The sustainability of cherry production is becoming an increasingly pressing need due to climate change and serious environmental problems, such as decreasing water availability and rising spring-summer temperatures, and the loss of biodiversity.
To remedy these problems, Serbian researchers from the University of Novi Sad studied the native germplasm of the cherry tree as a possible source of new rootstocks. The research, carried out on an experimental cherry orchard bred in a semi-arid, non-irrigated climate, showed that a judicious choice of rootstock allows cherry trees to grow moderately, with a good dwarfing effect, produce well and adapt to critical conditions without compromising cherry quality, provided that production efficiency goals are achieved through proper tree management.
The Serbian region where the new rootstocks were evaluated had a continental climate, characterised by extremely hot summers and cold winters. During the trial (2017-2021), the average annual T was 13°C, with daily maxima reaching 41°C and winter T dropping to -23°C. Rainfall totals varied from 500 to 700mm. The soil conditions were also not optimal for cherry cultivation, with a sandy-loam type soil (40% sand, 38% silt and 22% clay), a pH close to 8, a CaCO3 content of more than 3% and an organic C content of less than 2%.
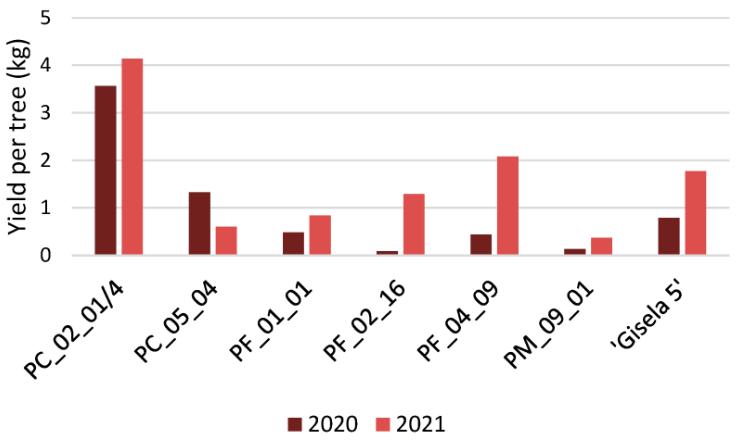
The trial was set up at the experimental farm of the Faculty of Agriculture of the University of Novi Sad by planting in a high-density planting (4m x 2m = 1250 trees/ha) rods of the Summit cv grafted on six rootstocks one of comparison, Gisela 5 (Prunus cerasus x Prunus canecens) and five new potential rootstocks, obtained from a clonal selection process performed in Serbia on local populations of Prunus cerasus cv Oblačinska (PC), Prunus fruticosa (PF) and Prunus mahaleb (PM).
The experimental results indicate the high adaptability to critical and unfavourable conditions of the trial for the autochthonous sour cherry selection named PC_02_01/4 and the clones of Prunus fruticosa. Furthermore, the PC_02_01/4 clone provided the best performance in terms of productivity and production efficiency during the whole trial, at the same time ensuring more than satisfactory cherry quality levels together with a good control of plant vigour.
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











