Microbial antagonists for the biocontrol
Post-harvest losses of fruits and vegetables are a major global issue and are often caused by rots induced by pathogenic fungi. Traditionally, the defense against these diseases relies on the use of synthetic fungicides, but growing environmental and health concerns are promoting the search for more eco-friendly alternatives.
Among the most promising strategies is the use of antagonistic microbial agents (i.e. microorganisms that counteract the development of pathogenic fungi), in combination with sodium bicarbonate, a low-impact compound already widely used in the food industry.
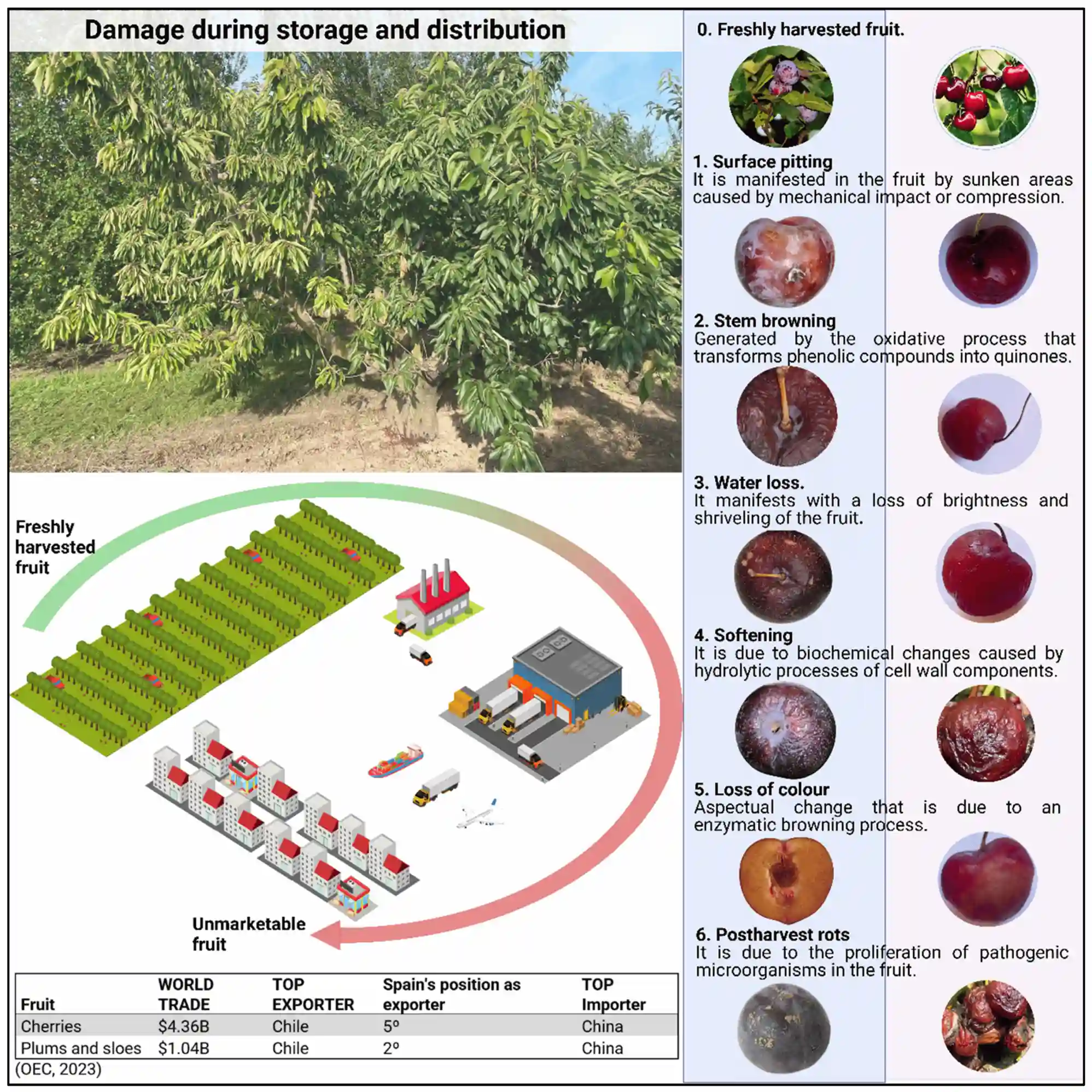 Figure 1. Factors contributing to the deterioration of plums and cherries before they reach the market.
