The health of propagation materials starts with the breeders
05 Apr 2023
Some considerations on how to better qualify varietal innovation through breeding certification programs for a new sustainable and competitive cherry crop.
Postharvest anthracnose of cherries (CPA) is a fungal disease that threatens cherry production, leading to significant economic losses. This disease is caused by fungi of the genus Colletotrichum, which affect the fruits during the postharvest stage.
The infection appears as dark brown or black lesions on the surface of the fruits, which gradually expand and deepen, eventually causing decay. Cherries are particularly vulnerable to fungal infections during harvesting and packaging, especially if they have been damaged.
A recent Chinese study aimed to understand the complexity of the pathogens responsible for postharvest anthracnose of cherries in China. It analyzed various cherry samples collected over two different growing seasons, including multiple cultivars. From these samples, 43 isolates of Colletotrichum were obtained and characterized, representing the species associated with anthracnose in the main cultivation regions.
The isolates were studied using a multi-locus phylogenetic analysis, employing seven genetic loci (ACT, CAL, CHS-1, GAPDH, HIS3, ITS, TUB2) to identify species differences and their geographical distribution. The results revealed the presence of seven Colletotrichum species, divided into two species complexes: Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (CGSC) and Colletotrichum acutatum (CASC).
Within the CGSC, the species identified were C. aenigma, C. fructicola, C. gloeosporioides, and C. siamense, while the CASC group included C. fioriniae, C. godetiae, and C. salicis. Each species exhibited different biological characteristics, influencing both the pathogen's behavior and its distribution across different cultivation areas.
Significant biological differences were observed between Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (CGSC) and Colletotrichum acutatum (CASC). The CGSC demonstrated faster mycelial growth, greater sporulation capacity, and more vigorous conidial germination compared to CASC. As a result, the species within this complex showed greater aggressiveness in infecting cherry fruits.
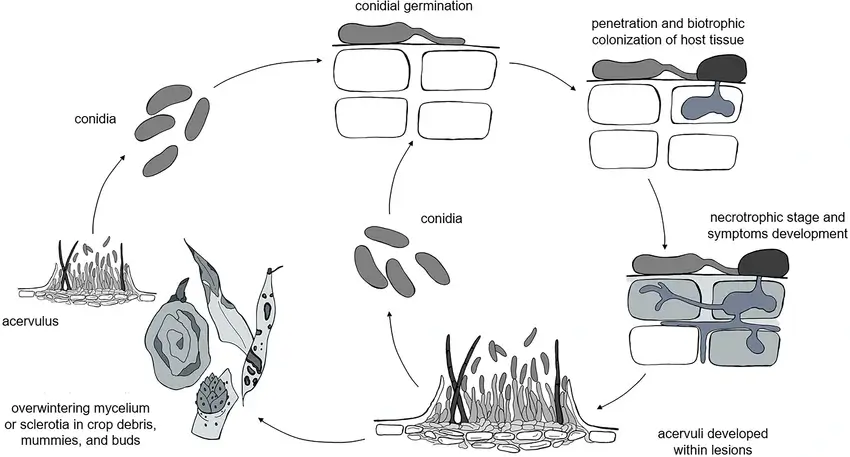
Conversely, CASC was found to be more adaptable to lower temperatures, indicating higher resistance to thermal stress. However, CGSC stood out for its superior pathogenicity, as it was able to produce a larger number of conidia and germinate more efficiently, leading to quicker and more intense infections.
Pathogenicity tests showed that, without the need for initial wounds, all Colletotrichum species could infect cherries, with increased virulence observed when the fruits were already damaged. In particular, Colletotrichum aenigma displayed the highest pathogenicity among the CGSC strains.
On the other hand, CASC species, such as Colletotrichum fioriniae and Colletotrichum godetiae, were able to infect wounded fruits and exhibited high pathogenicity; however, in absence of wounds, the pathogenicity of these species was lower, thereby reducing the risk of infection.
Beyond cherries, the study also tested the pathogenicity on other fruits such as cherry tomatoes, grapes, and blueberries. The results showed a high virulence of Colletotrichum aenigma and Colletotrichum siamense on grapes and blueberries, while Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Colletotrichum fioriniae were more virulent on tomatoes. However, infections on these other fruits occurred only when wounds were present, thus limiting the risk of infection under normal conditions.
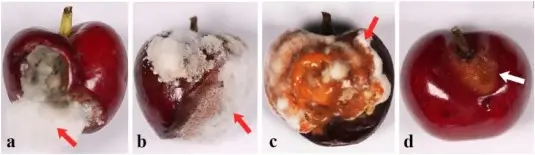
In conclusion, this study analyzed the fungal species of the Colletotrichum genus responsible for postharvest anthracnose of cherries in China, identifying the most virulent ones and providing a basis for developing targeted control strategies. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex (CGSC) was found to be more pathogenic than the Colletotrichum acutatum complex (CASC).
Moreover, the species within each complex showed specific host and environmental preferences. This suggests that postharvest disease management measures should be tailored to local conditions and prevalent species. The cherry production chain could benefit from more targeted environmental controls and harvesting and packaging practices that minimize fruit damage.
Source: Yang, X., Hu, S., Dong, D., & Zhang, C. (2024). Diversity of Colletotrichum species causing cherry postharvest anthracnose in China. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 134, 102390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2024.102390.
Images: Imexagro; Salotti et al, 2023; Yang et al, 2024.
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
05 Apr 2023
Some considerations on how to better qualify varietal innovation through breeding certification programs for a new sustainable and competitive cherry crop.
24 May 2024
Water availability influences cherry tree growth, yield and quality. The application of biostimulants results in the activation/regulation of metabolic pathways that influence processes that can improve production in both quantity and quality.
10 Mar 2026
A field trial in a cherry orchard in Izmir, in Turkey’s Aegean region, shows that bumblebee pollination with Bombus terrestris improves cherry size and weight. Results highlight larger fruit, fewer cherries per kilogram and higher profitability for export-oriented growers.
10 Mar 2026
Uno studio condotto in Argentina mostra come le ciliegie dolci scartate possano essere trasformate in polvere liofilizzata ricca di composti fenolici e utilizzate in film edibili a base di pectina, creando materiali attivi per il packaging alimentare con proprietà antiossidanti.