Tommaso Pantezzi - Fondazione E. Mach (IT)
Cherry Times technical-scientific committee
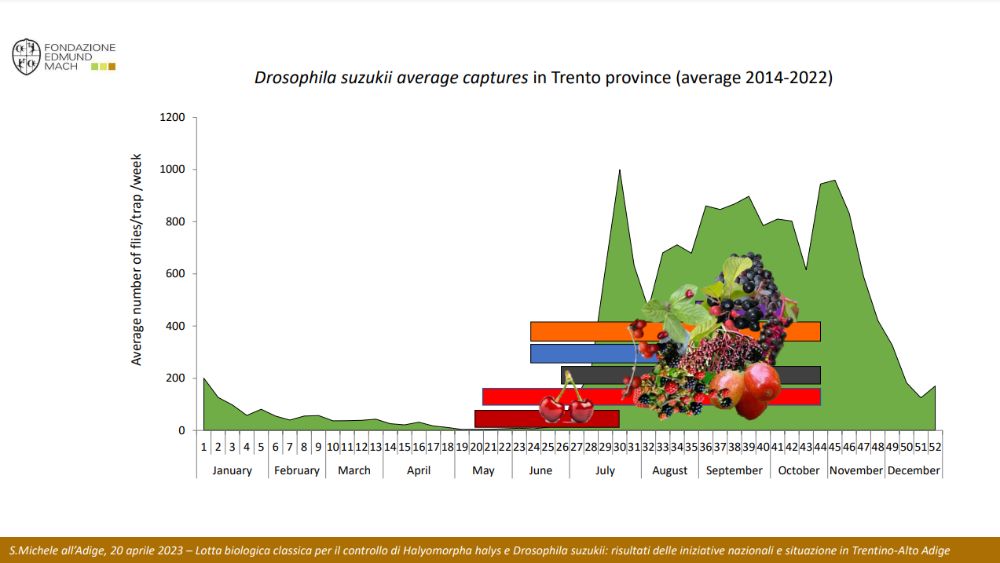
In the last decade, D. suzukii has been rapidly spreading across many countries comprised the North American mainland and Europe, after being first detected in 2008 in both California and Spain. More recently, it settled also in South America. Although a wide range of cultivated and wild soft-skinned fruits can serve as host berries, (particularly raspberries and blueberries), sweet cherries have shown a great host potential.
After making its appearance in 2009 in Trentino, Northeast Italy, D. suzukii rapidly spread across the territory of the province, quickly becoming the key pest for cherry growing. In Trentino, D. suzukii finds a very suitable situation due to climate and the presence of many cultivated and spontaneous host berries.
In Trentino the sweet cherries, are produced on a modest area (250 ha), but of high quality and very profitable, thanks also to the use of highly specialized cultivation techniques with dwarfing rootstocks and rain covers.
Unfortunately, the enormous biological potential manifested by D. suzukii and the scarce effectiveness of the insecticide treatments adopted by the producers as a first reaction, put the cherry production system in serious crisis. For this reason, researchers and experimenters at the E. Mach Foundation (FEM) are still working to provide as quickly as possible, effective and sustainable control techniques.
The integration of agronomic and sanitation practices besides to the chemical protection can create an unfavourable environment for the phytophagous limiting its presence. Some agronomic practices, such as the aeration of the canopy, grass mowing, avoiding any water stagnation, a rapid harvest schedule, removing the infested fruits from the crop are recommended.
The anti-insect nets must be spread well in advance of veraison and kept until the end of the harvest, as a valid integration to the chemical control against D. suzukii to limit the damage. Moreover, the active ingredients against D. suzukii are very few nowadays. The presence of poles and rain cover in the orchard makes it easier to place the net on the plot perimeter.
Furthermore, the nets (with a mesh that should not exceed1 mm² openings), permit the grower to wait for the homogeneity and the correct degree of fruit ripeness. They can also protect the crop from other potentially dangerous insects, such as the Asian bug Halyomorpha halys.
Despite of the evidence of the effectiveness of this technique, the cost for the purchase of the materials and the possible increase in temperature and humidity in some conditions, are the main problems.

The biological control is one of the last strategies applied during the last few years. The first experience was carried out with Trichopria drosophilae, one of the indigenous Drosophilidae’s parasitoids able to parasitize the pupal stage of D. suzukii.
During summer 2019, Leptopilina japonica has been captured on fruits of Prunus avium infested by D. suzukii in Trentino, giving the first report of the presence of an Asian larval parasitoid of D. suzukii in Europe.
In the following years L. japonica has been recorded across the territory, suggesting adventive population of this parasitoid, which may contributes in a significant manner to contrast the infestation of D. suzukii.
After the recent authorization to release the Asian exotic larval parasitoid Ganaspis brasiliensis, it was introduced both in 2021 and 2022 in 8 Italian regions (Trentino-Alto Adige, Valle d’Aosta, Piemonte, Veneto, Emilia Romagna, Campania, Sicilia, Puglia). It will be released also in 2023 in the same regions, included Lombardia and Toscana.
The first results of this biological control program have been presented in a recent congress held in San Michele all’Adige (Lotta biologica classica per il controllo di Halyomorpha halys e Drosophila suzukii: risultati delle iniziative nazionali e situazione in Trentino-Alto Adige Südtirol), in which was made evident that the parasitoids has been recorded after the first releases.
Cherry Times - All rights reserved