Figure 1. Factors contributing to the deterioration of plums and cherries before they reach the market.
A recent study from Spain evaluated the effectiveness of four yeasts (Cryptococcus laurentii, Trichosporon pullulans, Hanseniaspora uvarum, and Pichia guillermondii) and two bacteria (Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas syringae) against the main fungi responsible for post-harvest rots in sweet cherries and plums.
Study on cherries and plums
In particular, the study analyzed the cultivars “Sweethearts” (cherry) and “Angeleno” (plum). The treatments were tested both in situ, directly on the fruit, and in vivo, simulating storage and distribution conditions.
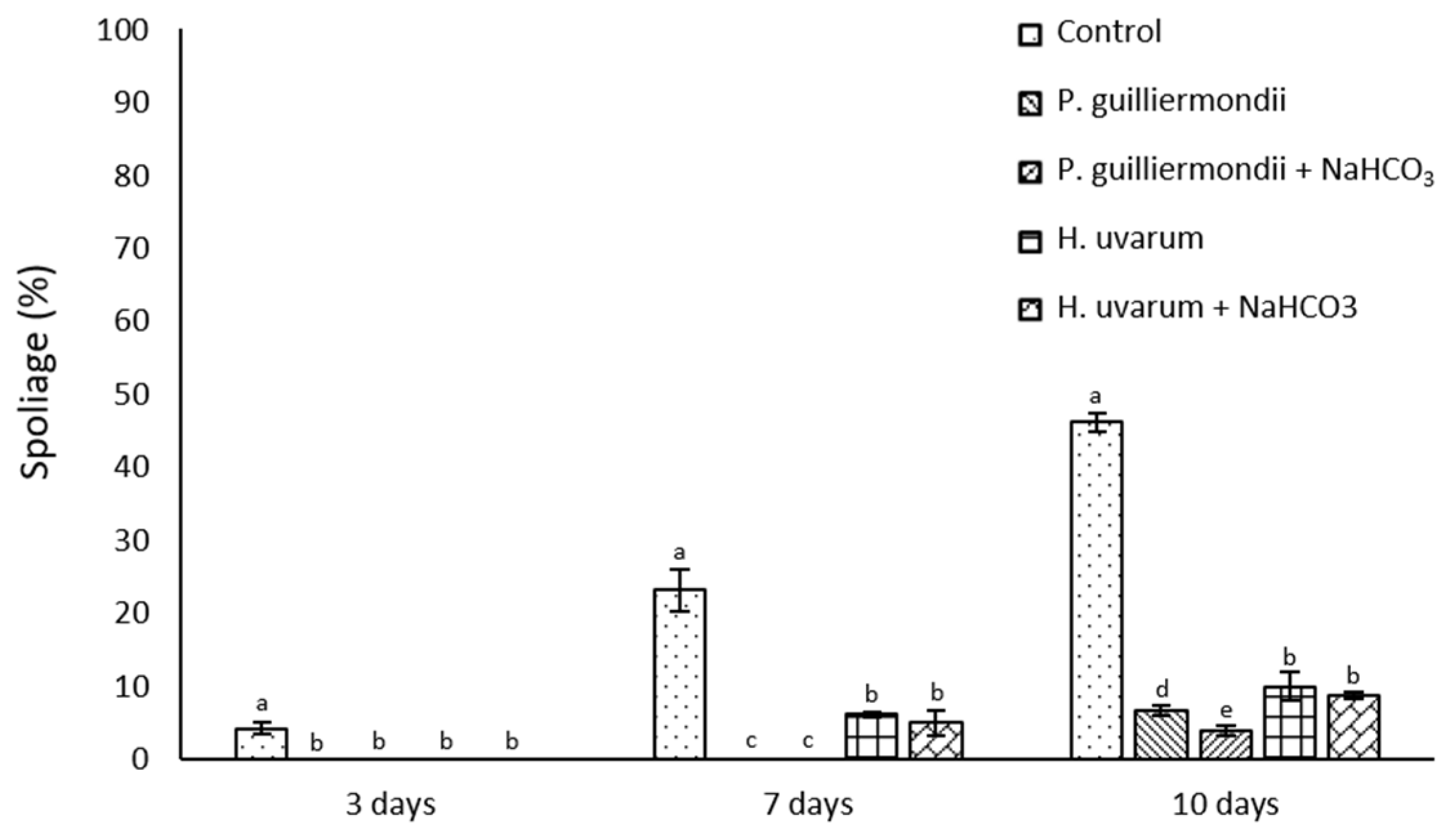 Figure 2. Influence of different inoculation concentrations of microbial antagonists (H. uvarum and P. guillermondii), either alone or in combination with sodium bicarbonate, on post-harvest sweet cheery under optimal conditions to induce biotic damage (25 °C and 90–100% HR). Means ± SD presented in each bar followed by the same letters are not significantly different (Tukey’s test, p < 0.05).
