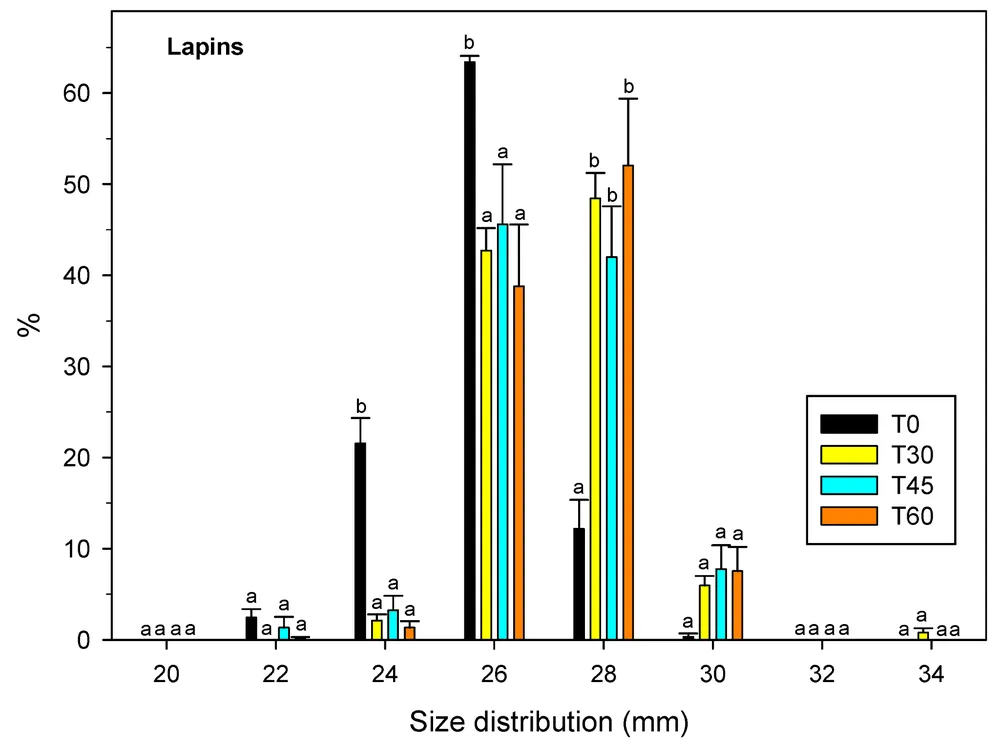 Figure 2A-B. Fruit size distribution at harvest for cv. ‘Bing’ and ‘Lapins’ sweet cherries depends on the rate of gibberellic acid (GA) application. Treatments: T0 (control), 0 ppm GA; T30, 15 + 15 ppm GA (pit-hardening + straw-colour); T45, 25 + 20 ppm GA (pit-hardening + straw-colour); T60, 30 + 30 ppm GA (pit-hardening + straw-colour). Different letters for each size show significantly different mean values for Fisher’s LSD test, with p-value < 0.05. NS: non-significant at p-value < 0.05.
Figure 2A-B. Fruit size distribution at harvest for cv. ‘Bing’ and ‘Lapins’ sweet cherries depends on the rate of gibberellic acid (GA) application. Treatments: T0 (control), 0 ppm GA; T30, 15 + 15 ppm GA (pit-hardening + straw-colour); T45, 25 + 20 ppm GA (pit-hardening + straw-colour); T60, 30 + 30 ppm GA (pit-hardening + straw-colour). Different letters for each size show significantly different mean values for Fisher’s LSD test, with p-value < 0.05. NS: non-significant at p-value < 0.05.
Therefore, GA treatment increased resistance without increasing tissue deformability and even reduced it, making the fruit stiffer during storage under high humidity conditions.
However, this may make them more susceptible to epidermal fractures, which warrants further investigation, especially for cultivars naturally prone to "box-cracking" during storage.
The study also found that more mature sweet cherries (color 3.5) were less sensitive to mechanical damage than less mature fruit (color 3.0).
This effect is due to an increase in tissue deformation capacity, making the fruit more resistant to external pressure and reducing visible damage.
Conclusions and practical applications
In conclusion, the results confirmed that gibberellic acid is an effective tool for improving the quality and firmness of sweet cherries, with positive effects that persist during and after storage.
However, its application must be carefully calibrated based on the variety and storage conditions to balance the benefits on fruit texture and the risk of possible side effects, such as excessive rigidity.
Optimizing the use of gibberellic acid can provide significant advantages for both producers and distributors, ensuring a high-quality product until consumption.
Source: Carrión-Antolí, A., Zoffoli, J. P., Serrano, M., Valero, D., & Naranjo, P. (2024). Preharvest Gibberellic Acid Treatment Increases Both Modulus of Elasticity and Resistance in Sweet Cherry Fruit (cv. ‘Bing’ and ‘Lapins’) at Harvest and Postharvest During Storage at 0° C. Agronomy, 14(11), 2738. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112738
Images: Carrión-Antolí et al., 2024
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna
Cherry Times - All rights reserved