Figure 2. Influence of different inoculation concentrations of microbial antagonists (H. uvarum and P. guillermondii), either alone or in combination with sodium bicarbonate, on post-harvest sweet cheery under optimal conditions to induce biotic damage (25 °C and 90–100% HR). Means ± SD presented in each bar followed by the same letters are not significantly different (Tukey’s test, p < 0.05).
Results showed that the yeasts P. guillermondii and H. uvarum had an effective protective action, especially when combined with sodium bicarbonate, inhibiting the development of pathogens such as Monilinia laxa and Botrytis cinerea, which cause brown rot and gray mold, respectively.
In the in situ tests, the synergistic effect between the antagonists and sodium bicarbonate proved particularly effective. This effect can be attributed to the bicarbonate’s ability to alter osmotic pressure, weakening fungal cell structures and thus enhancing the action of the antagonistic yeasts.
Effects of sodium bicarbonate
Furthermore, the combined use of bicarbonate (at 2%) improved fruit storage, maintaining its organoleptic properties and extending shelf life. However, in in vivo tests, simulating real transport and storage conditions, the efficacy of the combination did not reach the same levels observed in in situ tests, indicating the need for further studies to optimize practical applications of this method.
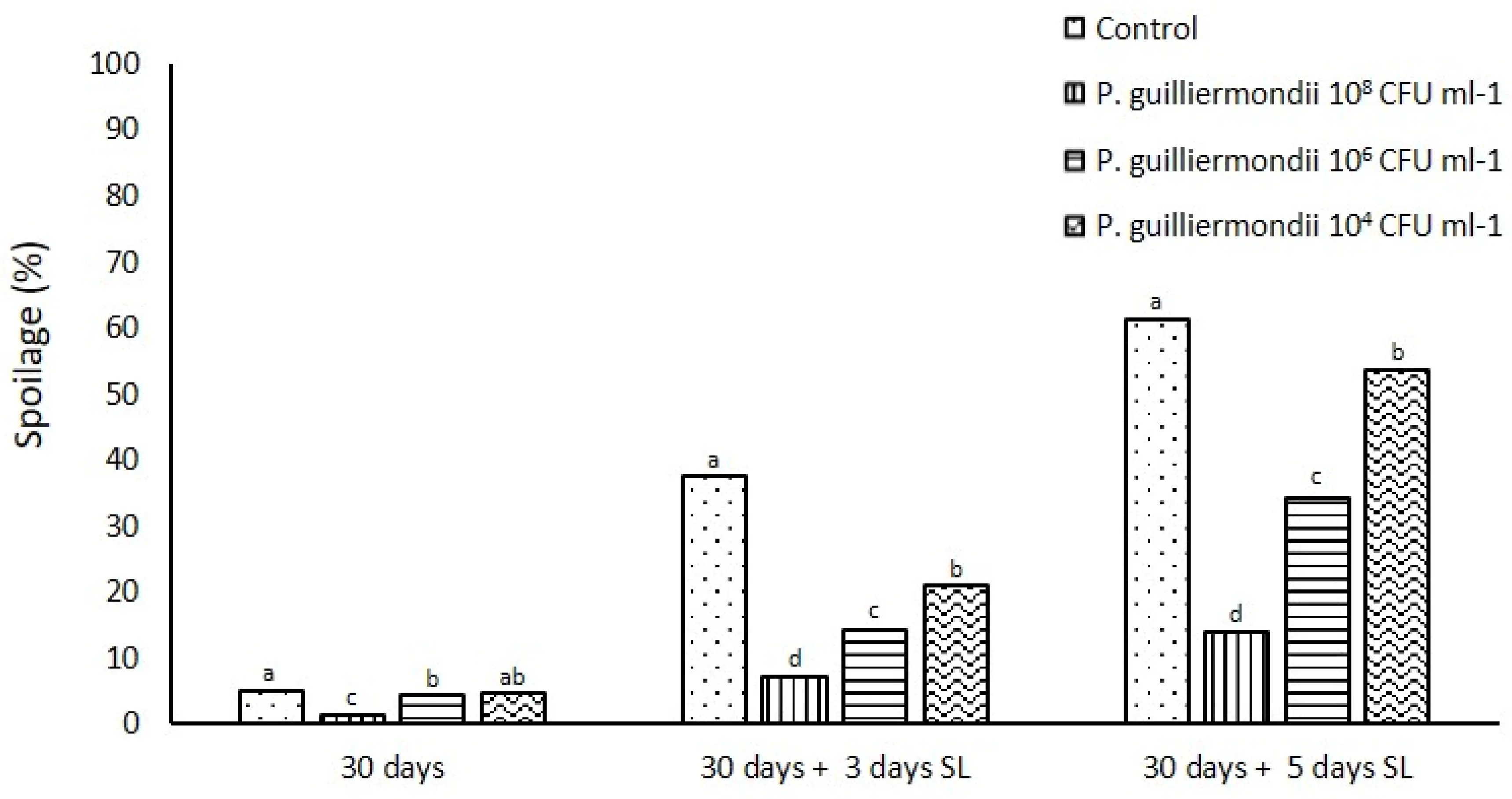 Figure 3. Influence of different inoculation concentrations of P. guilliermondii antagonist on post-harvest sweet cheery at refrigeration temperature (0 °C). Means ± SD presented in each bar followed by the same letters are not significantly different (Tukey’s test, p < 0.05).
Figure 3. Influence of different inoculation concentrations of P. guilliermondii antagonist on post-harvest sweet cheery at refrigeration temperature (0 °C). Means ± SD presented in each bar followed by the same letters are not significantly different (Tukey’s test, p < 0.05).
The concentration of microbial antagonists is an important factor. To ensure effective control of fungal infections, it is essential that the microbial population on the fruit surface is sufficiently dense to suppress pathogen development.
The tests showed that high concentrations of P. guillermondii significantly reduced the rate of cherry decay during marketing, while lower concentrations were less effective. Additionally, the use of preharvest treatments could represent an even more effective strategy to improve post-harvest disease control.
Prospects and limitations
Therefore, the combination of sodium bicarbonate and antagonistic microorganisms appears to be a promising alternative to synthetic fungicides for managing post-harvest diseases in cherries and plums. This strategy offers several advantages, including lower environmental impact, reduced likelihood of pathogen resistance development, and greater consumer acceptance.
However, for large-scale application, further studies are needed to assess the stability and effectiveness of these treatments under real operating conditions, as well as to fully understand the modes of action of the antagonistic microorganisms and the potential impact of antimicrobial metabolites (although generally considered negligible).
Source: Navajas-Preciado, B., Rocha-Pimienta, J., Martillanes, S., Galván, A., Izaguirre-Pérez, N., & Delgado-Adámez, J. (2024). Application of Microbial Antagonists in Combination with Sodium Bicarbonate to Control Post-Harvest Diseases of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) and Plums (Prunus salicina Lindl.). Applied Sciences, 14(23), 10978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142310978
Image source: Navajas Preciado et al., 2024; SL Fruit Service
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (ITA)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved













